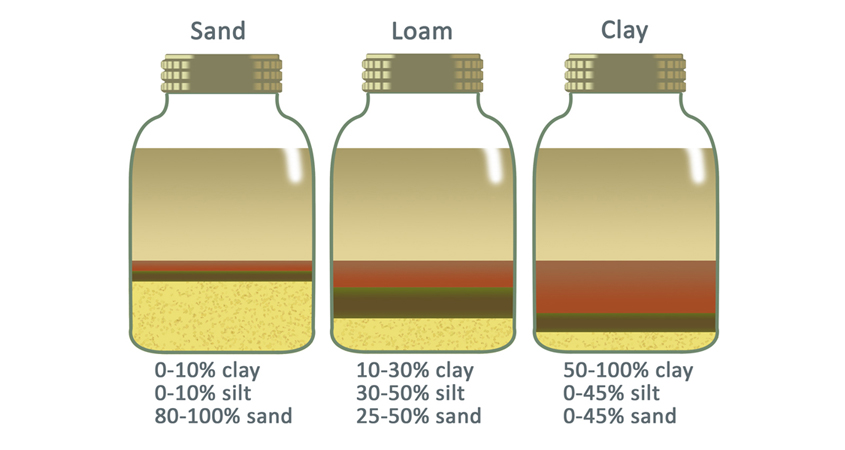
Your landscaping soil needs three things to feed the billions of microbes within it to transform brick-hard, lifeless dirt into healthy, living soil sponges: oxygen, water, and life. Think OWL to remember these important, interconnected factors.
Oxygen lets microbes breathe free
Oxygen is needed by healthy plant roots and soil organisms. Healthy soil has lots of tiny little pockets of air. When soils are eroded, graded, or disturbed, their structure becomes compacted and hard. Compaction takes place when tiny air and water bubbles are squeezed out of the soil. This kills the healthy microbes working to keep your soil replenished. Microbes can be killed by fertilizers, pesticides, or even heavy traffic from people or vehicles.
Water for your microbes and plants
Microbes and plans both need water to live. But too much water in your soil will displace oxygen, saturating the soil. This creates an anaerobic condition. It is the unhealthy microbes like bacteria, viruses, or parasites that prefer anaerobic soil. If this condition persists, diseases may develop. They will endanger the health of your garden.
Water is constantly moving through the soil. Water in the soil needs to be replenished as plants use it, as it evaporates from the soil surface, and as gravity pulls it down past the root zone of your plants.
Bring your soil to life
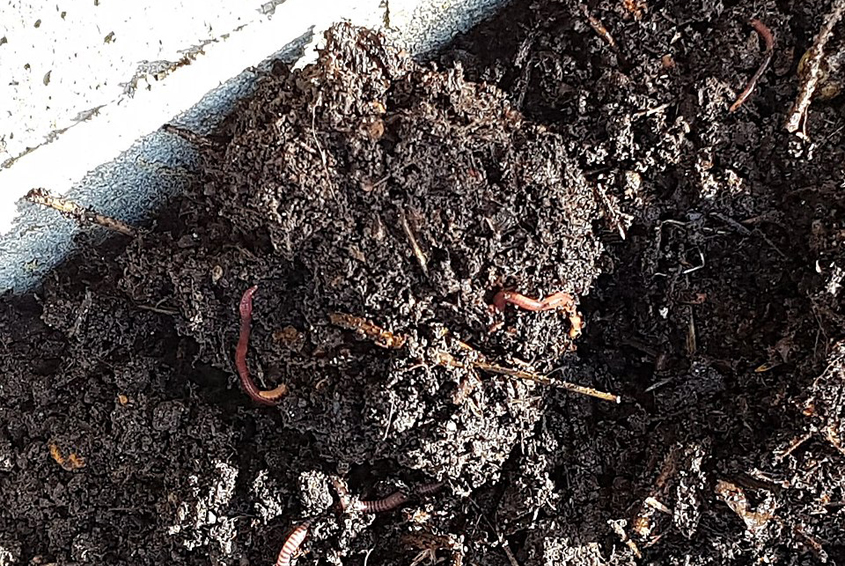

The microbes consume organic matter, and then they are consumed by bigger creatures (worms, ants, slugs, centipedes, larvae, etc.). They are consumed in turn by creatures further up nature’s food chain. Photo: Malcolm Fowles, Wikipedia
Life in the soil includes all the bacteria, protozoa, nematodes, and fungi, the food they eat, the excretions they make, and the root systems they sustain. Living microbes are most quickly incorporated into your soil by adding high-quality compost.
Plants attract microbes to their roots by feeding them carbon. Bacteria and fungi hold the soil together with microscopic glues and binders. The microbes consume organic matter, and then they are consumed by bigger creatures (worms, ants, slugs, centipedes, larvae, etc.). They are consumed in turn by creatures further up nature’s food chain.
Carbon and other nutrients cycle through these many life forms, creating healthy living soil, no matter what the soil type.
Without any of these elements, your landscaping will not thrive. Organic matter, planning and some labor may be involved, but creating healthy soil using the OWL method – Oxygen, Water and Life – will pay off in reduced maintenance, reduced inputs, reduced pollution on land and in our waterways, and the beauty of your thriving, healthy landscape.
This article is part of a year-long series inspired by the 71-page Sustainable Landscapes Program guidebook. The Water Authority and its partners also offer other great resources for landscaping upgrades, including free WaterSmart classes at WaterSmartSD.org.