State officials Thursday toured San Diego County water infrastructure to get a first-hand look at the region’s successful water portfolio approach for supply diversification.
California Natural Resources Agency Secretary Wade Crowfoot, Deputy Natural Resources Secretary Thomas Gibson, State Department of Food and Agriculture Secretary Karen Ross, and State Water Resources Board Chair E. Joaquin Esquivel were here to assess the region’s water projects as part of their new role in developing a water portfolio strategy for the state.

Portfolio approach benefits region
“The region is proof that the portfolio approach works,” said Water Authority Board Chair Jim Madaffer. “The Water Authority and its 24 member agencies continue to develop local projects and explore opportunities that would benefit the region, the state, Mexico and the Southwest.”
At a luncheon meeting and panel discussion at University of California, San Diego following the tour, the agency officials joined a group of more than 150 people to hear how the portfolio approach can help California and the Southwest meet water supply challenges.
Along with the Water Authority Board of Directors, elected officials, business, community and state and local leaders gathered in an auditorium at the Southwest Fisheries Science Center on the La Jolla campus.

“The state needs to look at a global approach to managing water,” said Water Authority Board Chair Jim Madaffer.
Madaffer said during the meeting that San Diego’s portfolio approach has been successful in increasing the region’s water supply reliability through diversification and innovation.
“The Water Authority’s model is one that can be replicated across the state to help ensure a secure water future for all Californians,” said Madaffer.
State agency leaders echoed Madaffer’s comments.
“San Diego has been a leader in the water portfolio approach,” said Wade Crowfoot. “We have to make the investments to build regional water resilience as part of the Governor’s order to develop a portfolio to manage water in California.”
Water resilience portfolio for 21st century
The Water Authority invited the officials to visit after Gov. Gavin Newsom issued an Executive Order in April, directing state agencies to “prepare a water resilience portfolio that meets the needs of California’s communities and environment through the 21st century.”
In his May letter to Newsom, Madaffer thanked the governor for the “wisdom and leadership” with the issuance of Executive Order N-10-19, and invited the governor to tour San Diego County’s cutting-edge water facilities.
Newsom’s order also directed his administration to “identify and assess a suite of complementary actions to ensure safe and resilient water supplies, flood protection and healthy waterways for the state’s communities, economy and environment.”
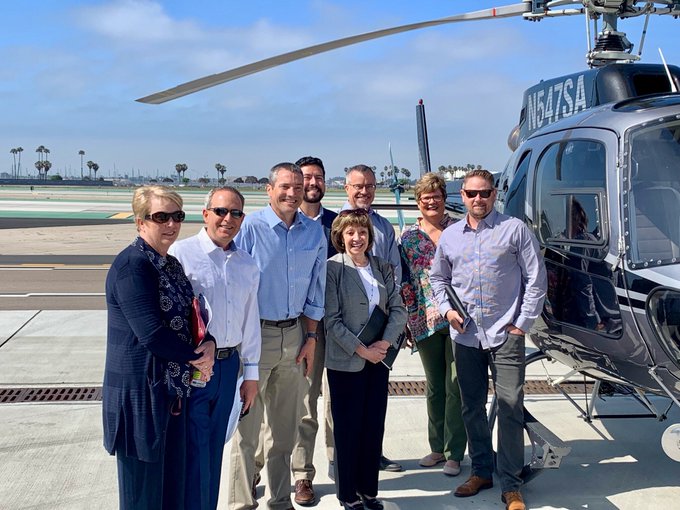

State and Water Authority officials before aerial and ground tour of regional water infrastructure. Photo: Water Authority
The California Natural Resources Agency, the California EPA, and the California Department of Food and Agriculture, in consultation with the Department of Finance, were directed by Gov. Newsom to, among other tasks, “identify key priorities for the administration’s water portfolio moving forward.”
“Governor Newsom wants us to think long and broadly on water,” said Crowfoot. “He wants us to get away from the silos and conflicts on water in California – the mindset of environment groups versus farmers, north versus south, urban versus rural – and work together on water resiliency.”
Significant investments in regional water strategy
“The Water Authority and its 24 member agencies have made significant investments in the last two decades to diversify our water supply, creating a portfolio of resources to support our region’s 3.3 million people and $231 billion economy,” said Madaffer.
During the tour, the officials got a first-hand look at some of those investments, including the San Vicente Reservoir, Olivenhain Reservoir, and the Claude “Bud” Lewis Carlsbad Desalination Plant.
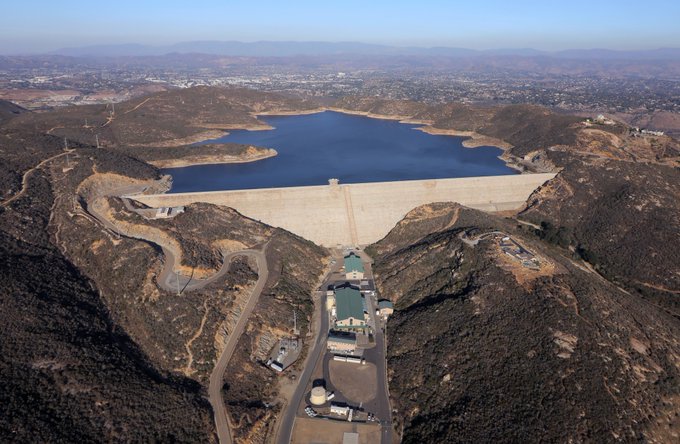

The Olivenhain Dam and Reservoir are a cornerstone of the San Diego County Water Authority’s Emergency and Carryover Storage Project, helping to protect the region from severe water supply shortages. Photo: Water Authority
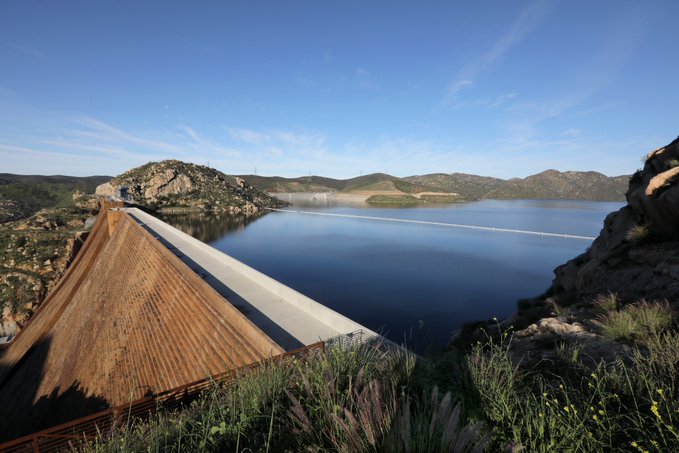

The Water Authority is exploring a battery storage project at the San Vicente Reservoir that would generate clean energy to help meet California’s climate goals. Photo: Water Authority
Global Warming creates water supply challenges
Scripps Institution of Oceanography research meteorologist Dan Cayan told the audience that temperatures and dry spells will increase in California in the future, making water storage, conservation, and forecasts even more critical.
“Global warming climate models show the Sierra Nevada snow pack will be 50% less in 2090 than today’s average April 1 snowpack,” said Cayan.
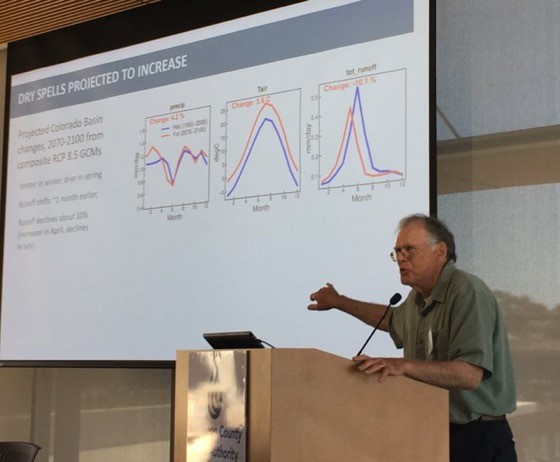
Scripps Institution of Oceanography research meteorologist Dan Cayan said temperatures and dry spells are expected to increase in California, making water storage, conservation and forecasts even more critical. Photo: Water Authority
Cayan said observations and climate model projections indicate climate change is occurring and will grow stronger. California should expect 1.5-2 degrees Fahrenheit warming by 2050, he said.
New regional pipeline study
Water Authority Assistant General Manager Dan Denham described a new study that will explore the viability of a regional pipeline to transfer water from the Colorado River to benefit multiple users in San Diego County and across the Southwest.
The pipeline system is one of a handful of ideas being discussed by San Diego County water leaders to enhance partnerships and solutions that make sense locally and more broadly as part of Governor Newsom’s Water Portfolio Program to develop resiliency statewide.
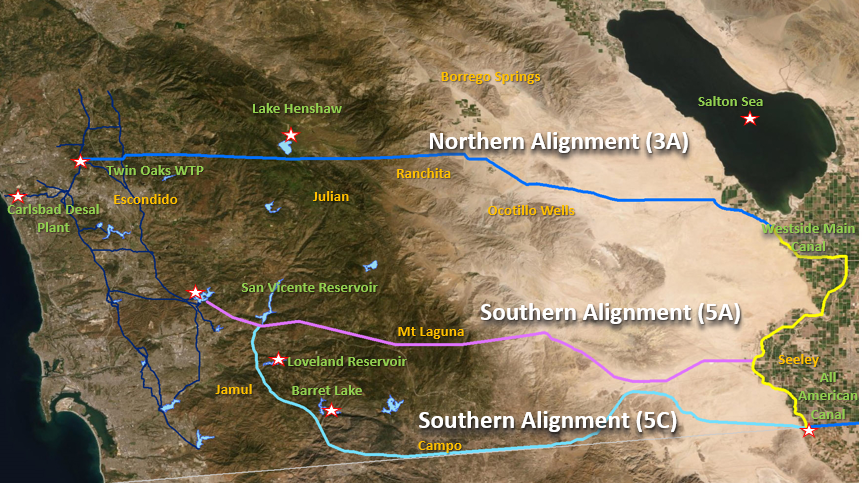
Map indicates three potential routes for a proposed regional pipeline system that would move Quantification Settlement Agreement water directly from the Imperial Valley to San Diego. Two of the routes (the light blue and purple lines) follow a southern route. The third proposed route, (shown in both a yellow and darker blue line) follows a northern path. Graphic: Water Authority
Creating a pipeline to transfer Colorado River water to the San Diego region has been studied periodically over decades.
But the new study is focused on how a regional pipeline could provide multiple benefits as part of a long-term water management strategy for California and the Southwest.
The expanded review will consider a system that could create much-needed storage opportunities for the Imperial Irrigation District that could support agriculture while addressing critical issues like the Salton Sea and the need for more renewable energy development.

 Sweetwater Authority Logo 2019
Sweetwater Authority Logo 2019




















