How Much Water Can Your New Landscape Conserve?
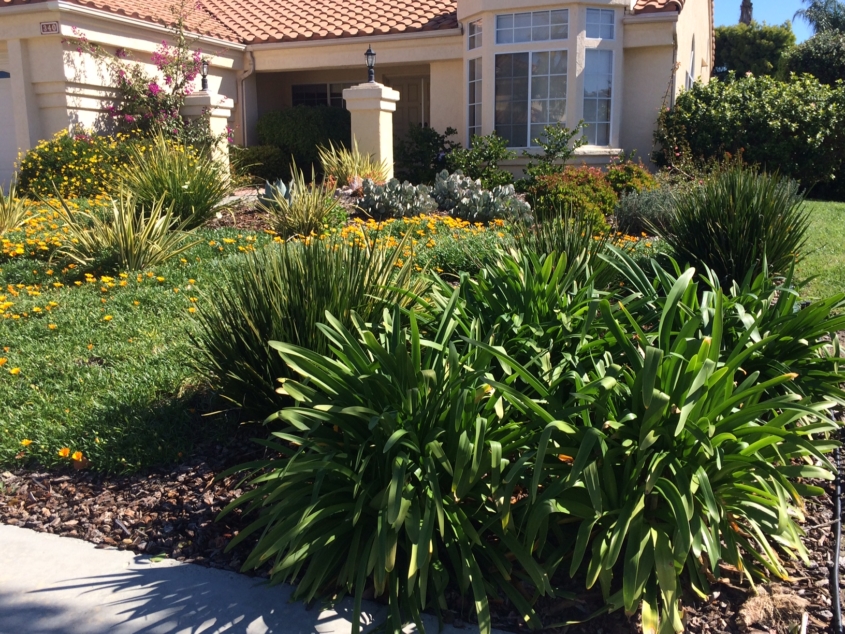
Landscape designs using the least amount of potable water necessary are greatly encouraged in arid or Mediterranean climates like in San Diego County. It’s an important motivation for homeowners to consider efficiency and sustainability to lower water use, saving a precious resource.
Maximizing your landscaping’s ability to capture and use natural rainfall can also help reduce or even completely eliminate your reliance on potable water for irrigation. Compare how much water your new landscape design will need against your existing landscaping’s water use. You’ll be able to estimate your future water savings.
Start by calculating the water use requirements of landscaping filled with plants that require high amounts of water, or moderate amounts, low or very low water requirements.
In these examples, evapotranspiration (ET), irrigation efficiency, and landscape area are exactly the same. The only difference: our examples are home to plants with different water requirements.
How to calculate your landscape’s water use
To calculate water use, you can refer to the San Diego Water Efficient Landscape Ordinance for guidance. Go to www.sdcounty.gov and search “Landscape Ordinance.” The four key variables are:
- Landscape Area (LA) – the square feet of area being landscaped with plants that require irrigation
- Evapotranspiration (ET) – this is the number in inches based on your San Diego Climate Zone
- Plant Factor (PF) – This is moderate, low, or very low depending on the plant selection
- Irrigation Efficiency (IE) – There is no such thing as a perfect irrigation system. Many factors can limit efficiency and impact your water use and the health of your plants.
Use a landscaped area of 1,000 square feet, with an ET of 51 inches annually, and IE of 0.7. Look at the big difference your plant selection can make in your water use.
Example 1: High Water Use plants (PF = 0.8) – 36,137 gallons of water per year
Example 2: Moderate Water Use plants (PF = 0.5) – 22, 586 gallons of water per year
Example 3: Low Water Use plants (PF = 0.2) – 9.034 gallons of water per year
Example 4: Very Low Water Use plants (PF = 0.1) – 4,517 gallons of water per year
From the highest estimate to the lowest estimate, you could potentially save 17,103 gallons of water every single year.
This article is part of a year-long series inspired by the 71-page Sustainable Landscapes Program guidebook. The Water Authority and its partners also offer other great resources for landscaping upgrades, including free WaterSmart classes at WaterSmartSD.org.