Where San Diego’s Water Comes From, Explained
Water in California, while always a hot topic, entered the national spotlight at the start of 2025. Where the San Diego region’s water comes from, how it’s provided and who’s in charge of what are big questions that water professionals address every day.
What are the biggest sources of water for San Diego County?
In 2024, about 60% of the region’s water supplies were from the Colorado River, about one-third were from local sources and the rest was from Northern California through the State Water Project. The State Water Project is operated by the State of California and is separate from the Central Valley Project operated by the federal government.
Regardless of the source, all the water delivered to homes and businesses across the region meets strict state and federal quality standards.
How has our region’s water supply changed over the years?
In 1991, San Diego County got 95% of its water from the Metropolitan Water District (MWD) in Los Angeles, leaving the region’s water supply outside of San Diego’s control. A lack of local resources left the region susceptible to supply cutbacks from its major single major source. In 1991, MWD imposed an supply reduction of 31%, prompting the San Diego region’s civic and business leaders to demand greater investments and increased control over the county’s water future. In the following three decades, the Water Authority invested roughly $3 billion in regional water reliability projects. That included cementing the largest water conservation-and-transfer deal in U.S. history to secure conserved water from the Imperial Valley, partnering with a private company to build the nation’s largest seawater desalination plant and super-sizing San Vicente Reservoir by raising the height of the World War II-era dam. Now San Diego has a locally controlled and diversified water supply to make sure the taps always turn on.
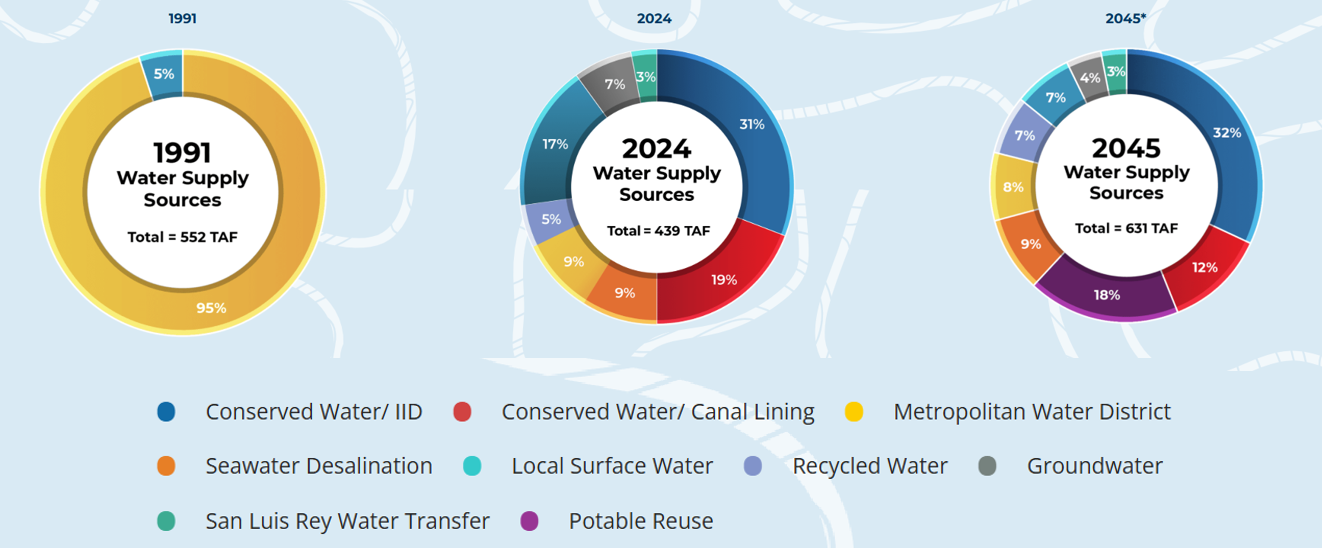
SDCWA’s water portfolio over the years.
Why doesn’t San Diego County use much groundwater?
Before 1947, the San Diego region relied heavily on local surface water runoff in normal and wet years, and on groundwater pumped from local aquifers during dry years when stream flows shriveled. As the economy and population grew exponentially, local resources became insufficient to meet the region’s water supply needs, and the region increasingly turned to imported water supplies. Today, groundwater is a small but important resource, especially in places like the South Bay where the aquifers are relatively large. Overall, it accounts for about 5 percent of the region’s water supply portfolio.
What is being done to create additional water supply here in the region?
Coordinating with 22 member agencies to develop long-term, local water reliability is a key component of the Water Authority’s mission. In fact, a growing number of local water sources across the San Diego region are managed by local retail agencies — and they are critical to ensuring long-term supply reliability. Local projects reduce demand on imported supplies and provide local agencies with more control.
In San Diego County, agencies are investing in seawater desalination, water recycling and water purification to create the water reliability our region needs to thrive.
What does the future of water look like for San Diego County?
Even in very dry years like 2025, regional investments mean there’s sufficient water to sustain our economy and quality of life. In fact, the region has done such a good job securing water, that it’s talking with other agencies across the Southwest about selling some of locally controlled water to combat rate increases in the county and support the larger regional economy.
For more information about San Diego’s water sources, click here.










