San Diego Reservoirs Offer Community Holiday Activities
San Diego County’s most popular reservoir recreation areas offer special holiday season events through 2024 and host winter activities during the region’s cooler months.
Holiday Spirit at Santee Lakes
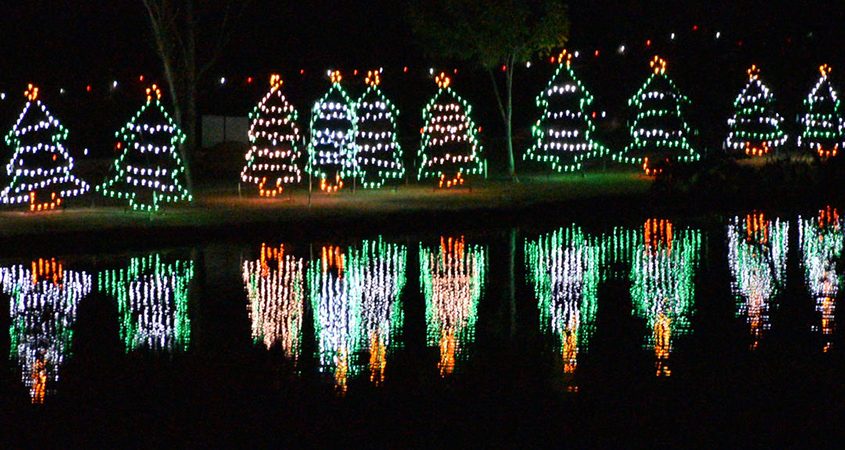

“Lights at the Lake” at the Santee Lakes Recreation Preserve features 100,000 lights and three dozen displays nightly through December 31. Photo: Santee Lakes Recreation Preserve
Enjoy San Diego County’s mild weather and spend Thanksgiving at Santee Lakes Recreation Preserve. Campground space is available. A three-night minimum stay is required, but you won’t want to leave.
Santee Lakes hosts its annual “Lights at the Lake” drive-through holiday show from Sunday, December 1, to December 31. The show will be moved to the Campground in 2024 for a brilliant camping experience.
Visitors will enjoy three dozen beautiful displays with over 100,000 lights to make holidays bright. You can walk through the tunnel of lights or use a golf cart. Hours are 5 p.m. through 8 p.m. (closed Christmas Eve and Christmas Day). You must buy tickets in advance. More information about Lights at the Lake here.
A full list of additional holiday events including Christmas cookie making, crafts, and holiday movies plus visits with Santa are listed on the Santee Lakes website.
For the third year in a row, Santee Lakes Recreation Preserve was nationally recognized by the Outdoor Hospitality Industry (formerly ARVC) as its large/mega park Plan-it Green Park of the Year for its environmentally friendly practices across all areas of park operations and its commitment to sustainability.
Originally opened to the public in 1961, today, Santee Lakes Recreation Preserve hosts over 760,000 visitors annually. The 190-acre park’s lakes are stocked with fish year-round. Other amenities include camping, cabin rentals, fishing, boating, playgrounds, walking trails, facility rentals, special events, and approximately 230 bird species.
Lake Jennings Open For Winter Fun

Lake Jennings hosts a holiday “Gratitude Walk” to benefit the San Diego Food Bank.
Share your Thanksgiving blessings and walk off the pumpkin pie at the Lake Jennings Gobble and Go Gratitude Walk. Walk the five-mile plus perimeter loop during the lake’s operating hours on November 25, 26, and 27. Bring a food item for donation to the San Diego Food Bank, and your day-use entry fee will be waived. Check this list of the most desired food donations. Please, no glass jars or homemade items.
Lake Jennings opened its annual trout fishing season on November 15 and is open daily except on Christmas Day from 6 a.m. to 5 p.m. through January 7. The lake will be restocked regularly every two weeks from November 25 through April 14 with 19,000 pounds of trout.
The lake will be open for its New Moon Fishing event on Saturday, November 30, and Saturday, December 28, from 6 a.m. to 10 p.m. Visitors can enjoy fishing, boating, hiking, picnicking, sunset watching, star gazing, and firepit rentals. Get more information about activities at https://lakejennings.org/
Lake Jennings is an exceptional destination during winter months for serious and casual wildlife viewers and photographers.
Sweetwater Reservoir Birdwatching in Winter Season
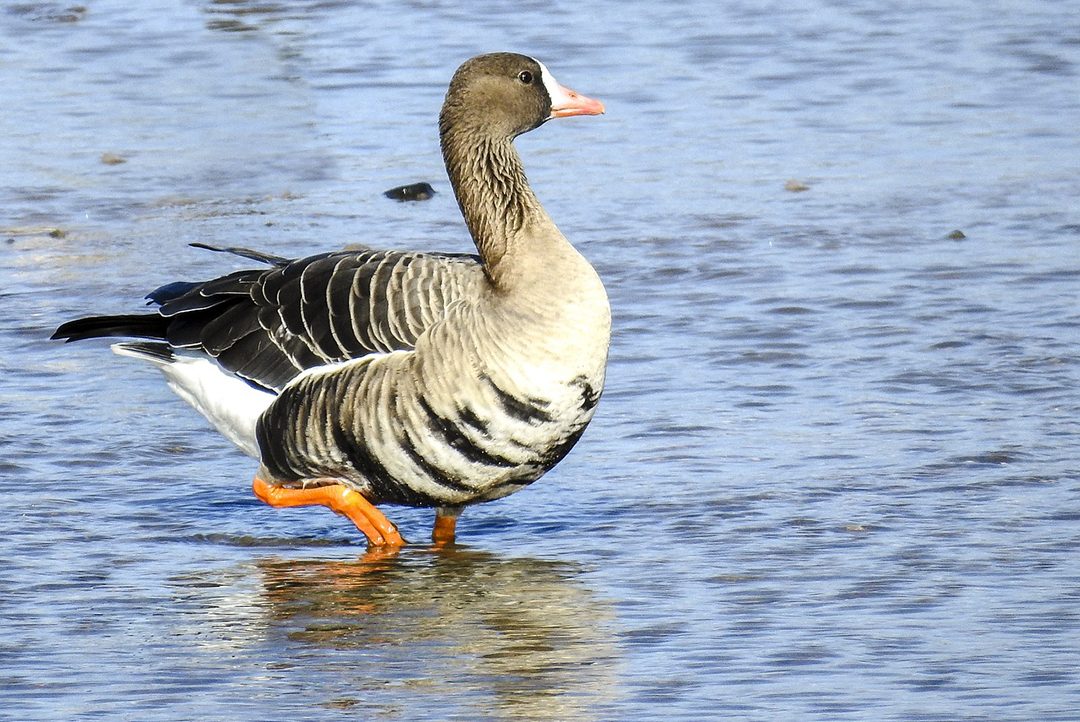

Look for the greater white-fronted goose at Sweetwater Reservoir. You may remember a greater white-fronted goose that landed on the field during a San Diego Padres playoff game in 2023. These birds breed in Alaska and Canada before heading south toward Mexico for the winter. Photo: Kathy Buscher
The range of habitats at the Sweetwater and Loveland Reservoirs supports diverse bird populations. Their proximity to the Pacific Flyway means many migratory species pass through on their way to warmer areas, making the winter months ideal for birdwatching and wildlife walks to burn off holiday meals.
Over 250 bird species have been documented at the Sweetwater Reservoir. Sweetwater Authority welcomes birds and other wildlife as part of its stewardship of the natural watershed, which helps keep reservoir water quality high and supports the balance of human and environmental needs.
View birds from public access areas at the Sweetwater Reservoir or Loveland Reservoir. Bring binoculars, a bird guide, and a notebook.