Income-qualifying residents in the San Diego region can still benefit from a grant-funded program replacing outdated toilers with high-efficiency models in 2024.
More than 6,000 high-efficiency toilets have been installed free of charge to date in under-represented communities across the region through a grant-funded program run by the San Diego County Water Authority.
Funding remains available to replace about 4,000 more outdated toilets with professionally installed, high-efficiency models at no cost. Eligible communities include mobile home communities, multi-family units, and income-qualifying single-family homes.
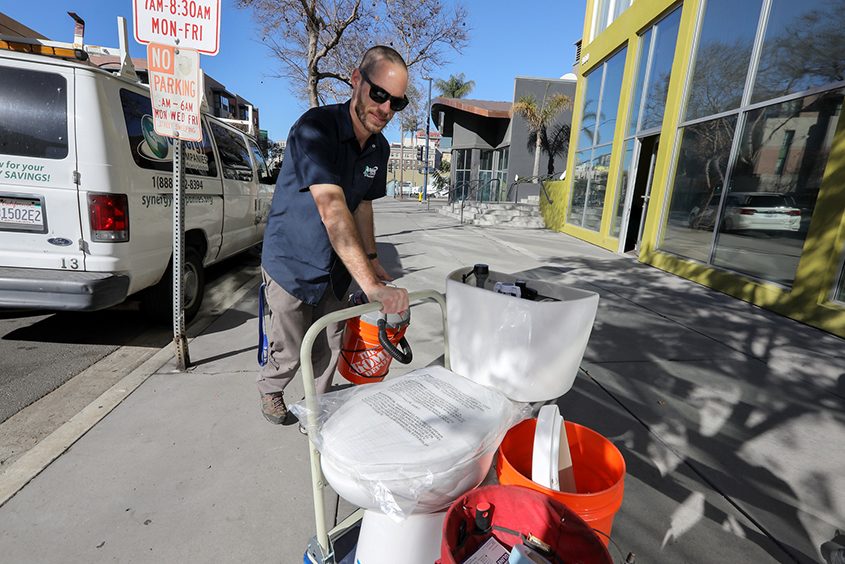

Qualified applicants for low-flow upgrades include mobile home communities, multi-family housing, and income-qualifying single-family homes. Photo: San Diego County Water Authority
Smart irrigation controllers are also available at no cost through the program. Participants must be residential customers within the Water Authority’s service area.
Learn more about the program, including eligibility requirements and the application process at Direct Install Program.
Free upgrades conserve water, save money
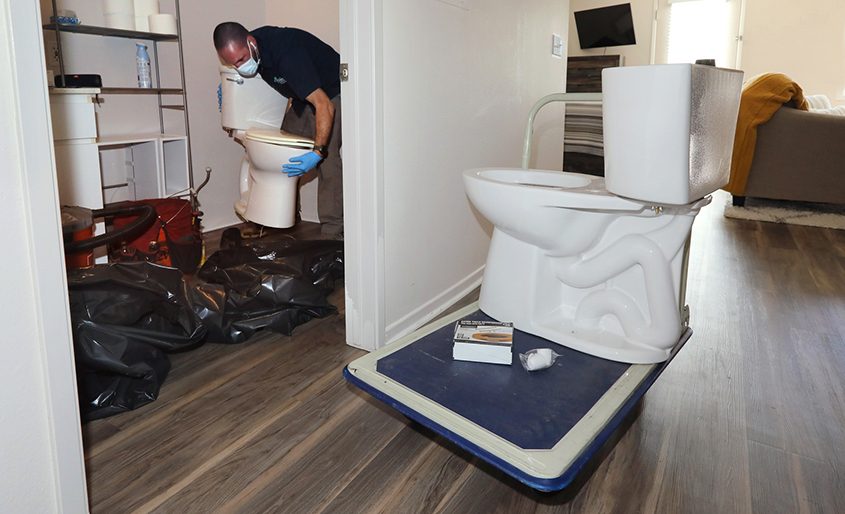

High-efficiency toilets and smart irrigation controllers conserve water while saving costs. Photo: San Diego County Water Authority
“This is a great way for residents to get a free home upgrade that conserves water and saves on water bills,” said Mel Katz, chair of the Water Authority’s Board of Directors. “Water affordability is a top priority for the Water Authority, and this program is one of many ways we are combatting inflationary pressures on water prices.”
Through the Direct Install Program, toilets that use 1.6 gallons or more per flush are replaced with premium, high-efficiency models that use half the water. The program is entirely funded by more than $4 million in grants from the California Department of Water Resources Integrated Regional Water Management and Urban Community Drought Relief programs and through the Metropolitan Water District of Southern California.
Water Authority pursues funding for region’s water system
In addition to the Direct Install Program, the Water Authority is taking numerous other steps to enhance affordability. For instance, the agency helped secure $25 million to cover overdue residential water bills resulting from the economic impacts of COVID-19.
The Water Authority also operates an industry-leading asset management program designed to avoid the extreme costs of emergency repairs on large-scale water pipelines.
In 2024, the Water Authority is working with Washington, D.C. officials to secure federal funds to defray the cost of generational upgrades to local dams and reservoirs.