The City of San Diego Public Utilities Department conducts regular surveys of its watersheds to monitor and maintain high water quality within those watersheds.
The City recently released its 2020 Watershed Sanitary Survey. Conducted and issued every five years since 1996 as required by California law, the report identifies actual or potential causes of local source water contamination that might adversely affect the quality and treatability of City of San Diego water.
The updated information is used as a basis for future watershed management and planning efforts. City of San Diego tap water meets all state and federal drinking water health standards, the primary standards for treating and monitoring water.
“Development and other activities in our watersheds can have a profound influence on the quality of our water,” said Shauna Lorance, director of the City of San Diego Public Utilities Department. “The Watershed Sanitary Survey is important for identifying potential negative impacts and ways to better protect our watersheds.”
Watershed protection critical to safe, reliable water supply
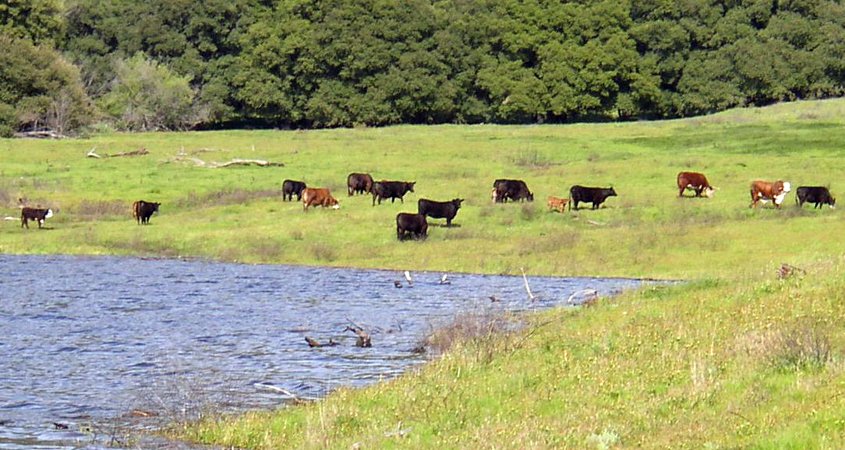

Everything that is on the land, whether a natural feature or a human activity like grazing cattle at this area near the Sutherland Reservoir, is part of the watershed. Photo: City of San Diego
A watershed is an area of land that drains water into a specific body of water. Everything that is on the land, whether a natural feature or a human activity, is part of the watershed. Many places San Diego County residents live, work, and play in are watershed areas.
There are 11 westward draining watersheds in San Diego County. Six are within the City of San Diego: San Dieguito River, Los Peñasquitos, Mission Bay and La Jolla, San Diego Bay, San Diego River, and Tijuana River.
The City of San Diego’s nine water supply reservoirs have a combined capacity of over 550,000 acre-feet and more than 900 square miles of watershed lands tributary to these reservoirs. Local runoff from watersheds captured in City reservoirs accounted for about 11% of total drinking water production from 2015-2020.
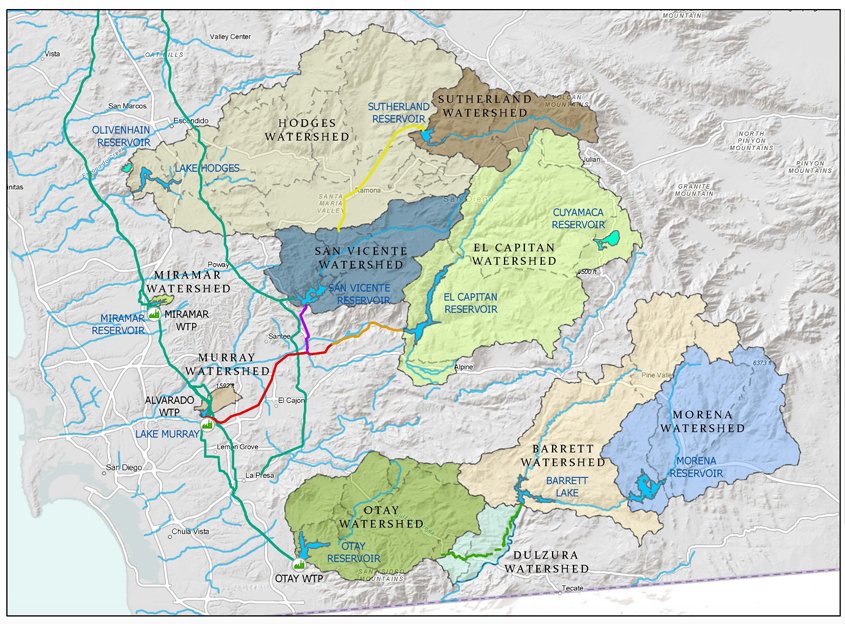
Six of San Diego County’s watershed regions lie within the City of San Diego boundaries. Map: City of San Diego
Reservoirs are critical components of the regional water supply system, as water is supplied to nearly two million people in the City of San Diego and neighboring communities. Protecting these water sources is vital to providing healthy and safe drinking water. The public can assist in preventing watershed damage through source reduction and preventing stormwater runoff.
The 2020 survey noted these changes since the 2015 Watershed Sanitary Survey:
- Total area of residential and commercial development in the watersheds increased slightly by about 2%.
- A total of 412 new construction permits were recorded for onsite wastewater treatment systems located within the watersheds.
- The number of fires occurring in the watersheds increased by about 8%.
- Leaking underground storage sites decreased by 53%.
- Sanitary sewer overflows increased by 36%.
The survey offers recommendations including continuing and expanding public awareness programs to help protect watershed, and implementing projects and programs to improve land management and water quality of source waters. All recommendations will be used for future watershed management and planning efforts.
The full 2020 Watershed Sanitary Survey, as well as past surveys, is available on the City’s website.
Editors Note: The City of San Diego is one of the San Diego County Water Authority’s 24 member agencies working collaboratively with the Water Authority to increase the value, reliability, and safety of water for ratepayers in San Diego County.






