Climate change and drought will impact San Diego County’s climate future, but regional water supply planning and adaptation measures will ensure a safe, reliable supply for the region.
Water supply strategy was one of the key points participants learned about during a Monday panel discussion, “San Diego County’s Climate Future,” hosted online by the San Diego County Water Authority, Citizens Water Academy, Leaders 20/20 and San Diego Green Drinks.
Panel moderator Kelley Gage, Water Authority Director of Water Resources, kicked off the climate conversation by describing the investments and steps taken by the Water Authority and its 24 member agencies to secure the region’s water future.
Water supply and San Diego County’s climate future
“Since our founding more than 75 years ago, our mission in partnership with our 24 member agencies is to ensure a clean and reliable supply of water for the region,” said Gage. “As part of that mission we’re involved in partnerships like the one that we have today and the research to ensure that we have planned for the impact of climate change in our water supplies.”
Gage said the Water Authority has developed a climate action plan.
“As part of our strategic planning we have developed a climate action plan which is an interdisciplinary effort to promote and coordinate implementation of climate change strategies and related activities across the Water Authority,” said Gage. “We have reached our goals for 2020 and we are on track for our 2030 goals.”
Atmospheric rivers and water management
The Water Authority partnered with the Scripps Institution of Oceanography, Center for Wester Weather and Water Extremes, at UC San Diego in 2020 to better predict atmospheric rivers and improve water management before, during, and after those seasonal storms. The Center and its partners share best practices in forecast-informed reservoir operations, increased research around atmospheric rivers and droughts, and develop strategies for mitigating flood risk and increasing water supply reliability.
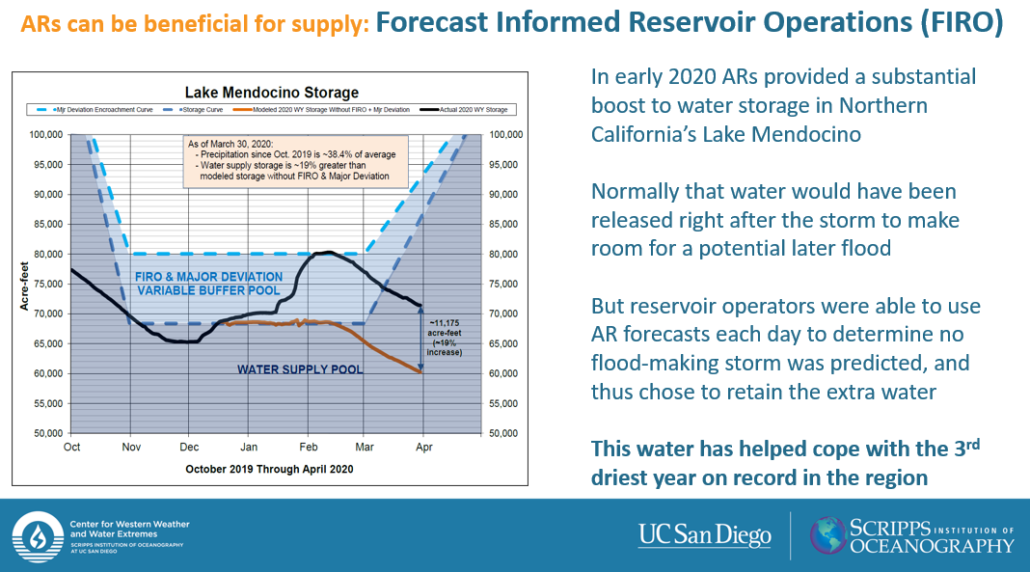
Stored water releases
Marty Ralph, Researcher in Climate, Atmospheric Science & Physical Oceanography at Scripps Institution of Oceanography, and Director of the Center for Western Weather and Water Extremes, opened the panel with information on advanced research around atmospheric rivers.
Atmospheric rivers are long narrow bands of airborne water vapor, providing up to half the annual precipitation and mountain snow that is key to California’s water supply. New research allows reservoir operators to use atmospheric river forecasts to better predict storm events and prevent unnecessary stored water releases.
“This stored water has helped to cope with the third driest year on record for the region,” said Ralph.
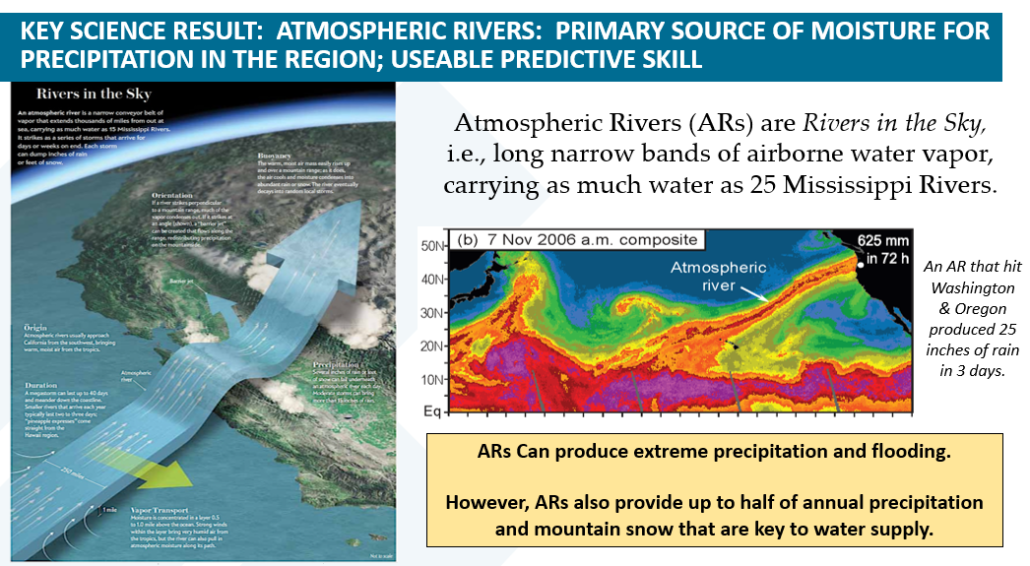
Atmospheric rivers more “impactful” with climate change
Another Scripps Institution of Oceanography researcher, Alexander “Sasha” Gershunov, said that California receives most the country’s extreme precipitation events due to atmospheric rivers. Low and medium intensity precipitation events are predicted to decrease, while high intensity precipitation events are predicted to increase, especially in California.
“With warming, atmospheric rivers get stronger, wetter, longer, and more impactful, and they also produce more of our annual precipitation total,” said Gershunov. “There are many implications of these changes from water resources management, to wildfires, to debris flows.”
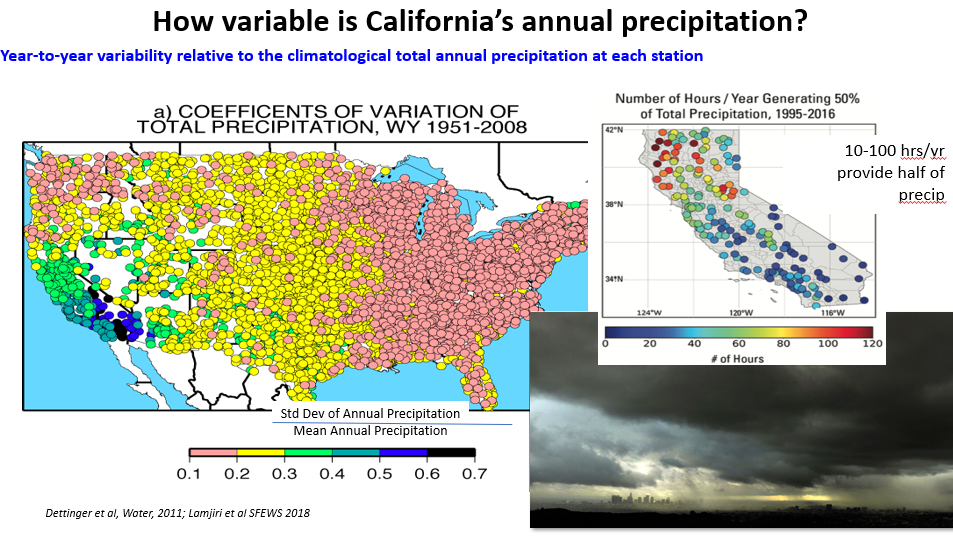
San Diego Regional Climate Collaborative
Darbi Berry, Program Manager at the San Diego Regional Climate Collaborative, described projects moving forward in the region to address equity issues related to water availability and pollution. Advancing the Nexus of Water and Equity looks at how different communities are impacted by a changing climate.
Increased variability in rainfall events and the potential for flooding in the San Diego region is a contributing factor to ongoing water quality issues in disadvantaged neighborhoods. One project carried out to address these equity issues is the National City, Paradise Creek project which re-graded a creek that was continuously overflowing and causing flood damage during atmospheric river events.

Watch the San Diego County’s Climate Future presentations by Marty Ralph, Sasha Gershunov, and by Darbi Berry here: https://bit.ly/3aBVt1Z