Reservoirs, Lakes Remain Closed to Fishing Due to COVID-19 Pandemic
Although San Diego County’s lakes and reservoirs remain closed to fishing and other recreational activities for safety reasons due to the coronavirus pandemic, staff and volunteers continue to work. Crews are maintaining facilities, providing security, and sharing photos of wildlife and native blooms enjoying the arrival of spring.
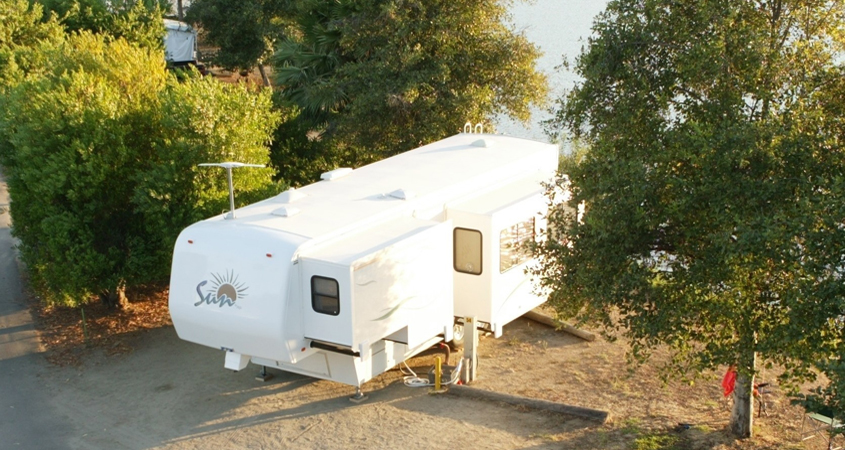

Popular overnight campsites remain open at Santee Lakes, operated by the Padre Dam Municipal Water District. Photo: Padre Dam Municipal Water District
Popular overnight campsites remain open at Santee Lakes, owned and operated by the Padre Dam Municipal Water District.
“Camper well-being is important to us and Santee Lakes didn’t want to displace people,” said Melissa McChesney, Padre Dam communications manager. She said that includes long-term campers who spent winter at the lake.
“It is important to note that Santee Lakes is not promoting recreation at this time, and the day use section of the park is closed,” said McChesney. “The park is able to provide a safe alternative to any RVers currently on the road in California because we have full electric, water, sewer and WiFi at each site. Santee Lakes is currently only taking reservations for self-contained RVs.”
Campers can reserve space for a maximum of six months. McChesney said campers should still shelter in place and practice physical distancing at the 300 campsites and 10 cabins.
At Santee Lakes, campers can also enjoy spring birdwatching. Two hundred and thirty different bird species have been spotted at the lake.
Nature takes flight at Lake Jennings
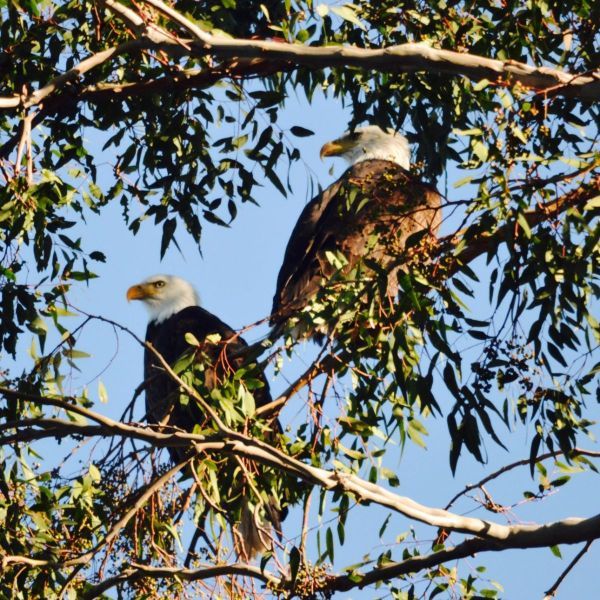

Two of the three resident bald eagles at Lake Jennings. Photo: Lake Jennings
At Lake Jennings, Recreation Manager Kira Haley says eight volunteers continue to live and work from their campground homes in recreational vehicles and campers. She said their days remain “pretty typical” even though they see more wildlife and not people.
“Our volunteers handle emerging maintenance, take calls from the public, and provide security,” said Haley. “They’re happy to be there, not having interaction with people during this time.”
Although new camping reservations are closed, Haley said campers currently at the Lake Jennings campgrounds were allowed to finish their stay. She said only one person, from out of state, will be the only camper at the entire park through the end of April.
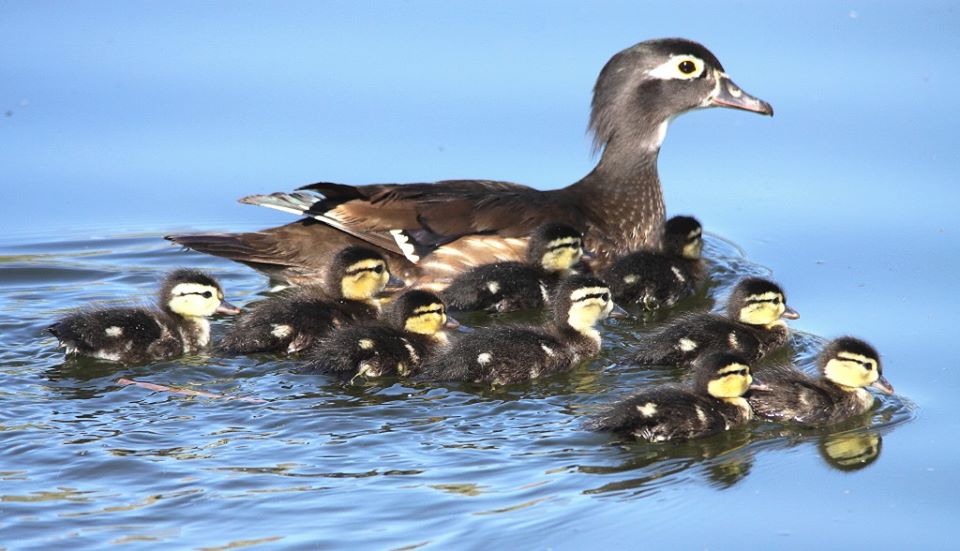

A wood duck and her ducklings swimming across Santee Lakes. Photo: Santee Lakes/Facebook
Haley and her volunteers are sharing photos of the active wildlife and plant growth on social media. Currently, there are three bald eagles at the lake.
On the Lake Jennings Facebook page, Haley noted with a photo of a bald eagle in flight, “Lake Jennings Social Distancing: Always keep an eagle’s wingspan between you and others.” According to National Geographic, a bald eagle’s typical wingspan measures from six to eight feet – the recommended social distancing minimum.
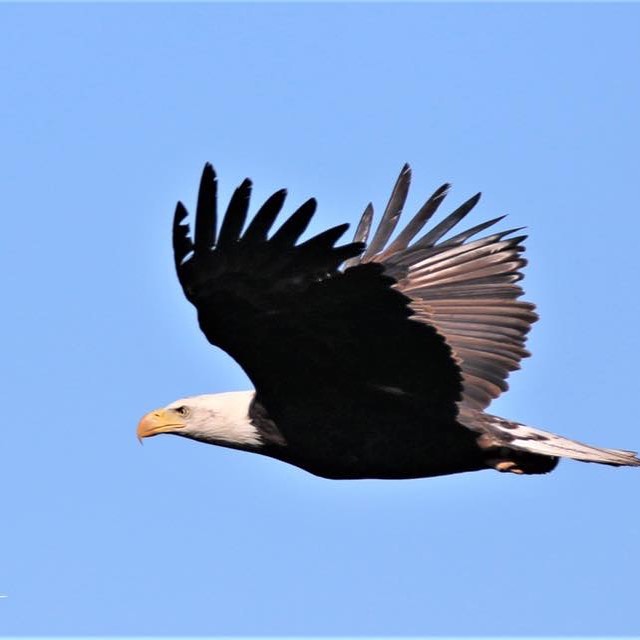

According to National Geographic, a bald eagle’s typical wingspan measures from six to eight feet – the recommended social distancing minimum. Photo: Lake Jennings/Facebook
City of San Diego lakes and reservoirs closed until further notice
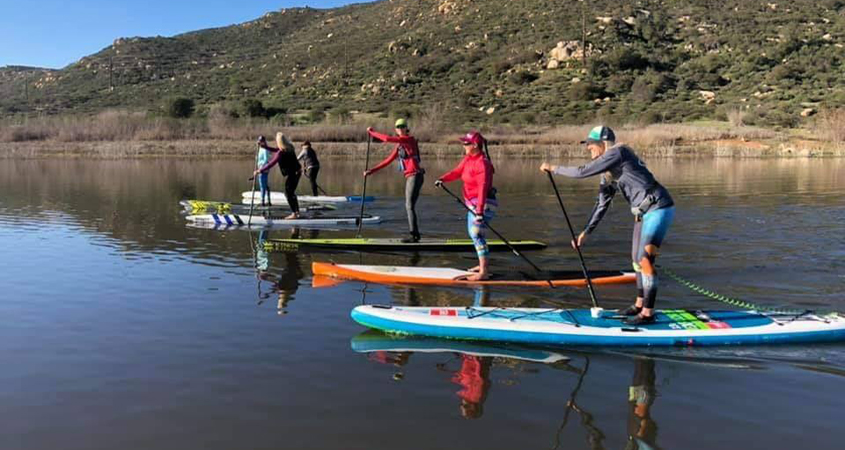

Paddleboarders will have to wait to get on Lake Hodges. The City of San Diego has closed all reservoirs due to the coronavirus pandemic. Photo: City of San Diego
The City of San Diego’s reservoirs and lakes are closed due to the coronavirus pandemic. The city closed the reservoirs to the public on March 18 to protect the public and minimize the spread of the COVID-19 virus. The nine water supply storage reservoirs are operated by the City’s Public Utilities Department.
3/27/20 Coronavirus Updates from Lake Jennings 🐟 – https://t.co/MpaIpNa8ZG pic.twitter.com/LBv6S1x3ln
— Lake Jennings (@lake_jennings) March 27, 2020