Drought is back in California. Federal and state agencies are warning of potential water shortages in the months ahead. Because of investments made by the San Diego County Water Authority, its member agencies and the region’s water ratepayers, San Diego County is safe from the threat of multiyear droughts.
“We are now facing the reality that it will be a second dry year for California and that is having a significant impact on our water supply,” said DWR Director Karla Nemeth in early April. “The Department of Water Resources is working with our federal and state partners to plan for the impacts of limited water supplies this summer for agriculture as well as urban and rural water users. We encourage everyone to look for ways to use water efficiently in their everyday lives.”
The San Diego region relies far less on supplies from Northern California than in previous decades. A severe drought in the early 1990s forced the region to confront the fact that continuing to provide safe and reliable water demanded a diverse portfolio of supplies instead of near-total reliance on a single source.
“We have sufficient water supplies whether it’s a normal year, which means normal rainfall,” said Jeff Stephenson, water resources manager at the San Diego County Water Authority. “A single dry year. Or a period of five straight dry years. Under those scenarios we have more than sufficient water supplies to meet the needs of the region.”
Investments and planning pay off
Stephenson credits three decades of efforts by the Water Authority and its 24 member agencies to diversify water sources, including contracts for water transfers with the Imperial Irrigation District and the Claude “Bud” Lewis Carlsbad Desalination Plant, as well as the development of additional water storage capacity in the region.
There are also several water reuse or recycling projects in development throughout San Diego County. The region’s dependence on imported water supply will decrease as these local supply sources are developed and become operational.

Construction is underway for Pure Water Oceanside, one of three potable reuse or recycling projects in San Diego County that will reduce the need for imported water while creating a sustainable, local supply. Photo: City of Oceanside/Jeremy Kemp
Approximately 43,000 acre-feet of recycled water is expected to be reused within the Water Authority’s service area annually by 2025. As the new and expanded potable reuse plants come online, they are projected to produce more than 112,000 acre-feet per year of new drinking water supplies by 2045, enough to meet nearly 18% of the region’s future water demand.
“Our member agencies throughout the region have developed more local supplies, such as recycled water,” Stephenson said. “In addition, the member agencies are developing potable reuse projects, including the city of San Diego’s pure water program which comes online in the future, and all of those supplies really make the region much more able to withstand drought periods.”
Revised drought contingency plan
As a result of the persistent drought conditions, and in accordance with its permit for the long-term operation of the State Water Project, DWR has submitted a revised Drought Contingency Plan to the California Department of Fish and Wildlife. The plan provides updated hydrologic conditions and outlines areas of concern for the joint operations of the State Water Project and the Central Valley Project, water quality, and environmental impacts.
In late-March, the State Water Resources Control Board mailed approximately 40,000 notices to water right holders, warning of persisting dry conditions and asking them to plan for potential shortages. Officials said the warnings, a result of two years of below average precipitation and below average state reservoir levels, will prompt early action to help minimize short term drought impacts.
“Planting crops and other decisions that are dictated by water supply are made early in the year, so early warnings are vital,” said Erik Ekdahl, deputy director for the Water Board’s Division of Water Rights. “These letters give water users time to prepare and help minimize the impacts of reduced supplies on businesses, farms and homes.”
The agency suggested in the letter that agricultural water users can implement practical actions now to improve their drought resilience, including reducing irrigated acreage, managing herd size, using innovative irrigation and diversifying water supply portfolios. Urban water users can conserve by putting in drought-resistant landscape, reducing outdoor irrigation and replacing older house fixtures and appliances with more efficient ones.
Increasing local supply sources
The San Diego County Water Authority and its member agencies continue to increase local supply sources and make investments to ensure a plentiful, safe, and reliable water supply for the region’s 3.3 million people and its $245 billion economy.
“Current conditions are a reminder of why the Water Authority and its member agencies have invested in locally controlled water sources and facilities such as dams and pipelines that can move water when and where it’s needed,” said the Water Authority’s Stephenson.
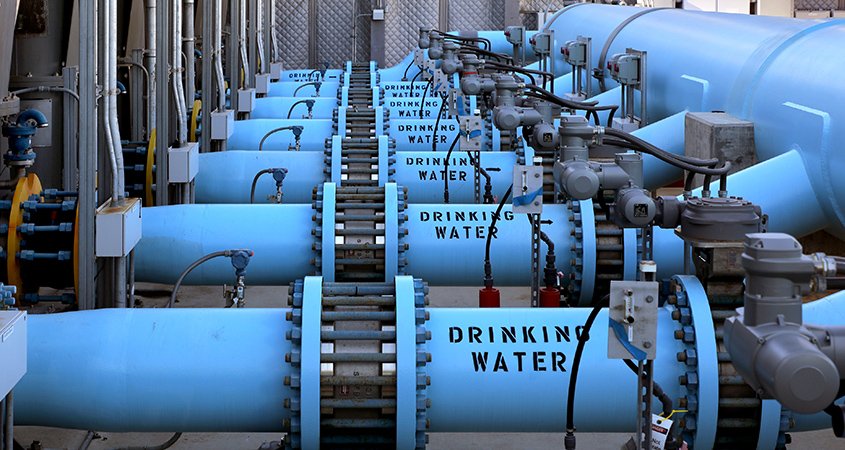

The Carlsbad plant uses reverse osmosis to produce approximately 10 percent of the region’s water supply; it is a core supply regardless of weather conditions, and it is blended with water from other sources for regional distribution. Photo: San Diego County Water Authority
Ever since the drought of the early 1990s, the San Diego County Water Authority and its 24 member agencies have been leading advocates for water-smart strategies such as low-flow toilets, low-water landscapes and other conservation tactics. One result is that per capita water use in the San Diego region is down by more than 50% over the past three decades.
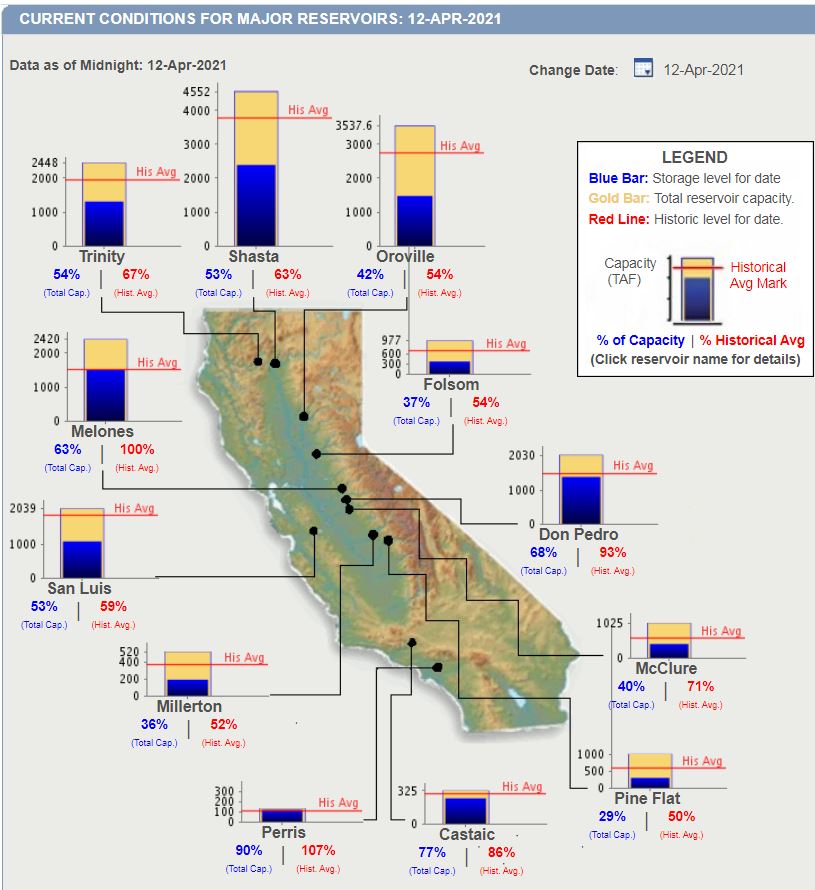
“We are now facing the reality that it will be a second dry year for California and that is having a significant impact on our water supply,” said DWR Director Karla Nemeth in early April 2021. Graphic: California Department of Water Resources








