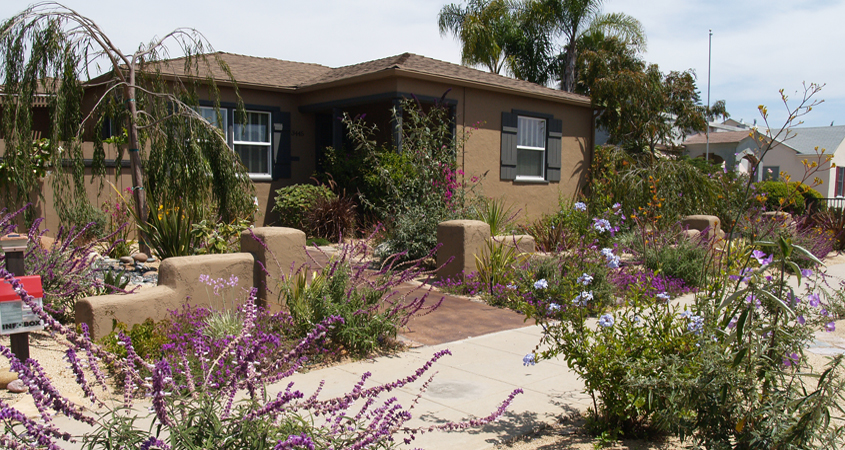
Drought-Tolerant Plant Giveaway Popular in Fallbrook
More than 130 people took advantage of a drought-tolerant plant giveaway program offered by the Fallbrook Public Utility District. Since picking up their free succulents in November, homeowners have started their drought-tolerant home garden projects.
Participants were provided empty flats and invited to select from an assortment of three-inch potted succulents to suit their needs. Each person took home approximately 28 plants.
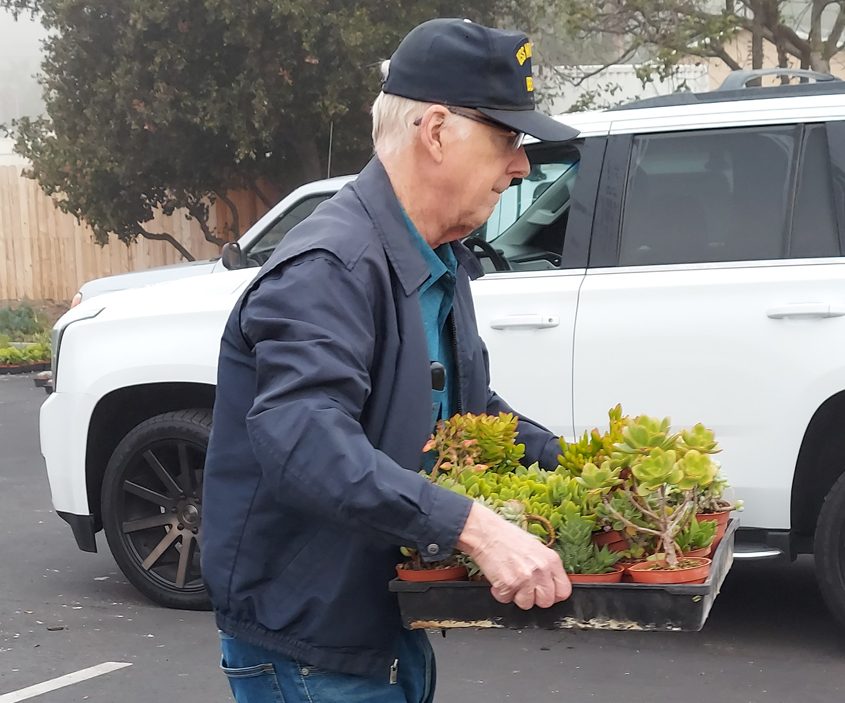

More than 130 Fallbrook residents could take advantage of the giveaway program. Photo: Fallbrook Public Utility District
The hardy, brightly colored succulents help people transform their landscaping by replacing thirsty plants and turf. Drought-tolerant plants ease the workload of gardening and add beautiful color while also saving water.
The program was made possible thanks to grant funding from the Metropolitan Water District of Southern California. The plants were sourced locally from Silverthorn Nursery, which uses FPUD’s recycled water to irrigate.
Fallbrook homeowners save water with succulents
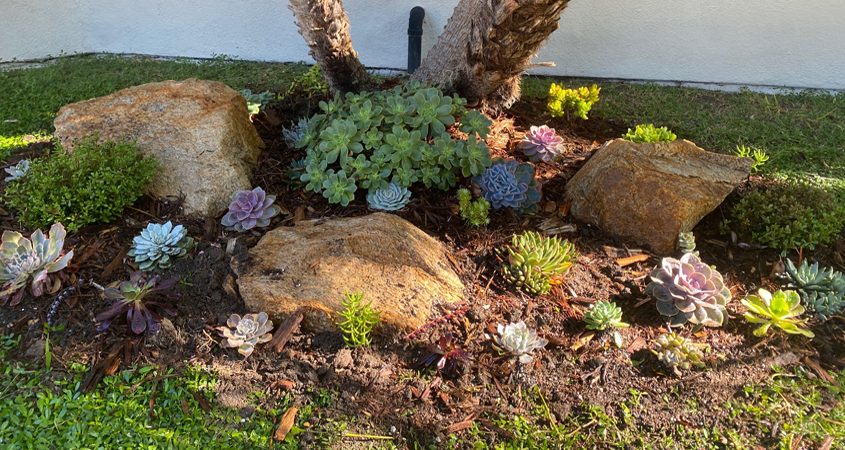

Homeowner Peggy Hanne sent in a photo of her freshly planted succulents. Photo: Fallbrook Public Utility District
“Thank you for the plants. They are doing really well,” said homeowner Peggy Hanne, who proudly shared a photo of her transformed garden.
Maryanne Polyascko, a retired Fallbrook teacher, said she was so grateful for the plants and having less weed-pulling, watering, and gardening to do.
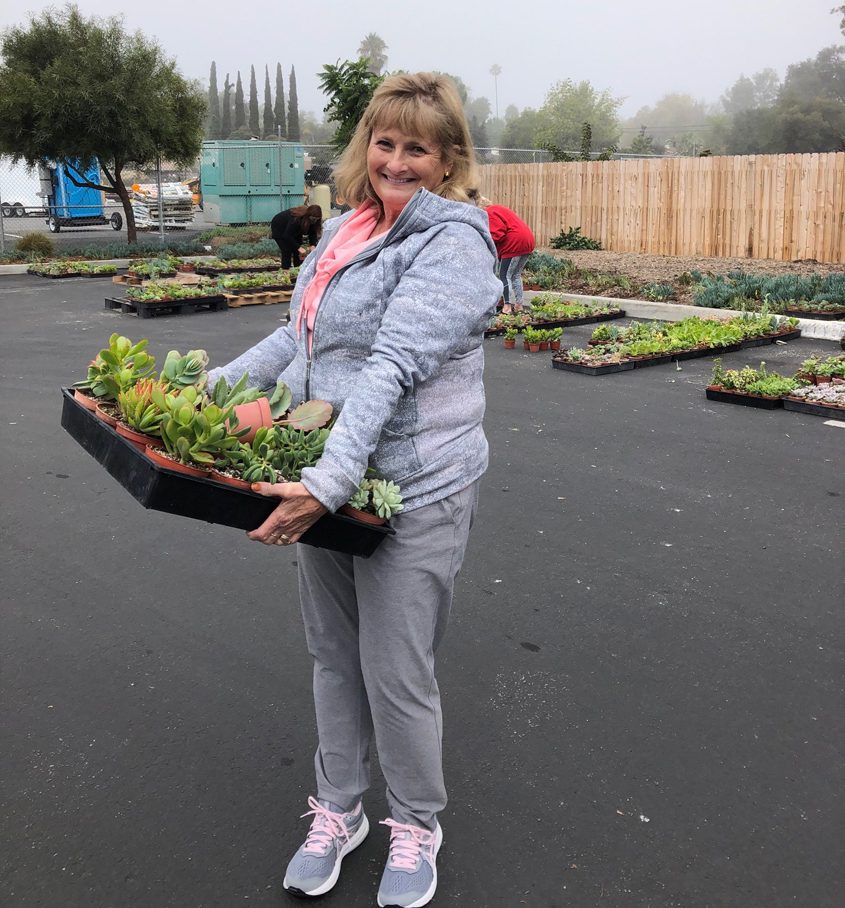

Maryanne Polyascko takes her free succulents home. Photo: Fallbrook Public Utility District
Other homeowners reported using the plants to protect their properties.
“I planted them to stabilize the ground behind my house from erosion,” said Mike Osborne. “I filled in all the areas that were devoid of vegetation.”
In addition to being drought-tolerant, succulents are also considered a smart choice in wildfire-prone areas. San Diego-based author and horticulturalist Debra Lee Baldwin is an expert on succulent gardens and recommends their use as a firebreak. While the plants alone won’t save a home from burning, “Surrounding a house with water-filled plants can serve as one more weapon in a homeowner’s arsenal against wildfire,” writes Baldwin.
The Fallbrook Public Utility District will be eligible again in two years to apply for more grant funding to offer another plant giveaway.
(Editor’s note: The Fallbrook Public Utility District is one of the San Diego County Water Authority’s 24 member agencies that deliver water across the metropolitan San Diego region.)