Water Authority Board Approves 2020 Urban Water Management Plan
The San Diego County Water Authority Board of Directors May 27 approved the Water Authority’s 2020 Urban Water Management Plan for timely submission to the state. The plan highlights how regional investments in a “water portfolio approach” to supply management and a sustained emphasis on water-use efficiency mean that San Diego County will continue to have reliable water supplies through the 2045 planning horizon – even during multiple dry years.
The Board approved the final plan following a public hearing on March 25 and a 60-day public comment period which ended May 6. The final 2020 UWMP will be submitted to the California Department of Water Resources by the July 1, 2021, deadline.
“Successful efforts to create a reliable water supply coupled with the development of new local sources by the Water Authority and its 24 member agencies ensure that the region will weather dry times over the next two decades,” said Water Authority Board Chair Gary Croucher. “We continue to collaborate with our member agencies on investments in infrastructure and local supply sources to benefit the region’s ratepayers now and in future years.”
Collaboration with member agencies
The Water Authority started the current UWMP process in September 2018, coordinating closely with its 24 member agencies, most of which must submit their own plans to the state. Member agencies provided input into the final plan as part of the Water Authority’s ongoing effort to align local and regional projections as closely as possible while still following applicable guidelines and using regional models. The plan’s long-range demand forecast shows an increase in regional demands of less than 1% per year through 2045. This change in demand is consistent with the change forecasted by other large water suppliers in the state, including the City of San Diego and the Metropolitan Water District of Southern California.
Multiple supply and demand projections factor into Urban Water Management Plans, which are mandated by the state to ensure sufficient supplies over 25 years. The plans are not used to set water rates; rates are set annually based on multiple financial factors at the time, not long-term projections about water supplies.
Water supply availability
Urban Water Management Plans are dictated by statutory guidelines, Water Authority Board direction and an agreement with the San Diego Association of Governments to use its regional growth forecast. The plans also support state laws that link approval for large housing developments to water supply availability.
By law, the plans must be updated every five years. Per state guidelines, the Water Authority’s Urban Water Management Plan includes:
- Projected water demands under normal weather and dry weather scenarios
- Conservation savings information
- A process to conduct an annual water supply and demand assessment
- Supply reliability analysis
The demand forecast accounts for changes in socio-economic factors, such as the number of projected housing units, the mix of single-family and multi-family dwellings, and employment growth.
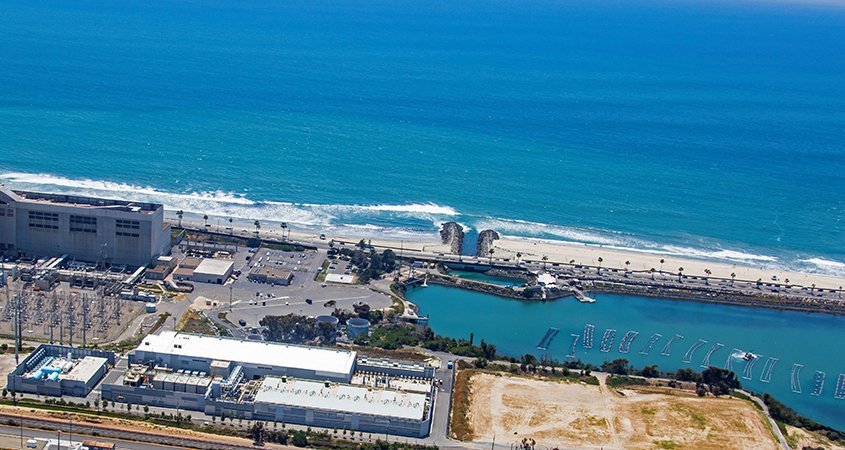

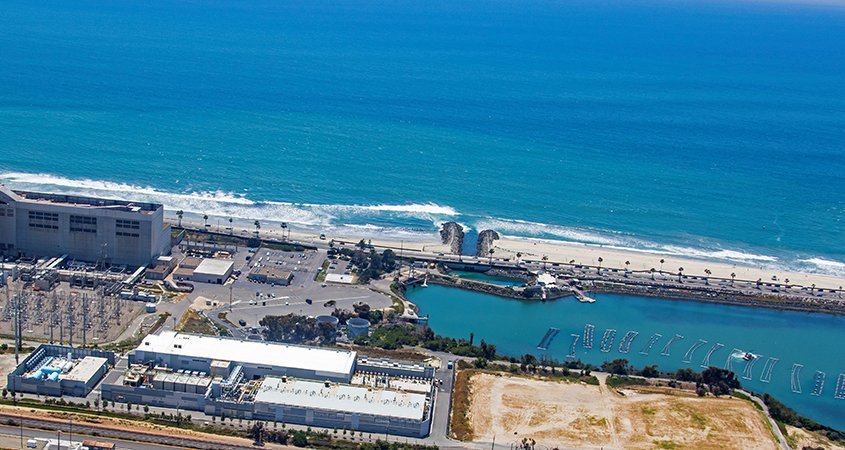
The 2020 UWMP highlights the value of the Water Authority’s long-term strategy to invest in highly reliable and locally controlled supplies from the Claude “Bud” Lewis Carlsbad Desalination Plant. Photo: San Diego County Water Authority
Investments in local water supply
Conservation projections account for continued adoption of water-use efficiency measures, compliance with landscape water-use ordinances for new residential construction, and continued installations of sustainable landscapes at existing homes. Since 1991, San Diego County ratepayers have conserved more than 1 million acre-feet of water, and per capita potable water use in the region decreased nearly 50% between fiscal years 1990 and 2020.
The 2020 UWMP also highlights the value of the Water Authority’s long-term strategy to invest in highly reliable and locally controlled supplies from the Claude “Bud” Lewis Carlsbad Desalination Plant and the nation’s largest conservation-and-transfer agreement, which provides high-priority, low-cost water from the Colorado River.
In addition to the UWMP, the Water Authority also regularly updates its Regional Water Facilities Optimization and Master Plan, which focuses on the infrastructure necessary to meet projected long-term demands, and its Long-Range Financing Plan. Those documents work together to ensure the right mix of supplies and facilities to meet the region’s needs at an affordable cost.
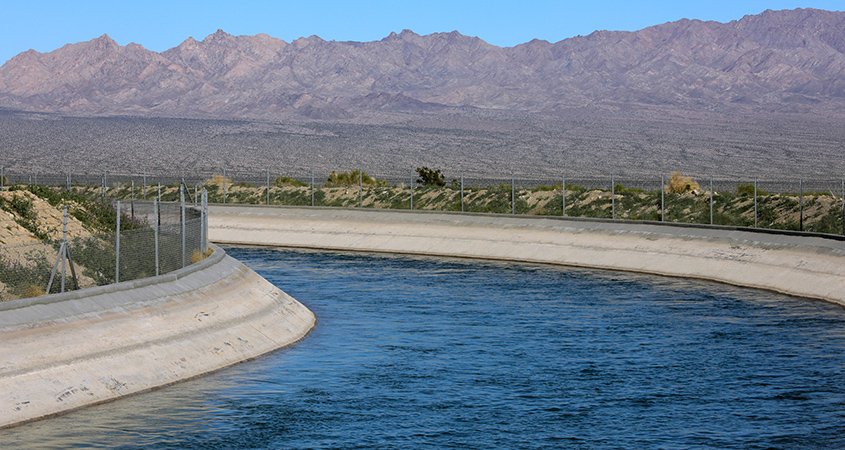

The nation’s largest conservation-and-transfer agreement, which provides high-priority, low-cost water from the Colorado River, is one of several investments that ensures a reliable, plentiful water supply for the San Diego County region. Photo: San Diego County Water Authority