After a wet and snowy start, California’s winter has gone bust. The 2019-2020 water year started off with robust precipitation after a series of storms in November and early December 2019.
But the new year has not been as bountiful. Dry conditions in January and February added little to the Sierra Nevada snowpack.
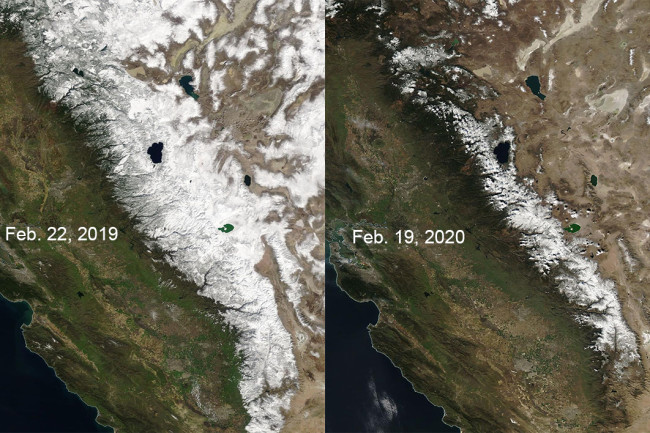
Left: 2019, Right: 2020. Sierra Nevada snowpack is below normal for this time of year, at about 58% statewide. Graphic: NASA/National Weather Service via NWS Sacramento
Drought-resilient water supplies through diversification
Due to California’s climatological variability, including periods of drought, the Water Authority and its 24 member agencies have diversified water supply sources. Those successful efforts ensure supply reliability for the region’s 3.3 million residents and its $245 billion regional economy.
“Based on current supply levels, the Water Authority and its 24 member agencies will meet anticipated demands through a combination of drought-resilient local and regional water resources,” said Goldy Herbon, Water Authority senior water resources specialist.
Water supplies will meet demand
Herbon said the Claude “Bud” Lewis Carlsbad Desalination Plant, conserved agricultural water transfers, savings from canal lining projects and continued water-use efficiency measures are among the reasons the region’s water supply will meet demand.
The multi-decade water supply diversification plan, along with major infrastructure improvements and forward-thinking policies, also promote fiscal and environmental responsibility.
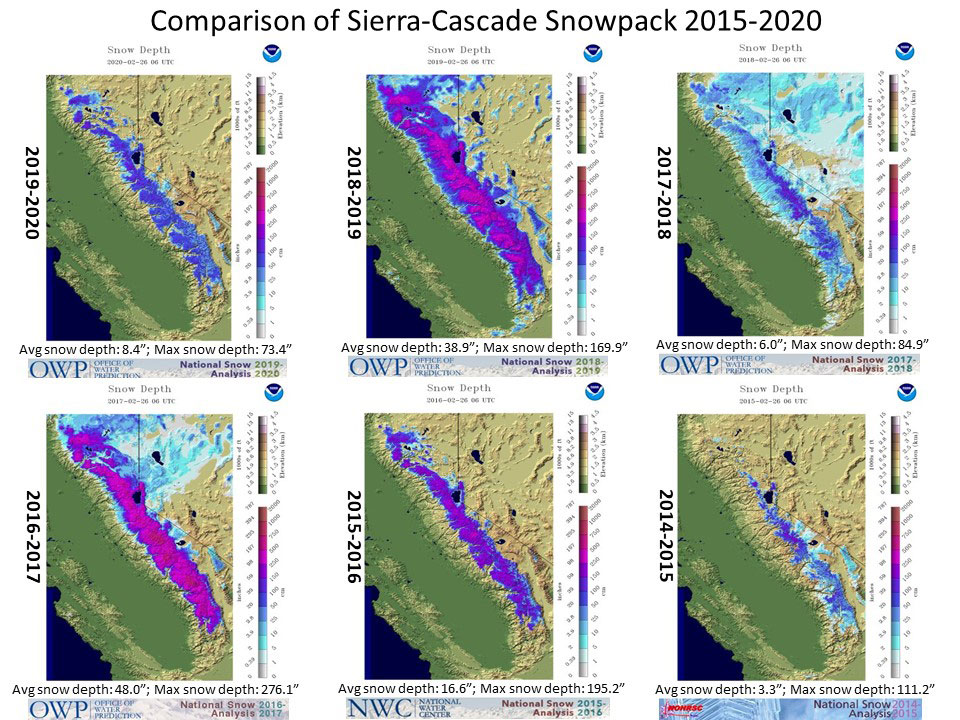
“A comparison of the snowpack across the Sierra-Cascade range over the past 6 years shows the true variability of a California wet season. While numbers are similar to the 2017-2018 winter, snow did extend into somewhat lower elevations back then.” NWS Sacramento, February 26, 2020
Dry times in Northern California
While rainfall totals have been closer to average in most of Northern California, downtown Sacramento and downtown San Francisco did not receive any precipitation in February, according to the National Weather Service. The last time San Francisco saw a dry February was in 1864, according to the NWS.

Rainfall above historical average in San Diego
Southern California is faring better, with rainfall at 125% of the historical average at Lindbergh Field in San Diego.
Most major California reservoirs are at or above the historical averages for late-February.
The state’s largest six reservoirs currently hold between 92% (Oroville) and 132% (Melones) of their historical averages for February 26. Lake Shasta, California’s largest surface reservoir, is 107% of its historical average and sits at 78% of capacity, according to the California Department of Water Resources.
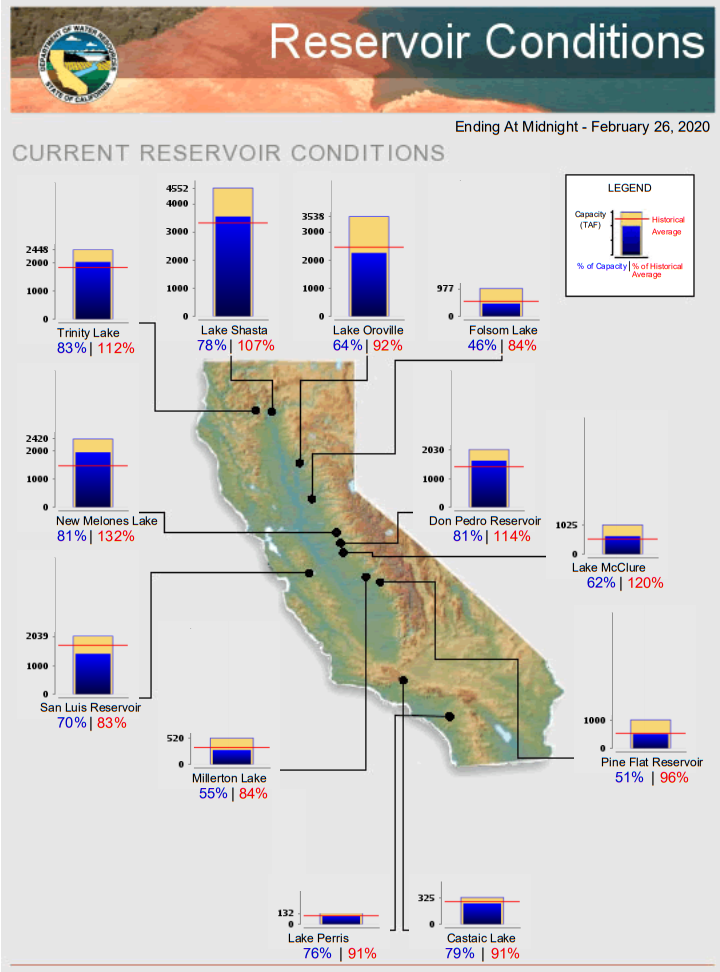
California’s largest six reservoirs hold between 92% and 132% of their historical averages for Feb. 27. Lake Shasta, California’s largest surface reservoir, is at 107% of its historical average and is at 78% of capacity. Graphic: California Department of Water Resources
The Department of Water Resources February 27 conducted the third manual snow survey of 2020 at Phillips Station. The manual survey recorded 29 inches of snow depth and a snow water equivalent of 11.5 inches, which is 47% of the March average for this location, according to a DWR news release. The snow water equivalent measures the amount of water contained in the snowpack, which provides a more accurate forecast of spring runoff.
Spring storms could boost snowpack
“Right now, 2020 is on track to be a below-average year but we could still see large storms in March and April that will improve the current snowpack,” said Sean de Guzman, chief of DWR’s Snow Surveys and Water Supply Forecasting Section. “While periods of dry conditions are expected in California, climate change has made them more unpredictable and extreme which is why we must always use the water we have wisely.”
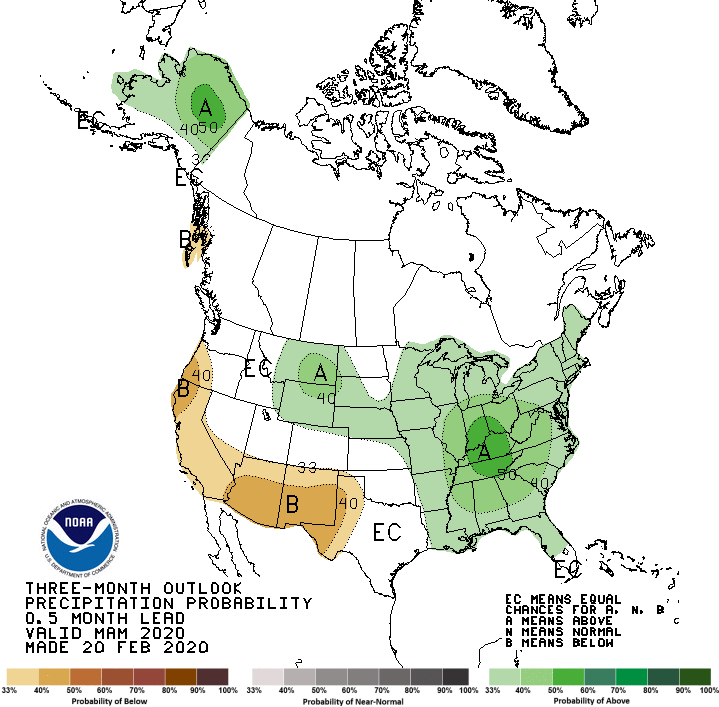
The seasonal outlook for March, April, and May sees below-normal chances for a wet period across California and the Southwest U.S. while most areas are favored to be warmer than usual. Graphic: National Weather Service Climate Prediction Center
Looking ahead, the National Weather Service Climate Prediction Center forecast favors above-normal temperatures and below-normal precipitation through May for most of California.
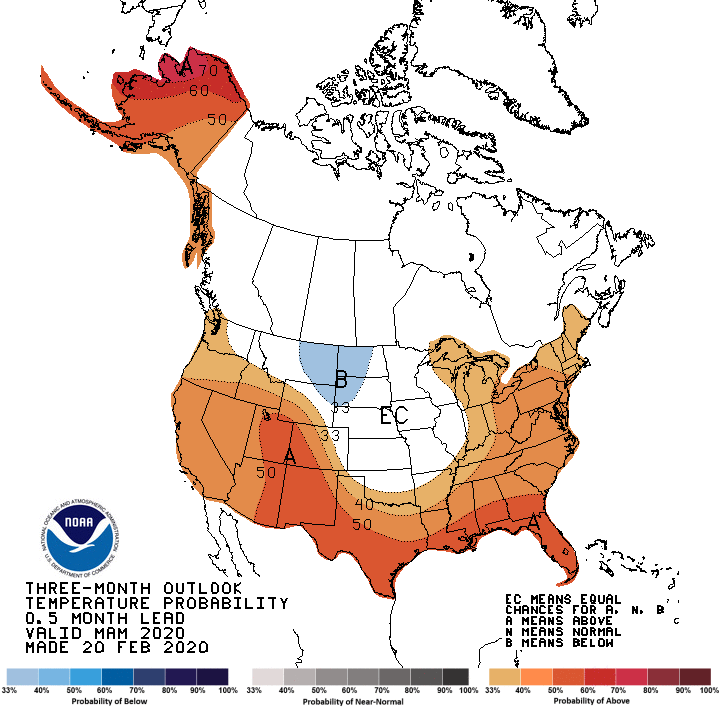
The National Weather Service Climate Prediction Center forecast favors above-normal temperatures and below normal precipitation through May for most of California. Graphic: National Weather Service Climate Prediction Center









