The California Department of Water Resources May 1 conducted the fifth snow survey of the season at Phillips Station. The manual survey recorded 59 inches of snow depth and a snow water equivalent of 30 inches, which is 241% of average for this location on May 1. The last time there was measurable snow at the Phillips snow course on May 1 was 2020, when only 1.5 inches of snow and .5 inches of snow water equivalent was measured
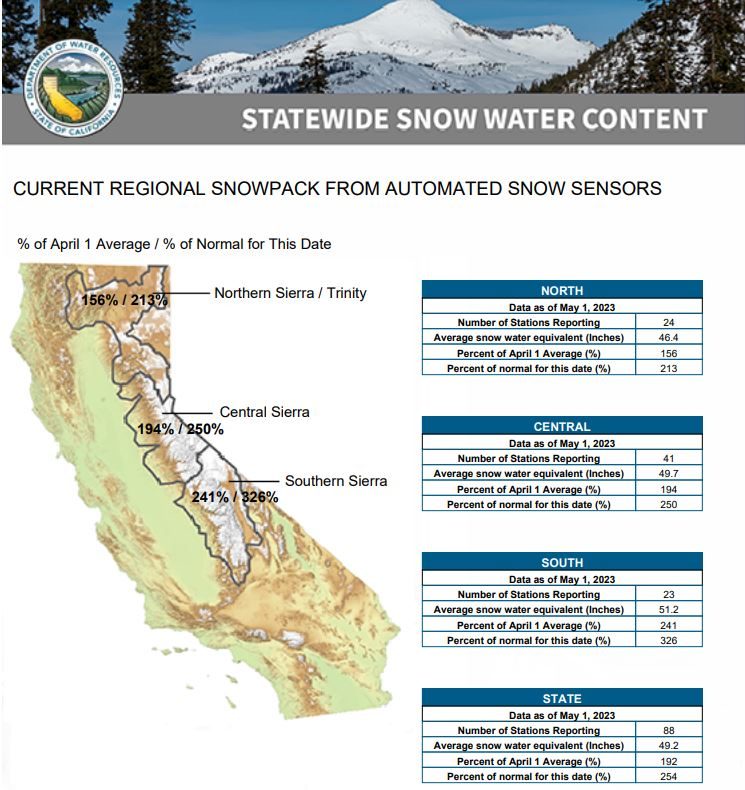
DWR’s electronic readings from 130 snow sensors placed throughout the state indicate the statewide snowpack’s snow water equivalent is 49.2 inches, or 254% of average for May 1.
The snow water equivalent measures the amount of water still contained in the snowpack and is a key component of DWR’s water supply run-off forecast.
“While providing a significant boost to California’s water supplies, this year’s massive snowpack is posing continued flood risks in the San Joaquin Valley,” said DWR Director Karla Nemeth. “The snowpack will not disappear in one week or one month but will lead to sustained high flows across the San Joaquin and Tulare Basins over the next several months and this data will help us inform water managers and ultimately help protect communities in these regions.”
Snowmelt runoff forecasts
Snow surveys like the one at Phillips Station are critical to planning for impacts of the coming snowmelt runoff on communities. DWR uses the most updated technology to gather data from snow surveys, a network of 130 remote snow sensors, and airborne snow observatory data to gather information on current real-world conditions to create the most accurate snowmelt runoff forecasts possible. These runoff forecasts, published through DWR’s Bulletin 120, allow reservoir operators to plan for anticipated inflows and water managers downstream of reservoirs to plan and prepare for flood risks.
Despite a brief increase in temperatures in late April, the statewide snowpack overall melted at a slower pace than average over the month of April due to below average temperatures early in the month and increased cloud cover. An average of 12 inches of the snowpack’s snow water equivalent has melted in the past month and it now contains an average of 49.2 inches.
Water supply, flood control planning
“No matter how you look at the data, only a handful of years in the historical record compared to this year’s results,” said Sean de Guzman, manager of DWR’s Snow Surveys and Water Supply Forecasting Unit. “Survey results from our partners in the California Cooperative Snow Surveys Program and other data, including data from Airborne Snow Observatory flights, allow us to incorporate these data into our models to provide the most accurate snowmelt runoff forecasts possible right now to inform water supply, flood control, and planning.”
Climate Change and snowpack averages
According to historical records, only the April 1 measurements from the years 1952, 1969, 1983 and this year were above 200 percent, although it is difficult to directly compare individual years across the decades due to changes in the number of snow courses measured over time.
Due to the impact of climate change on California’s snowpack, since 2021, snowpack averages have been calculated using a timeframe of 1991 through 2020 so that results better reflect the current climate conditions.
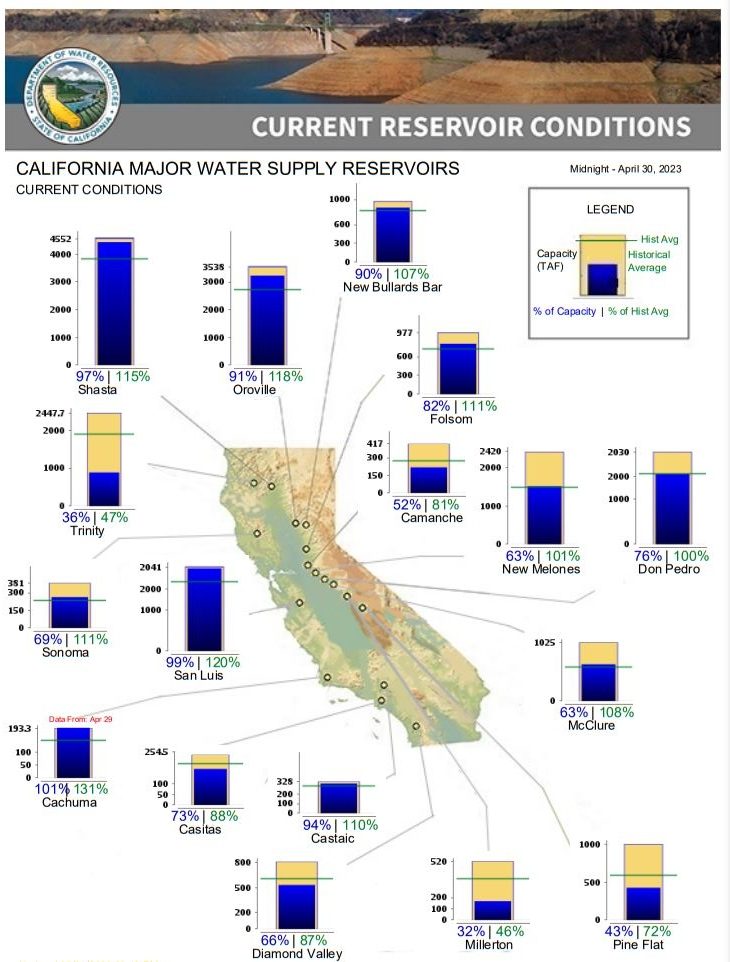
DWR is maximizing the amount of water that can be stored and diverted from this record snowpack.
In April, DWR announced a 100% allocation of requested supplies from the State Water Project, which delivers water to 29 public water agencies that serve 27 million Californians and 750,000 acres of farmland. The last time the SWP allocated 100% was in 2006. DWR is also maximizing the amount of water that can be diverted towards recharging groundwater basins so more water is stored for future use in underground reservoirs.
Flooding impacts in California
Last week, Governor Newsom visited the Tulare Basin to tour flood impacts first hand, met with community leaders and emphasized the state’s commitment to supporting and providing appropriate assistance to counties impacted by recent and anticipated flooding this spring and summer.
Snowmelt runoff forecasts are an instrumental part of the assistance provided by DWR’s State-Federal Flood Operations Center (FOC), which is supporting emergency response in the Tulare Lake Basin and Lower San Joaquin River by providing technical and materials assistance to support ongoing flood response activities.
Storms this year have caused impacts across the state including flooding in the community of Pajaro and communities in Sacramento, Tulare, and Merced counties. The FOC has helped Californians by providing more than 1.4 million sandbags, 1 million square feet of plastic sheeting, and 9,000 feet of reinforcing muscle wall, across the state since January.
(Editor’s Note: Information in this story was provided by the California Department of Water Resources).









 Sweetwater Authority Logo 2019
Sweetwater Authority Logo 2019

