Rave Reviews for Vallecitos Water Academy Facilities Tour
The reviews are in for the 2024 Vallecitos Water District’s annual Water Academy, featuring a tour of the District’s facilities.
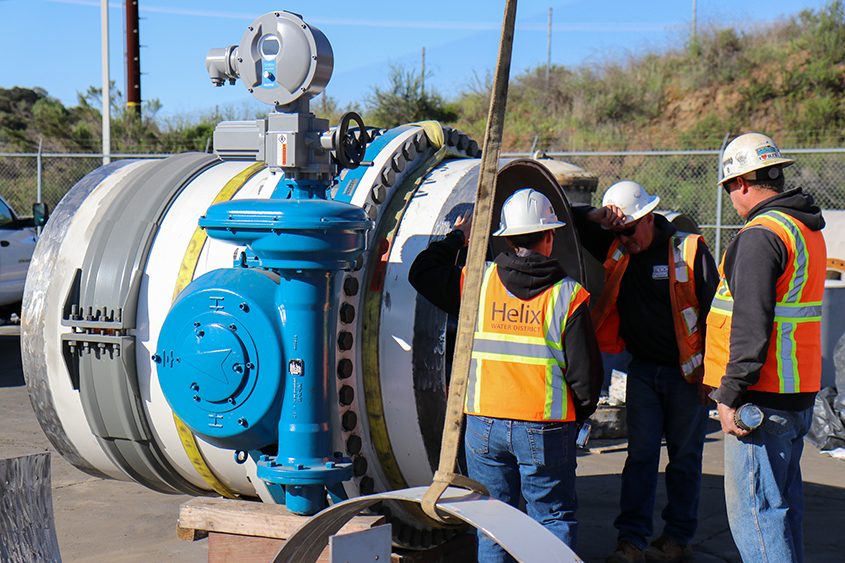
Participants raved about their opportunity to learn firsthand about the District’s operations from its professional staff in multiple disciplines, including James H. Gumpel, P.E., Vallecitos Water District General Manager.
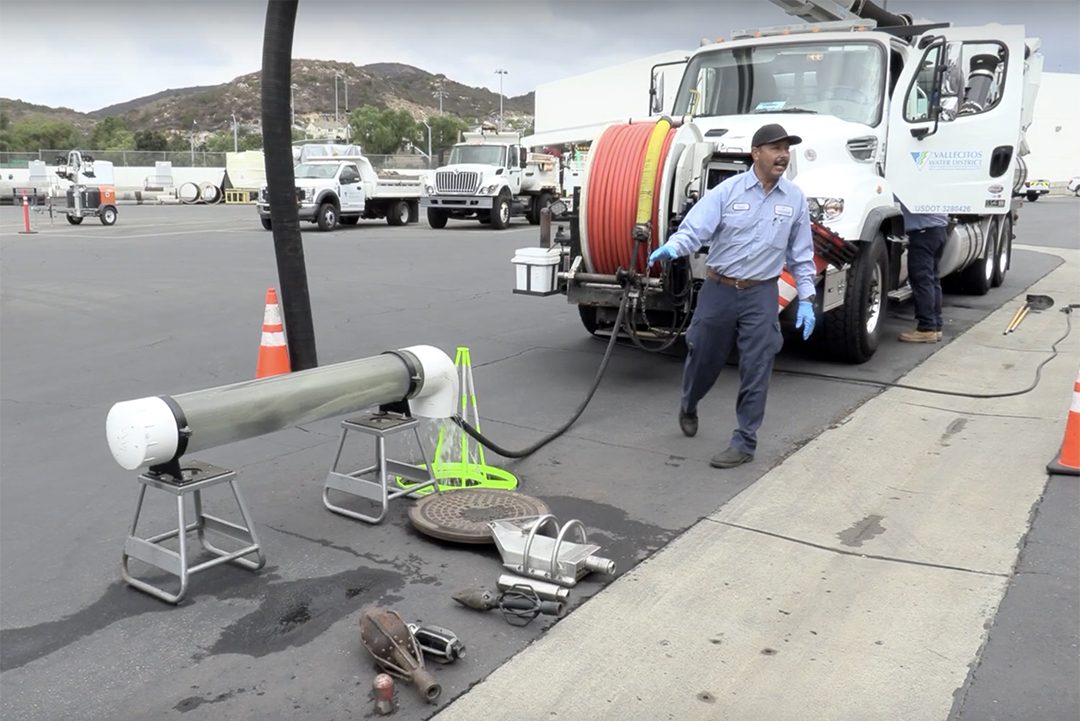

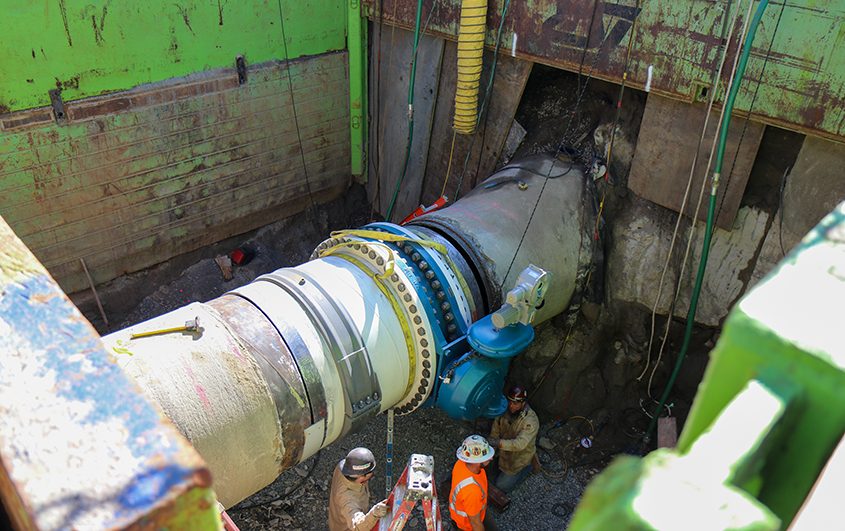
Raul Rodarte, Wastewater Collections Worker II, offers a demonstration during the facilities tour. Photo: Vallecitos Water District
Among the stops along the tour:
- Water Operations Control Room
- Wastewater Collections
- Warehouse, Construction, and Training Facilities
- Maintenance and Repair Shops and Mechanics Bay
- Sustainable Demonstration Garden and Meters
See a video of the facilities tour events.
Water Academy Tour Highlights
The District’s Wastewater Collections Department demonstrated how it keeps sewer pipes clean with a combination truck. The CCTV camera van was also on display. A recorded video showed how the camera system inspects the District’s sewer pipes.
Wastewater Collections staff are also trained as the District’s Confined Space Rescue Team. They discussed how the team’s preparedness and training to address emergencies immediately, instead of waiting for first responders, can save lives.
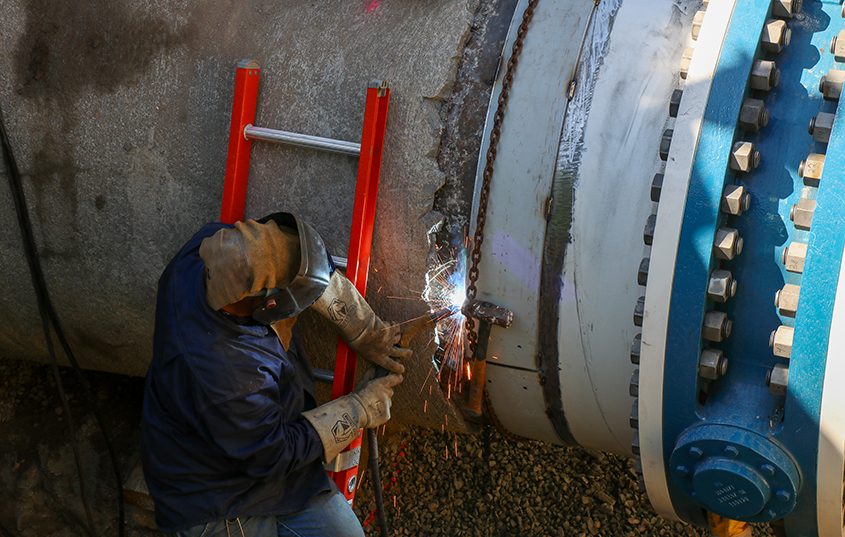
At the District’s welding shop and mechanics bay, mechanics explained how performing repairs in-house saves District customers money.
The Maintenance Services Department discussed the essential emergency repair parts maintained in the warehouse which allows construction crews to expedite water main repairs and return service to the customers as soon as possible.
Close Up Look At Equipment
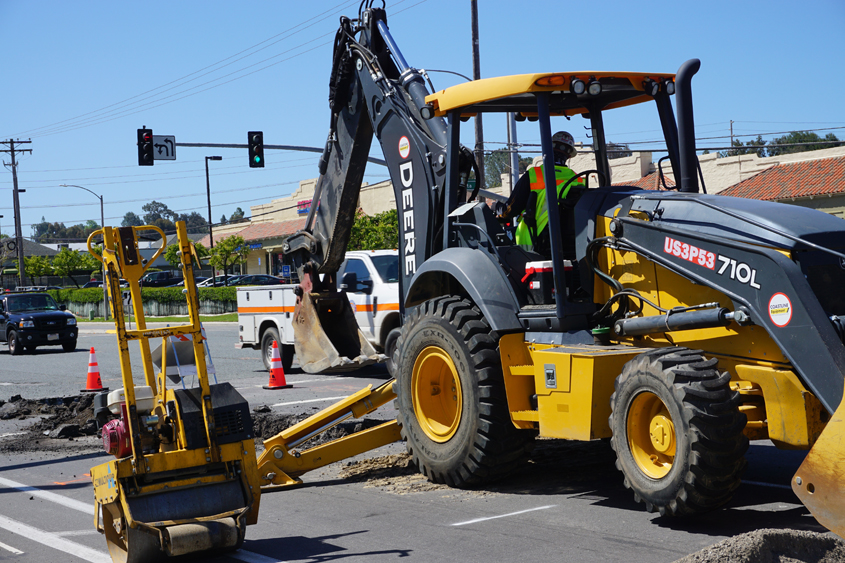
Water Academy participants also got a presentation by the Construction Department with a closeup look at heavy equipment in operation, including a Mini-Excavator, Backhoe, Skid Steer, Hydro Excavator and Service Truck, and a 10-wheeler Dump Truck. All the equipment enables Vallecitos Water District personnel to repair water mains as quickly as possible to return customers to service.
Water Operations personnel demonstrated the Neutral Output – Discharge Elimination System (NO-DES) trailer, which functions as a portable water filtration unit. It removes minerals that can settle in water mains over many years. This helps to maintain high water quality for the District’s customers.
Vallecitos Water District is among the first agencies in San Diego County to purchase one of these units. It also helps the District comply with regulations that require urban retail water suppliers to submit water loss audits to the State of California annually. Water agencies are required to account for every drop of water and reduce water waste wherever possible.
Staff Demonstrate Specialized Skills
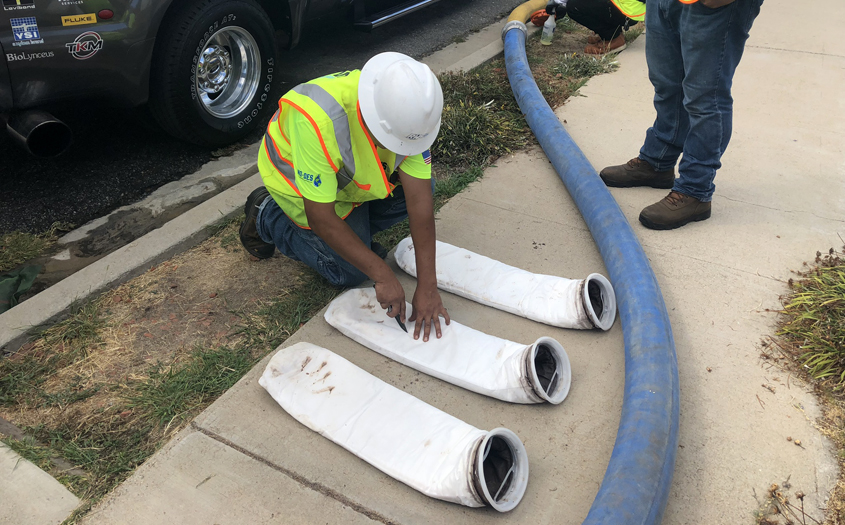
At the District’s Spill Emergency Response Plan Training Center, participants learned how Vallecitos employees practice responding to sewer spills and watched a demonstration. All water used for training and the demonstration is potable water rather than actual wastewater. A combination truck was set up downstream to demonstrate how a sewer spill would be mitigated and collected.
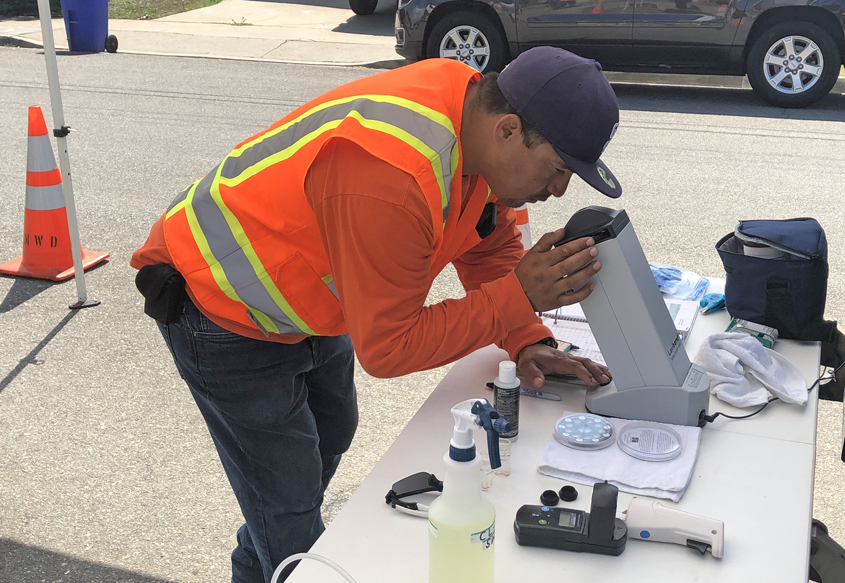
Water Operations field and lab testing equipment were on display. Several tests were run to show how lab testing in-house delivers faster, more cost-efficient results. Additionally, staff showed customers how, by adding CO2 to a water sample, the pH (measure of acidity or basicity) is changed.
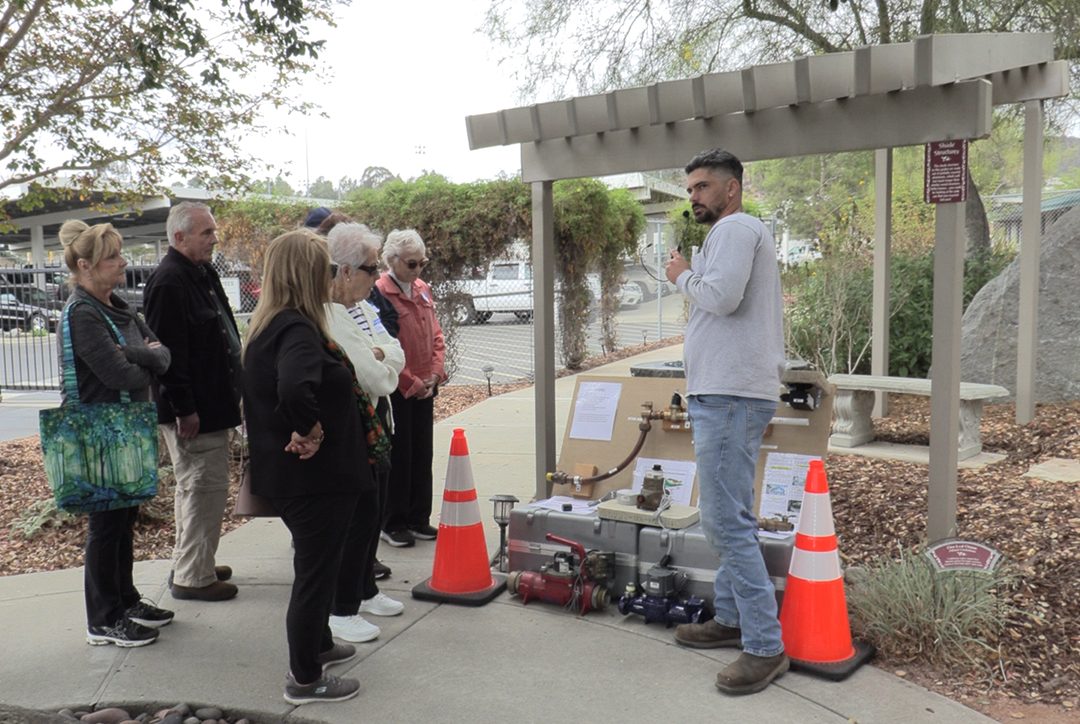

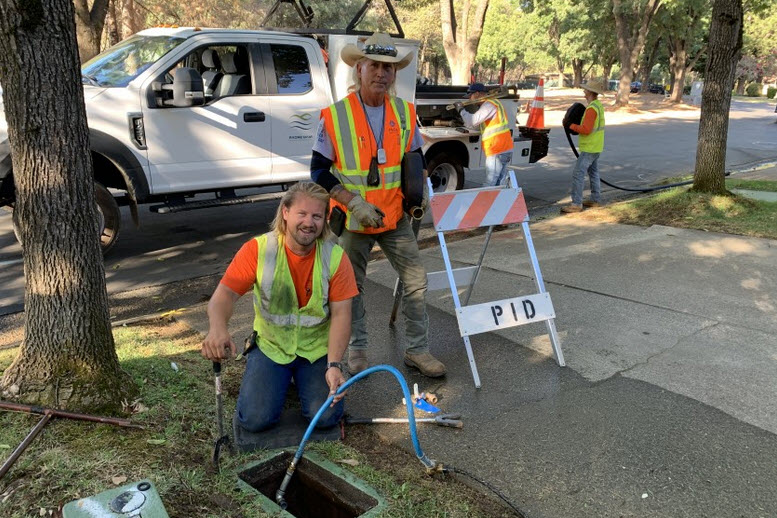
Vallecitos Water District customers learn how to check their meters at home. Photo: Vallecitos Water District
Employees in the Meter Department showed customers how to read their own meters and how to check for leaks.
No Vallecitos Water District tour is complete without a stroll through its Sustainable Demonstration Garden, including its new seed library and garden features.
Positive Participant Feedback For Facilities Tour
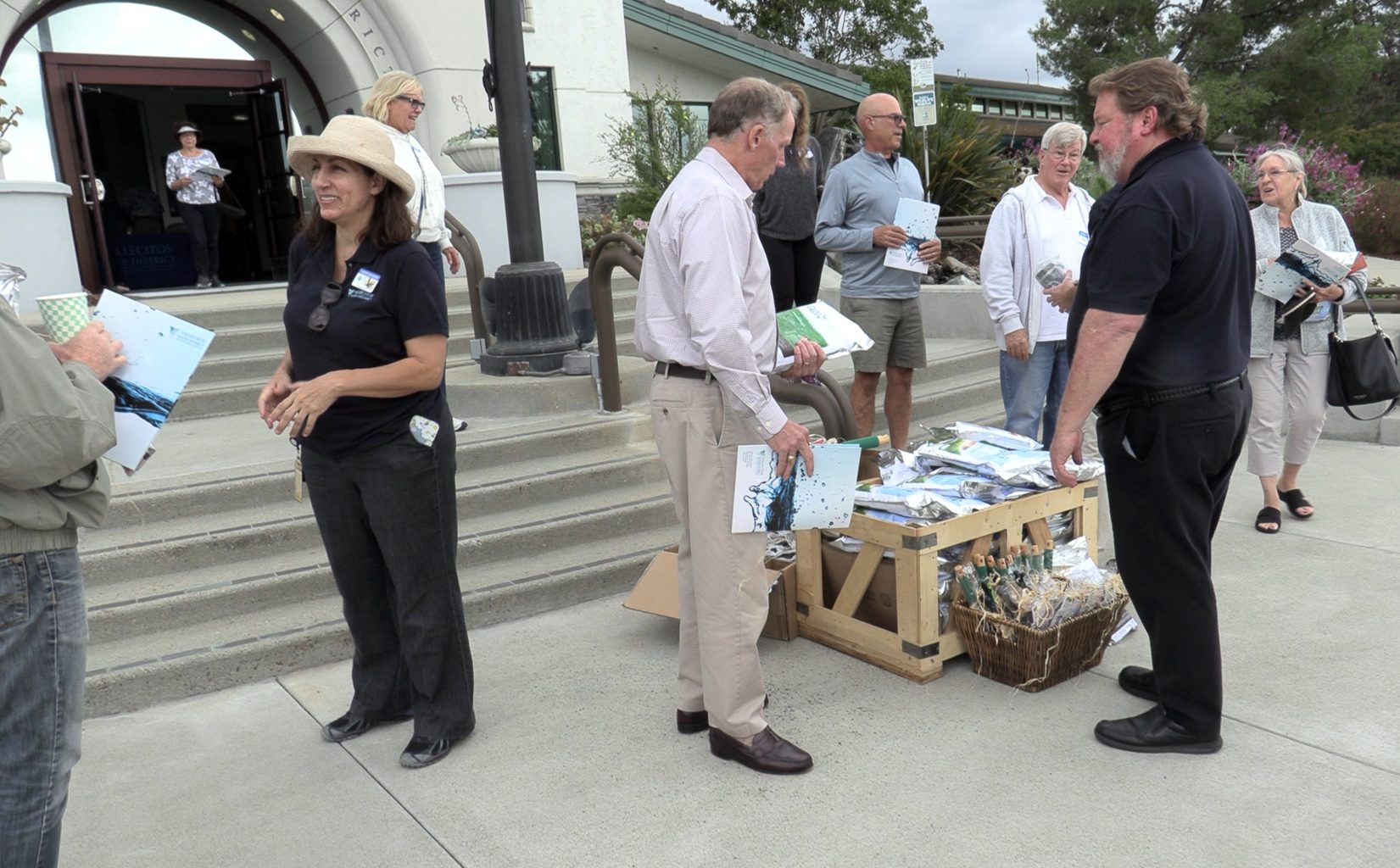

Participants in the Vallecitos Water District facilities tour offered positive feedback from their experience. Photo: Vallecitos Water District
Participants received samples of PureGreen fertilizer from Encina and water bottles and had fun with trivia questions to conclude the tour.
Participant reviews highlighted the complexity of the operation, the friendly staff, and how much they learned.
“(The) complexity of providing water to a high population density coastal area. Good people with good management” wrote Frank Yakos.
“Previous to today I already had a very positive impression of VWD. Today’s information increased my positive impression immensely,” wrote Diane Veach.
“Learned something interesting from each presenter, learned a lot! Loved how friendly everyone is,” wrote Ann Kreile.
“I’m impressed with everything! Clean facility! Great staff! Great presentation!” raved Nancy Sims.
“Thanks! Keep up the good work!” said it all for Michael Wilkinson.