Pure Water San Diego Phase 1 Construction in North City Area
Construction work is underway in several areas of San Diego, building major infrastructure projects for Phase 1 of Pure Water San Diego.
Phase 1 of Pure Water San Diego, including pipelines, pump stations, and treatment facilities, has started in Morena, Bay Park, Clairemont, University City, Miramar, and Scripps Ranch communities. It is a milestone toward the realization of securing a local, drought-resilient water supply for San Diegans for generations to come.
Nearly 50% of San Diego’s water supply
Pure Water is the City of San Diego’s largest-ever infrastructure program that will provide nearly half of San Diego’s water supply by 2035. Pure Water will use purification technology to clean recycled wastewater and is a cost-effective investment for San Diego’s water supply needs.
Residents, businesses, and commuters may be impacted by road closures, detours, and construction noise during construction. Construction for this project will primarily take place on weeknights from 7 p.m. to 5 a.m., except on Nobel Drive, when construction will take place on weekdays from 8:30 a.m. to 3:30 p.m. Tunneling work will be done around the clock with adherence to noise requirements.
Pure Water project will reduce dependence on imported water
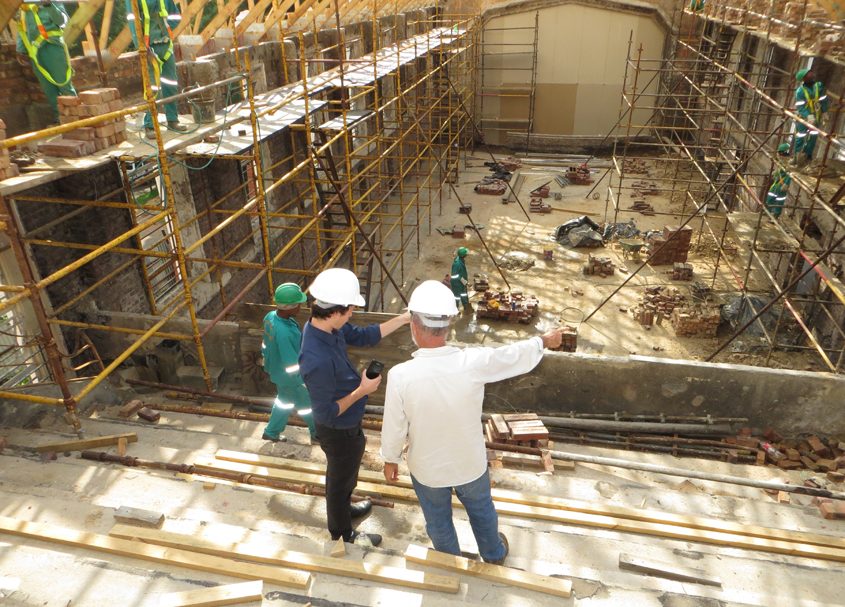

“Potholing” is underground work that finds the location and depth of existing utilities in the public right-of-way. Potholing is currently being done for the Morena Northern Pipeline & Tunnels and the North City Pure Water San Diego Pipeline projects. Photo: City of San Diego
Upon its completion, Pure Water San Diego will contribute 30 million gallons per day of high-quality purified water, reducing the City’s dependence on imported water.
The Morena Northern Pipelines and Tunnels project now underway will connect to the Morena Pipelines Middle Alignment to the south and the North City Water Reclamation Plant to the north.
Water pipelines
This project includes portions of two 10.5-mile pipelines: one 48-inch wastewater pipeline, which will carry wastewater north to the North City facilities for purification, and one 30-inch brine line that will carry the byproduct from water purification south to the Point Loma Wastewater Treatment Plant.
This project begins on Genesee Avenue and Appleton Street and continues on Genesee Avenue, Nobel Drive, Towne Centre Drive, and Executive Drive. Tunneling will be completed at Genesee Avenue and State Route 52 (San Clemente Creek), at Genesee Avenue and Rose Creek Canyon, and under Interstate 805.
Securing San Diego’s sustainable water future
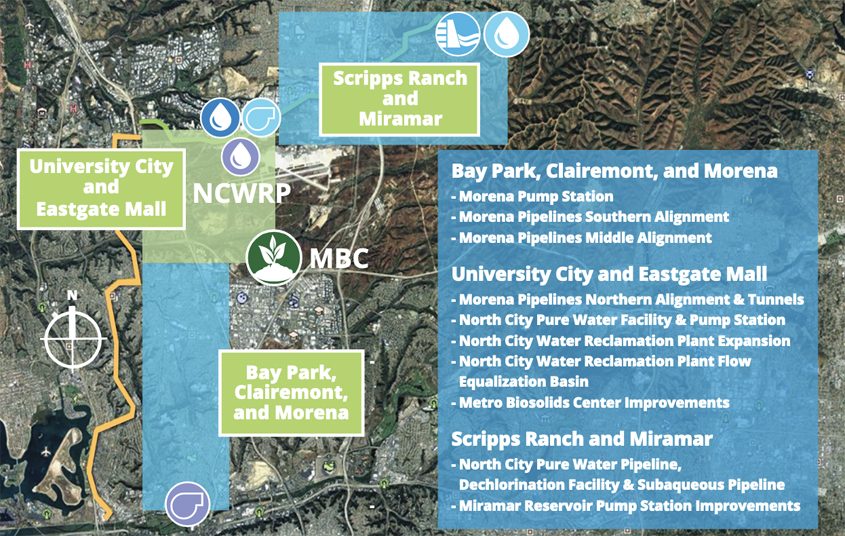
This project begins on Genesee Avenue and Appleton Street and continues on Genesee Avenue, Nobel Drive, Towne Centre Drive, and Executive Drive. Tunneling will be completed at Genesee Avenue and State Route 52 (San Clemente Creek), at Genesee Avenue and Rose Creek Canyon, and under Interstate 805. Map: City of San Diego
Currently, the City of San Diego depends primarily on a reliable imported water supply to deliver clean and safe drinking water to its communities. The investment in advanced water purification with the construction of Pure Water San Diego will help secure a high-quality, safe, local, and drought-proof water supply for the future. Phase 1 is scheduled to be completed and commence operation in 2024. Pure Water San Diego will eventually provide nearly half of San Diego’s water supply locally by 2035 with the completion of Phase 2.
Purified water produced at the completed plant will be delivered to the Miramar Reservoir, blended with the City of San Diego’s imported and local water sources, and treated again at the existing Miramar Water Treatment Plant. After this process, the water will be distributed to customers.
You can take a virtual tour of Pure Water San Diego’s demonstration facility at virtualtour.purewatersd.org More information about the Program can be found at www.purewatersd.org.
(Editor’s Note: The City of San Diego is one of the San Diego County Water Authority’s 24 member agencies that deliver water across the metropolitan San Diego region.)