As partners, the City of San Diego and the San Diego County Water Authority will begin negotiations on a project development agreement with the BHE Kiewit Team to develop Phase 1 of the potential San Vicente Energy Storage Facility Project, which could generate enough energy for about 135,000 households.
The proposed project is subject to a full environmental review and regulatory approvals. If the Water Authority and City of San Diego decide to proceed after completing environmental review, the San Vicente Energy Storage Facility would provide up to 500 megawatts of long-duration stored energy upon completion to help meet peak electrical demands throughout Southern California and help meet California’s renewable energy goals.
“Reliable, clean source of energy”
“On top of providing a reliable, clean source of energy and helping our City and the state of California meet our climate goals, this project has the potential to create well-paying local jobs,” said San Diego Mayor Todd Gloria. “I’m proud of the City’s partnership on this project and look forward to it moving though the regulatory approval process to fruition.”
The Water Authority’s Board of Directors on January 27, approved entering into negotiations with BHE Kiewit, along with a $4.6 million contract with AECOM Technical Services, Inc. to perform environmental work for the project.
The Board also approved a $1.6 million amendment to a professional services contract with Black & Veatch Corp. to support project development agreement negotiations, provide technical expertise for a California Independent System Operator interconnection application, perform preliminary design and engineering reviews, and assist with preparing a Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) license application.
Water Authority Board Chair Gary Croucher said the Board’s action will help propel the potential project forward by getting started on environmental review and other necessary requirements. “The San Vicente Energy Storage Facility Project meets multiple goals for the San Diego region, including protection from blackouts and supporting climate-friendly energy sources,” said Croucher. “We’re excited to get moving.”
Phase 1
Phase 1 work includes activities required to complete site investigations, design, and engineering; support state and federal environmental reviews; support the acquisition of a CAISO interconnection agreement; support the acquisition of a FERC license; and collaborate with project partners to achieve commercialization.
Four proposals were received and evaluated for the project development contract. Teams submitted written proposals followed by interviews in December. Evaluators considered each team’s understanding of the scope of work, technical and specialized qualifications, strategies to commercialize the project, and financial capabilities.
Pumped energy storage facility project
The panel unanimously recommended starting negotiations with the BHE Kiewit Team, which includes BHE Renewables, LLC, and Kiewit Development Company. BHE Renewables, LLC, is a wholly owned subsidiary of Berkshire Hathaway Energy Company. The Water Authority Board today also approved negotiating with Rye Development, LLC, if negotiations with the BHE Kiewit Team are not successful.
California sources nearly one-third of its power from renewables, mainly solar and wind. The target for renewable energy in California is 60% by 2030. Such a major shift to renewables will require new kinds of investments, markets and business practices. Electric grids need to be more flexible; new kinds of power supplies will help deliver energy flexibility when needed; and new pricing systems are needed to send clear signals to developers and financial markets that these projects need to move forward.
Pumped energy storage projects, such as the San Vicente Energy Storage Facility, are designed to store excess renewable energy from solar and wind during the day, and then discharge that energy when energy use increases in the evening and renewable energy is not as plentiful.
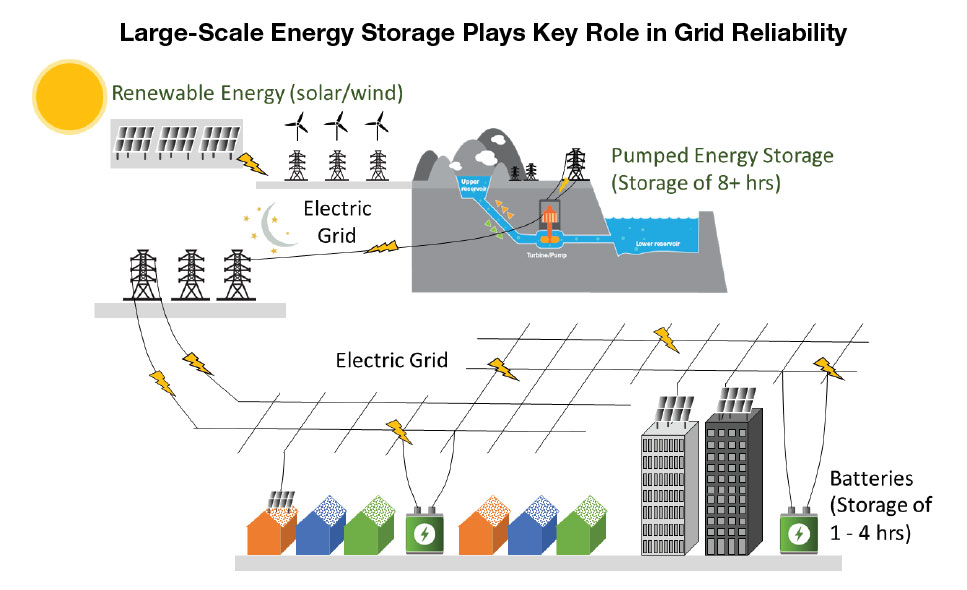
The San Diego County Water Authority and the City of San Diego are partners in developing the San Vicente Energy Storage Facility. The pumped storage energy project at San Vicente Reservoir could store 4,000 megawatt-hours per day of energy, or 500 megawatts of capacity for eight hours. Graphic: San Diego County Water Authority
The San Vicente project would create a small upper reservoir above the existing, City-owned San Vicente Reservoir, along with a tunnel system and an underground powerhouse to connect the two reservoirs. As planned, the powerhouse would contain four reversible pump turbines.
During off-peak periods – when power is inexpensive and renewable supplies from wind and solar facilities exceed demand – turbines would pump water to the upper reservoir where it would act as a battery of stored potential energy. During high energy use, the system would discharge water from the upper reservoir downhill through the turbines, producing energy. The exchange between the two reservoirs would not consume water.
San Vicente Reservoir is near major electricity transmission interconnection facilities, which would allow the project to play a central role in integrating solar and wind energy from across the Southwest for use in San Diego County.
The San Vicente project is largely immune to the challenges faced by some conventional hydropower facilities because it would rely on an existing reservoir that holds primarily imported water and does not fluctuate significantly from year to year.
For more details about the San Vicente Energy Storage Facility go to: www.sdcwa.org/projects/san-vicente-pumping-facilities/.
(Editor’s Note: The City of San Diego is one of the San Diego County Water Authority’s 24 member agencies that deliver water across the metropolitan San Diego region.)








