State Agencies Commend COVID-19 Wastewater Monitoring by City of San Diego
The City of San Diego Public Utilities Department’s wastewater monitoring of coronavirus has received recognition from two state agencies.
The City’s Public Utilities Department was one of five California utilities participating in the Center for Disease Control’s National Wastewater Surveillance System program in cooperation with the State Water Quality Control Board.
The California Water Monitoring Council cited the City’s wastewater monitoring efforts, including its participation in U.S. Department of Health and Human Services pilot studies to investigate the logistics of implementing wastewater-based epidemiology nationally.
“The monitoring of wastewater can provide key information that is helpful in understanding and preventing the spread of COVID-19,” said Shauna Lorance, Director of the Public Utilities Department. “We are very proud to continue providing assistance to state and federal agencies with these efforts.”
Pioneering effort assesses COVID-19 spread through wastewater testing
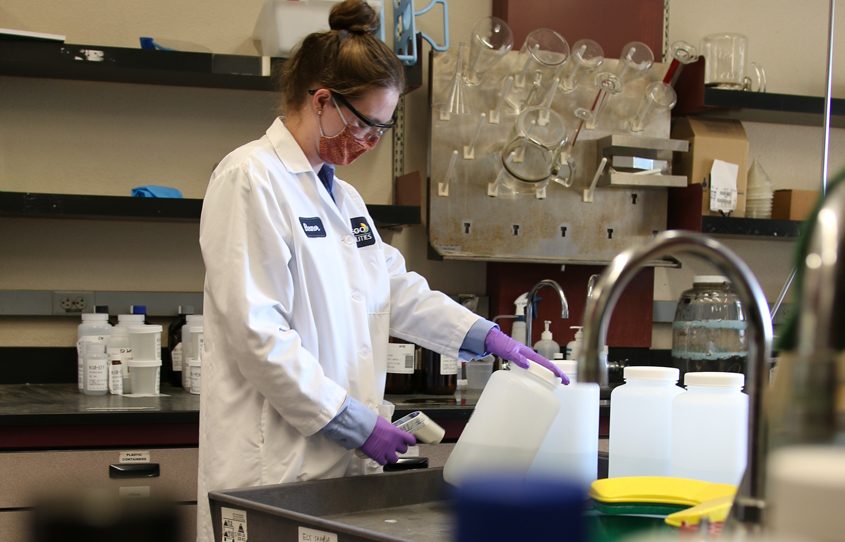

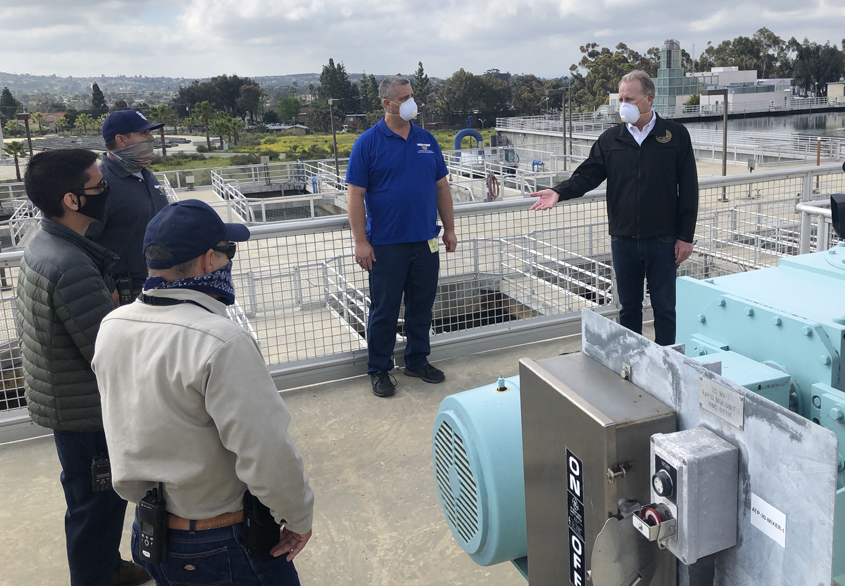
The California Water Monitoring Council cited the City’s wastewater monitoring efforts, including its participation in U.S. Department of Health and Human Services pilot studies to investigate the logistics of implementing wastewater-based epidemiology nationally. Photo: City of San Diego
Multiple California agencies and institutions pioneered an approach to better assess the spread of COVID-19 through testing wastewater. This approach yields information about the prevalence of the disease in populations several days sooner than individual testing or hospitalization records, according to the California State Water Quality Control Board.
Both the Control Board and the California Water Monitoring Council expressed their appreciation for the City’s assistance in separate resolutions.
Critical role in understanding spread of the virus
Since the beginning of the pandemic, the City of San Diego has been voluntarily involved with multiple studies for COVID-19 monitoring of wastewater. City staff efforts began before the development of federal and state epidemiology programs. Data collected by City staff played a critical role in understanding the spread, movement, and control of the virus. The City will share information from the studies with the public when they are completed.
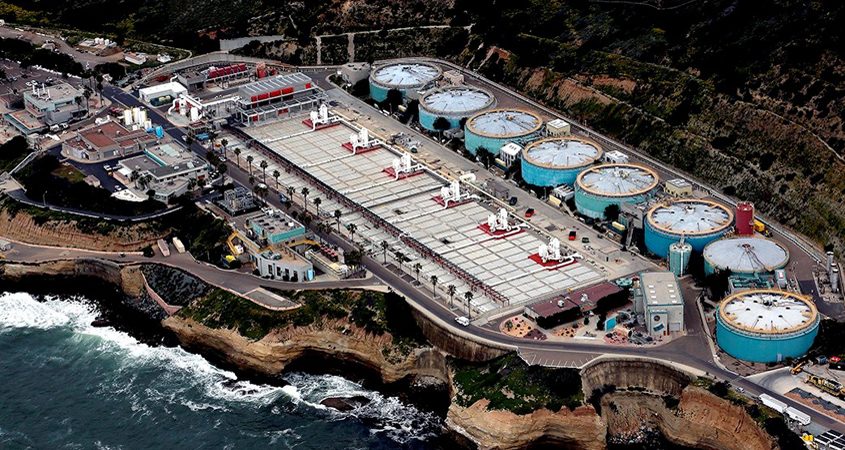

The City of San Diego processes wastewater at its Point Loma treatment plant. Photo: City of San Diego
The City participated in additional wastewater studies related to COVID-19, including those by San Diego State University, the University of Arizona, and the Southern California Coastal Water Research Project.
San Diego’s collection, treatment, and disposal of wastewater are carefully monitored and meet all regulations ensuring the health and safety of its employees, community members, and the environment. While the presence and viability of COVID -19 in wastewater is still being examined by the scientific community, the City’s wastewater treatment process has proven to be very effective in removing other commonly found viruses and bacteria.
(Editor’s note: The City of San Diego is one of the San Diego County Water Authority’s 24 member agencies that deliver water across the metropolitan San Diego region.)