Installing WaterSmart Living Irrigation
Successfully installing WaterSmart Living irrigation starts long before you get out your tools. You need to complete an assessment of your landscape plan’s specific water needs, draw a complete plan showing the layout, then select your irrigation and purchase your irrigation equipment. If your soil needs amendments (and it almost certainly does), you must get this done first. With all of this important prep work complete, you can start to implement the design.
Five key steps to success
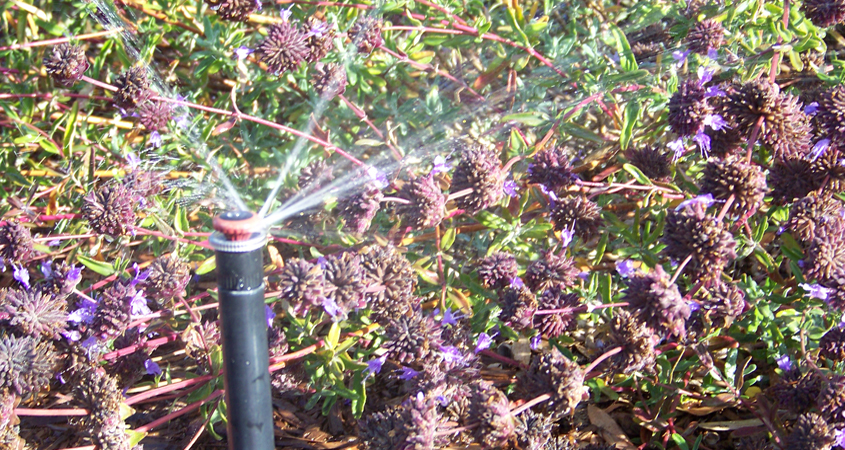

Be sure your irrigation plan considers hills and slopes to prevent waste and erosion. Photo: Pixabay
Step 1: Read the instructions from the manufacturer and familiarize yourself with all the parts of your new irrigation system. Often the manufacturer will provide YouTube video demonstrations which can be extremely helpful.
Step 2: Starting from the main connection to the water line, dig trenches for all the pipes according to your irrigation plan. Ideally, the main connection to the water line will be downstream of the water meter and upstream of the connection to the house.
If you tie into a rear yard hose bib, be aware that the water pressure will be lower because the water for your house is regulated by a separate pressure regulator.
Step 3: Lay an extra pipe sleeve or two under any new hardscape elements. This allows you to add pipes or wires in the future. Be sure to cover the ends of the pipe with duct tape before covering and mark the location on your landscape plan.
Step 4: If you are using drip irrigation, you may want to hold off installing your drip emitters until after planting is complete. With your new plants in the ground, you can place the emitters precisely where the water best irrigates your new plants. Be sure to place them at least six inches away from the plant’s stem to prevent rot.
Step 5: Consult your local irrigation supply store or the major irrigation manufacturers if you need more detailed installation guides or help with troubleshooting. Manufacturers offer toll-free customer service phone help, online chats, and email.
_____________________________________________________

(Editor’s Note: The San Diego County Water Authority and its 24 member agencies offer programs, resources, and incentives to improve water-use efficiency for residential, commercial, and agricultural users. WaterSmart choices are a way of life in the region. Stay WaterSmart San Diego! For more water-use efficiency resources, go to WaterSmart.SD.org.)















 Sweetwater Authority Logo 2019
Sweetwater Authority Logo 2019