Using Compost and Mulch to Build Healthy Soil
When undertaking a WaterSmart landscape renovation, strive to continuously feed as much organic matter as possible to the landscape soil to keep it healthy. Start first with compost and mulch to jump-start the process. Eventually, your plants will feed themselves with their own leaf litter.
Organic matter feeds microbes living in the soil that make soil fluffy. It’s similar to bread rising because of yeast.
Learn more about healthy soil in this instructional video
Compost and mulch – what’s the difference?
Compost is a soil amendment. It looks like soil and it’s hard to tell what it once was. That is because it is food scraps, landscape debris and/or manure from livestock, or biosolids (human manure) and other organic matter that already has been partially consumed and mostly decomposed by micro-organisms. Good compost brings oxygen, water, and life in one package.
Compost can be store-bought or made at home. The compost-making process, or composting, involves creating optimal conditions for the microbes to do their transformative work. When compost looks like soil, it can be worked directly into the soil. The more coarse or visible the bits of the compost are, the more likely it is to be used as mulch on top of the soil rather than as an incorporated amendment.
Compost works in several ways. First, the compost itself contains particles improving soil structure. Next, as compost decomposes in soil it encourages the formation of soil macroaggregates. The resulting macroaggregates are composed of existing soil particles and decomposed organic matter, which combine to create a more stable and better functioning soil structure.
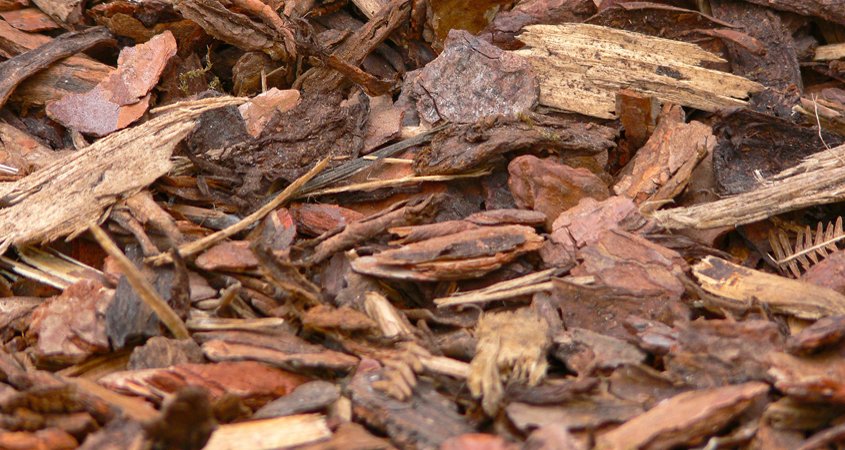

Mulch builds soil structure over time and holds in moisture. Photo: Monsterkoi/Pixabay
Mulch is a soil topping. Mulch may be organic or inorganic material covering soil. It’s made of larger particles and looks like recycled debris. Mulch can be made from organic matter such as grass clippings, leaf litter, and shredded wood trimmings, or inorganic materials such as gravel or decomposed granite.
The microbes in healthy, biologically diverse mulch bind the organic matter together, forming a thick blanket. This cover protects soil and plant roots from temperature change, keeps moisture in by slowing evaporation from the surface of the soil, and keeps weeds from sprouting by reducing sunlight penetration to the soil surface.
Mulch always stays on top of the soil. Unlike compost, it is never worked in. Recycled organic debris is the most effective type of mulch because it builds soil structure over time and provides a durable, protective surface barrier. The smaller the debris and the more mixed leaves with wood chips, the faster it decomposes. When building soil, small and mixed is best.
Composted material, especially coarse composts, also can be used as mulch. Artificial and inorganic mulches (decomposed granite, gravel, rubber chips, and other rubble) are primarily decorative since they do not contribute to soil life or plant health. They may be used in limited applications such as pathways.
__________________________________________________

(Editor’s Note: The San Diego County Water Authority and its 24 member agencies offer programs, resources, and incentives to improve water-use efficiency for residential, commercial, and agricultural users. WaterSmart choices are a way of life in the region. Stay WaterSmart San Diego! For more water-use efficiency resources, go to WaterSmart.SD.org.)