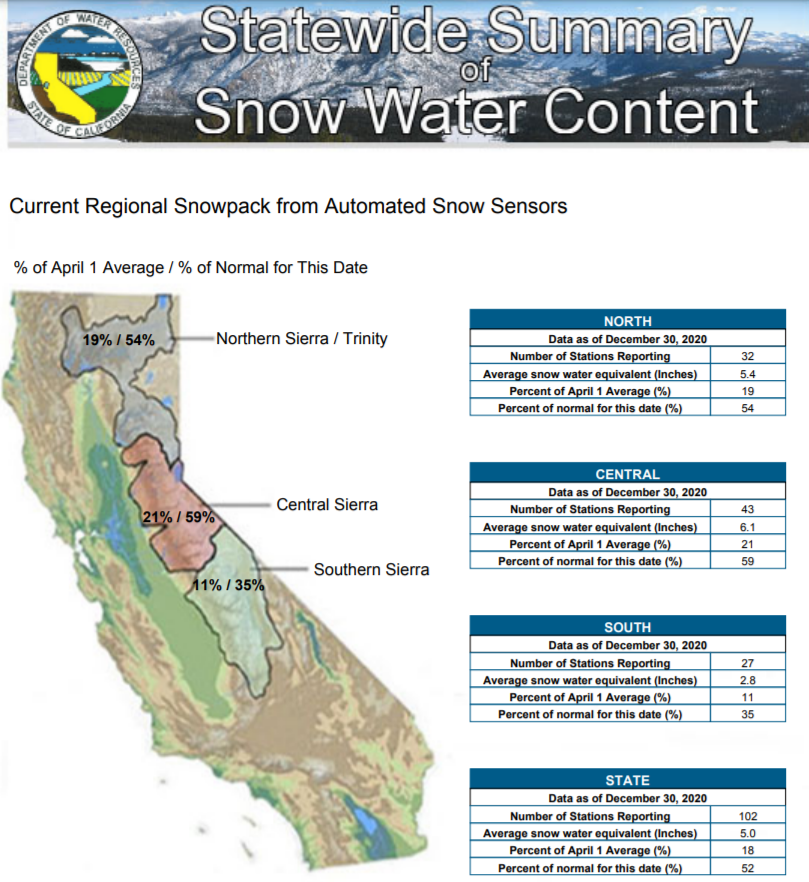
A dry start to California’s water year is reflected in the season’s first snow survey of the Sierra Nevada snowpack. The statewide snowpack is 52% of average for Dec. 30. On average, the Sierra snowpack supplies about 30% of California’s water needs.
The California Department of Water Resources manual survey at Phillips Station recorded 30.5 inches of snow depth and a snow water equivalent of 10.5 inches, which is 93% of the January 1 average at that location, according to DWR officials. The snow water equivalent,or SWE, measures the amount of water contained in the snowpack and is a key component of DWR’s water supply forecast.
While the Phillips Station measurement was positive, DWR’s electronic readings from 130 stations placed throughout California show the statewide snowpack’s SWE is 5 inches, or 52% of the December 30 average.
“The snow survey results reflect California’s dry start to the water year and provide an important reminder that our state’s variable weather conditions are made more extreme by climate change,” said DWR Director Karla Nemeth. “We still have several months left to bring us up to average, but we should prepare now for extended dry conditions. The Department, along with other state agencies and local water districts, is prepared to support communities should conditions remain dry.”
Water supply diversity meets regional demand
“The first snowpack survey of the water year points to California’s climate variability, which is why a diverse water portfolio is needed to provide a reliable supply,” said Goldy Herbon, San Diego County Water Authority senior water resources specialist. “The Water Authority and its 24 member agencies have successfully diversified water sources, and continue to expand those sources, to ensure our supply meets the needs of the region’s 3.3 million people and its $245 billion economy.”
The supply sources include water from the Claude “Bud” Lewis Carlsbad Desalination Plant, where ten workers volunteered to live on-site in 2020 to keep the water flowing during the coronavirus pandemic.
Climate change brings less snow
When the Sierra Nevada snowpack melts, it feeds into rivers and is stored in reservoirs across California. Reservoirs are tapped as needed during the dry months. However, state officials again said that climate change is affecting California’s snowpack, as more precipitation falls as rain and less as snow. And they urged Californians to make water conservation a “way of life.”
“Today’s survey brought a first glimpse of how the state’s snowpack is shaping up, but there is a lot of winter still ahead,” said Sean de Guzman, chief of DWR’s Snow Surveys and Water Supply Forecasting Section. “While the dry conditions during late summer and fall have led to a below average snowpack, it is still encouraging to have the amount of snow we already have with two of the three typically wettest months still to come.”
DWR conducts five snow surveys at Phillips Station each winter near the first of each month, January through April and, if necessary, May. Guzman said the next survey is scheduled for February 2.

Sean De Guzman (R), chief of the California Department of Water Resources Snow Surveys and Water Supply Forecasting Section, and Jeremy Hill, DWR water resources engineer, conduct the first snow survey of the 2021 season at Phillips Station in the Sierra Nevada. Photo: Kelly M. Grow/DWR





