Helix Water District Creates WaterSmart Demonstration Landscape
Helix Water District recently completed a new demonstration landscape outside of its administration building in La Mesa. The project is intended to inspire and educate the surrounding communities to install WaterSmart landscaping, and it serves as an example that residents can use to help design their own landscaping.
The demonstration landscape includes three unique WaterSmart gardens on the streets around the building, including a Mediterranean garden on University Avenue, a desert landscape on Lee Avenue and a California native landscape along the building’s main entrance on Quince Street. The three gardens exemplify different types of plants that thrive in the climate of San Diego County and only need half to one-fifth of the water that a traditional lawn needs.
“Our new demonstration landscape shows customers that water-efficient landscaping is not just one style,” said Helix Water District Board President Mark Gracyk. “You can choose plants that compliment your home and personal taste – there is an option for everyone.”
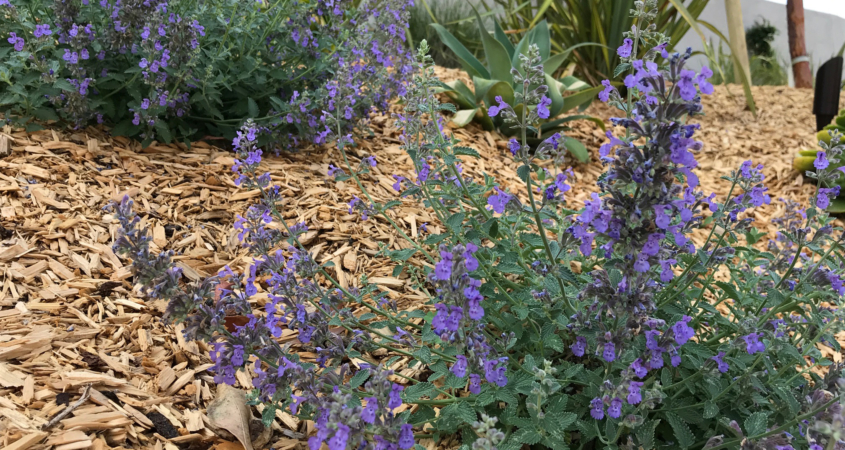

The native plants in the demonstration garden show that WaterSmart landscaping not only saves water and maintenance costs but can be beautiful too. Photo: Helix Water District
Interactive garden gives residents visual design inspiration
Each garden is full of a variety of flowers of different colors and textures. Plant markers are placed to identify each plant and QR codes provide easy access to plant names, sun and water needs, mature size and photos when scanned through the camera of a smartphone.
The water district also created an interactive webpage https://hwd.com/demonstration-landscape where customers can make a list of their favorite plants and download design plans. Information on water-efficient irrigation and rebate programs is also available.

The garden includes interactive elements such as descriptive signs with QR codes that visitors can scan to learn more about specific plants. Photo: Helix Water District
“We’ve made it easy for customers to learn about WaterSmart plants and landscaping,” said Gracyk.
WaterSmart landscapes provide homes for wildlife and pollinators
In addition to requiring less water, WaterSmart landscapes also require less maintenance and provide habitat for local wildlife and pollinators such as honeybees, birds and butterflies.
“Outdoor water use typically accounts for half of a home’s total water use,” said Helix Water District Board Vice President DeAna Verbeke. “With our new demonstration garden, we’re encouraging people to upgrade to a WaterSmart landscape by showing them that water-wise plants are not only sustainable but beautiful as well.”
The project was partially funded through a grant from the Metropolitan Water District of Southern California.
Helix Water District provides water treatment and distribution for 277,000 people in the cities of El Cajon, La Mesa and Lemon Grove, the community of Spring Valley and areas of Lakeside – east of downtown San Diego. Helix is also a founding member of The Water Conservation Garden, a nearly six-acre water-wise demonstration garden in El Cajon.