Pure Water Oceanside Provides New Local Supply of Drinking Water
Pure Water Oceanside is the first operating advanced water purification facility in San Diego County, providing a new local supply. The facility was officially dedicated with a celebration Tuesday in Oceanside. Elected officials and water leaders throughout Southern California commemorated the milestone which coincided with World Water Day.
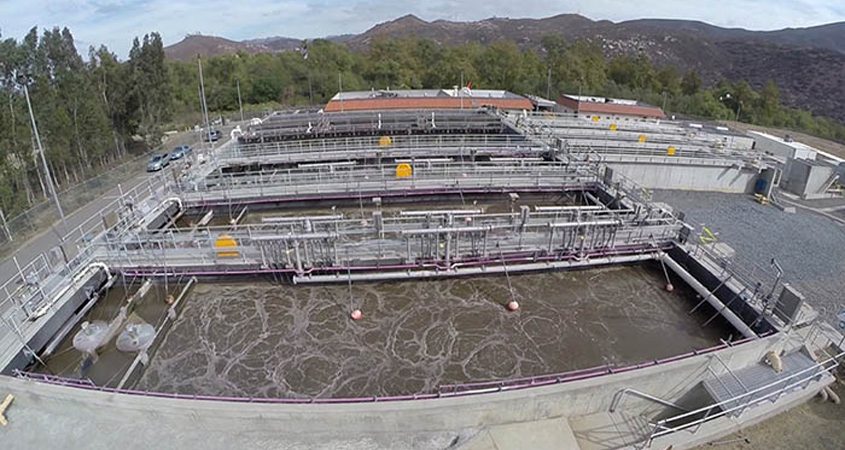
Pure Water Oceanside purifies recycled water to create a new local source of high-quality drinking water that is clean, safe, drought-proof and environmentally sound.
“On this World Water Day, we celebrate the City of Oceanside’s contribution to managing our invaluable water resources with the opening of Pure Water Oceanside,” said Cari Dale, City of Oceanside water utilities director. “Today we made history by moving one step closer to achieving the goal of greater water independence for not only our city, residents and businesses, but also the region as a whole.”
20% of Oceanside’s drinking water supply
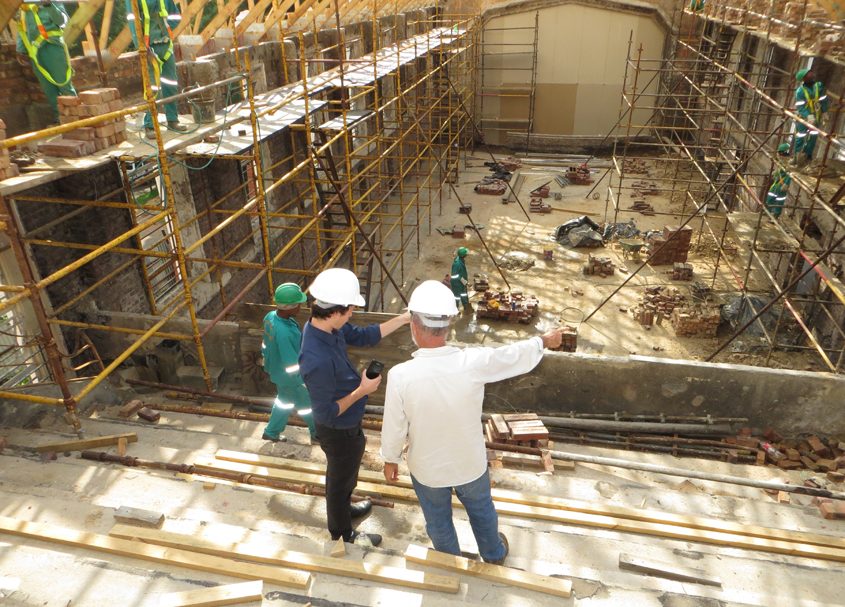
The $70 million project uses advanced technology, including ultrafiltration, reverse osmosis and advanced oxidation to provide 3 million gallons per day or more than 20% of the City of Oceanside’s drinking water supply. The source of the recycled water to create the purified water is from the city’s own San Luis Rey Water Reclamation Facility.
The City of Oceanside dedicated Pure Water Oceanside today on #WorldWaterDay💧The facility purifies recycled water to provide more than 20% of Oceanside’s drinking water supply. San Diego County Water Authority GM Sandra Kerl: “To see this project come to fruition is monumental.” pic.twitter.com/Flcaakzapx
— Ed Joyce (@EdJoyce) March 22, 2022
Drought-proof water supply
“Pure Water Oceanside exemplifies our commitment to innovative projects that improve the lives of the citizens who call our great city home,” said City of Oceanside Mayor Esther Sanchez. “Not only will the project safeguard against ongoing drought concerns, but it will also improve the quality and quantity of our local aquifer and reduce our reliance on imported water, ensuring clean and reliable water is available for future generations.”
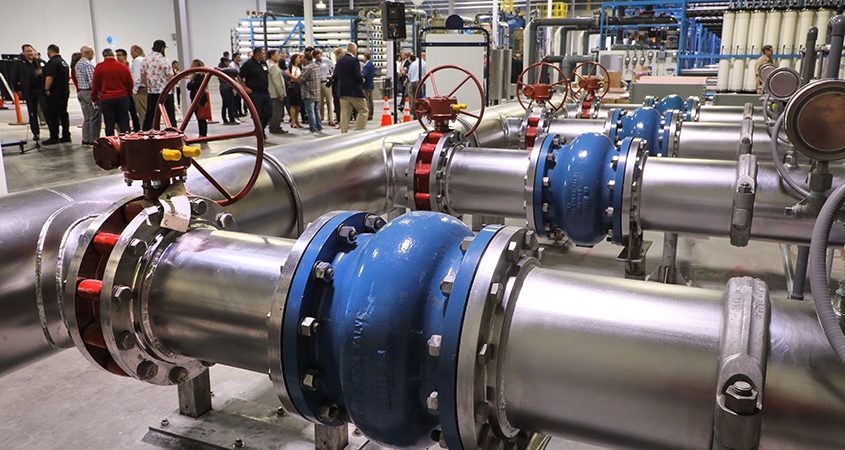

The $70 million project uses advanced technology, including ultrafiltration, reverse osmosis and advanced oxidation to provide 3 million gallons per day or more than 20% of the City of Oceanside’s drinking water supply. Photo: San Diego County Water Authority
Pure Water Oceanside addresses a variety of challenges faced by the city. Before the project went online, Oceanside imported most of its water from the Sacramento Bay Delta and the Colorado River, hundreds of miles away. This imported water is subject to rising costs out of the city’s control, requires an enormous amount of energy to transport and is vulnerable to natural disasters and earthquakes. Pure Water Oceanside addresses these challenges by diversifying the city’s water supply and reducing its reliance on imported water.
The launching of Pure Water Oceanside coincides with a larger movement for the region as a whole to create sustainable water supplies in San Diego County. In addition to Pure Water Oceanside, two other water reuse projects are planned for the region: the East County Advanced Water Purification Program and Pure Water San Diego.
(Editor’s note: The City of Oceanside, City of San Diego, Padre Dam Municipal Water District, and the Helix Water District are four of the San Diego County Water Authority’s 24 member agencies that deliver water across the metropolitan San Diego region.)