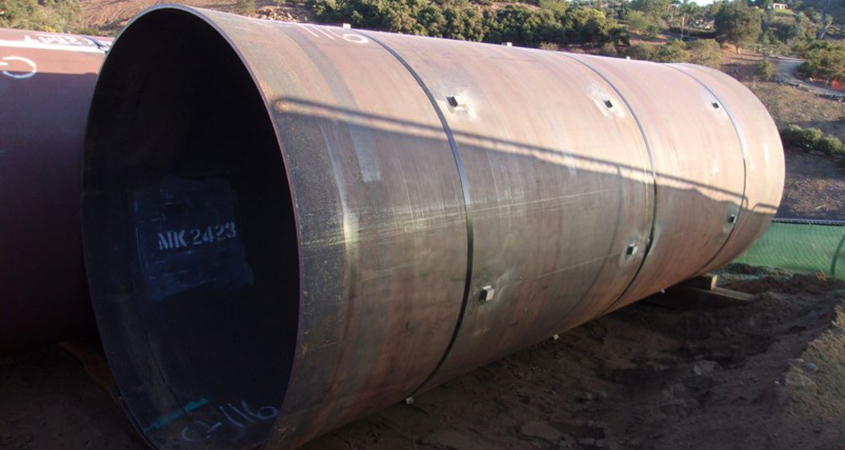
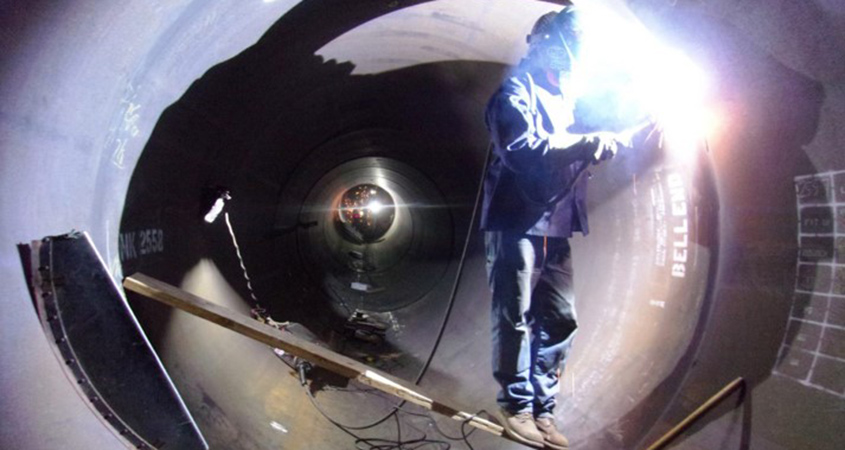
A method of replacing sewer pipe without digging or removing the old pipe – trenchless pipe repair – is saving Vallecitos Water District ratepayers money and reducing traffic delays. It’s another example of how water agencies in San Diego County are tapping cost-effective technology.
The district is using the trenchless method to extend the life of its service pipelines while avoiding the disruption of excavation trenches and traffic rerouting around work areas on public streets. Instead of digging the pipeline up to replace it, the sewer line is rehabilitated from inside the pipe. This trenchless technology method increases the efficiency and the service life of the pipe without having to replace it; eliminating paving, reducing traffic interruptions, as well as saving the District and in turn its ratepayers money.
“Traditional installation methods cause such a disruption to customers daily routine, so we’re really lucky when this type of project presents itself to the District,” said Jason Hubbard, a senior engineer with the district. “Our residents are going to have a much better day without navigating a large construction zone – they can also be quite noisy and dusty. Bottom line, everyone’s happy.”
Avoiding disruption to customers from trenches and traffic rerouting
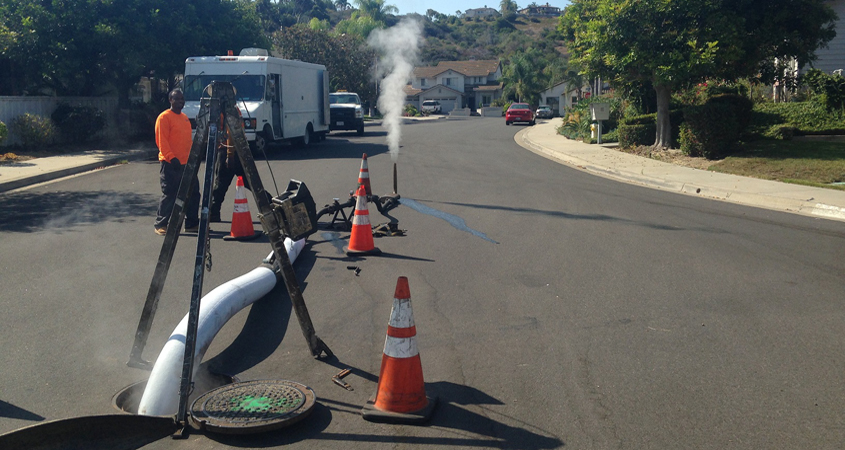

By avoiding the need for exacation, streets can be kept open and functioning while work progresses. Photo: Vallecitos Water District
Pipeline integrity can be lost due to a combination of many factors such as missing pieces, cracks, pinholes, offsets at joints, and root intrusion. Numerous methods, technologies and practices are used by water agencies to ensure pipeline integrity.
The Vallecitos Water District works to find innovative technologies to ensure continuing water, wastewater, and reclamation services to a population of 103,000 residents within its 45-square-mile service area. There are 358 miles of water pipelines and 276 miles of sewer pipelines in the VWD’s 45-square-mile service area, serving more than 103,000 residents. The pipelines are designed, built, and operated to be safe, reliable, and sustainable to achieve pipe integrity. This means ensuring a pipeline and all its related components are running properly, no small task.
“We constantly work to maintain a reliable sewer conveyance system by utilizing a plethora of innovative and cost-effective technologies,” said Hubbard.
Trenchless technology also results in cost savings
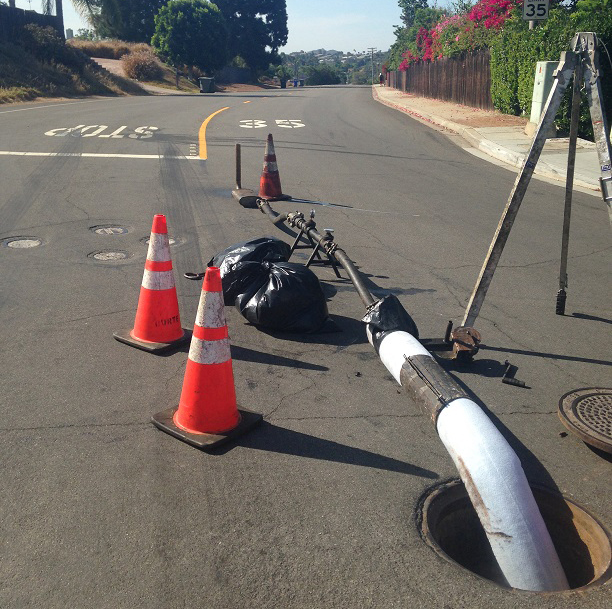

Trrenchless technology is also cost effect in addition to being less disruption to customers. Photo: Vallecitos Water District
VWD employed two types of trenchless rehabilitation methods, cured-in-place-pipe (CIPP) liners and spiral wound liners to maintain District pipes. CIPP liners are epoxy saturated felt tubes, which are inserted into the existing pipe, then cured and hardened by steam. There are no joints or seams. Spiral Wound Liners use an above groundwinding machine to feed interlocking PVC profile into an old pipe.
Both methods result in a new “pipe within a pipe.” Little to no digging is involved in this trenchless process, making for a less disruptive and more cost-effective method than traditional “dig and replace” pipe repair methods. The liner can be inserted using water or air pressure. Liner technology is particularly effective in hard to reach areas, such as easements. For projects along residential and business streets, the trenchless method reduces disruptions and impacts to businesses and neighborhoods.
This technology helped the Vallecitos Water District to rehabilitate 1,595 feet of sewer pipe. The district plans to rehabilitate another 2,300 feet in 2020. Sections of critical infrastructure were rehabilitated at an affordable price due to the CIPP and spiral wound liner options. No sewer laterals were cut, and work was done without a sewer bypass. The project was completed with a savings to the District of $37,000 under the estimated budget. The lining part of the operation took less than three hours.