It’s that time of the year in California, when water managers, climatologists and meteorologists look at the factors that determine what the winter will bring during Water Year 2020-21 (October 1, 2020 – September 30, 2021).
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration recently said that La Niña conditions are present in the tropical Pacific, “with an approximately 85% chance of La Niña lasting through the winter.” Forecasters currently think this La Niña will be on the stronger side. For California, those conditions typically mean a drier winter, with increasingly dry conditions heading into 2021.
Fortunately for the San Diego region, any impacts from La Niña will be lessened because of the region’s development of a diversified water supply portfolio. Following a record number of acres burned from wildfires in 2020, La Niña would only increase fire danger.
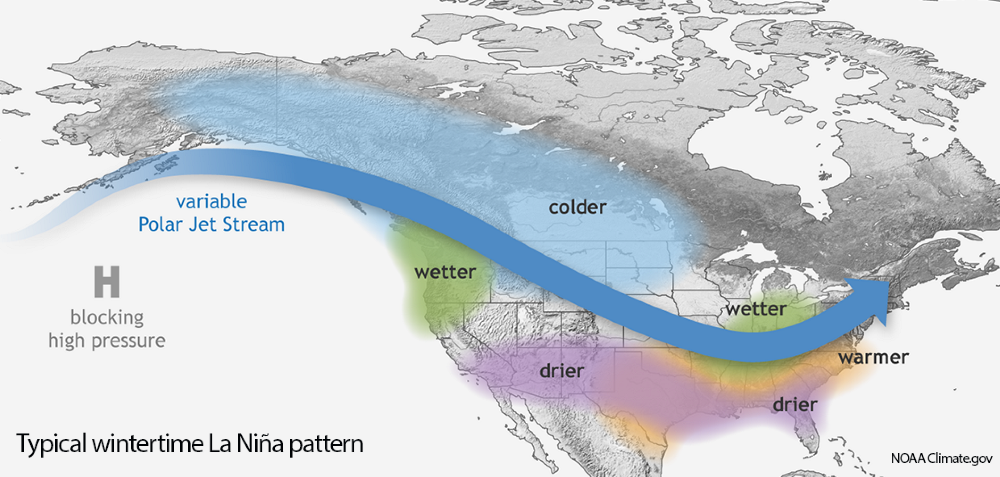
La Niña continues in the tropical Pacific, with an approximately 85% chance of lasting through the winter, according to NOAA’s October 2020 La Niña update. Graphic: NOAA
Water Year 2020
But, whether the forecasts come to fruition, and what that means for California’s water supply, won’t be fully known until next spring. What we know now is that the water year that just ended (October 1, 2019 – September 30, 2020) varied across the state.
While Northern California was mostly dry, parts of Southern California experienced above average precipitation, according to the California Department of Water Resources. The agency said that the water year ended below average and pointed to the impact of climate change on the California’s water supply.
Impacts of climate change
“California is experiencing the impacts of climate change with devastating wildfires, record temperatures, variability in precipitation, and a smaller snowpack,” said DWR Director Karla Nemeth. “We must continue to invest in our infrastructure to prepare the state to cope with more extreme weather for the state’s needs today and in the future.”
For Water Year 2020, a lack of precipitation resulted in a snowpack of just 50% of average on April 1, as measured by the California Cooperative Snow Survey Program, making it the 10th smallest snowpack in California since 1950, according to the DWR. California’s reservoirs received just a third of the water runoff from precipitation and snowmelt that they did during the same time period a year ago.
The wet season got off to a slow start, but a series of storms in late November and early December pushed 2019 precipitation to near or above average in central and southern California, according to Goldy Herbon, San Diego County Water Authority senior water resources specialist.
Driest February on record
“The wet start didn’t last with dry conditions taking hold over most of the state in January, and then most of California experienced its driest February on record,” said Herbon.
While precipitation picked up in March 2020 for Southern California, statewide snowpack in mid-March was only 38% of average.
“The dry north/wet south precipitation pattern continued in March and April, with some locations in Southern California setting many daily precipitation records, San Diego included, as northern California precipitation levels remained below average,” said Herbon.
Water supplies in “excellent shape”
Despite the below average year in northern California, Herbon said statewide water supplies are in “excellent shape” thanks to above average precipitation the previous year and good reservoir storage. DWR reports that statewide reservoir storage through the end of September 2020 was projected to be 93% of average.
In the San Diego region, a wet spring boosted rainfall totals to near or above normal.

Regional precipitation during Water Year 2020. Graphic: National Weather Service San Diego