As spring temperatures rise, San Diego County residents know wildfire season is not far behind. Although wildfire is a serious threat during warm, dry summer and fall months, wildfire can strike year-round especially in wildland interface areas. Regional landscaping must follow fire safe guidelines in design, plant selection and consistent maintenance.
Protecting your home with firefighting plants
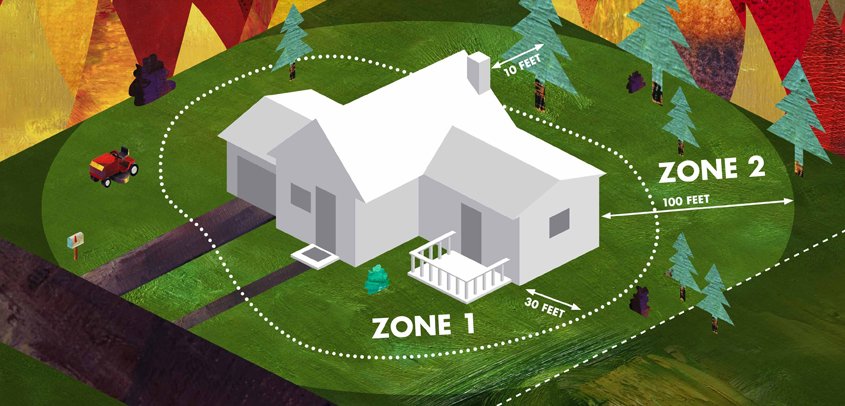
Diagram from CAL FIRE illustrating the three zones for defensible space. Illustration: CAL FIRE
Plan your landscaping using three different zones
Zone 1: Landscapes should resist ignition and provide 35 feet of actively maintained defensible space around structures and access areas through smart design elements and plant selection. This maximizes fire prevention and allows access by fire crews to protect your property from fire if necessary.
Zone 2: Careful thinning of native vegetation for at least 65 additional feet, for a total of 100 feet of defensible space will reduce the chance of airborne embers from catching and spreading fire.
Zone 3: Some plants begin growth and start the germination process after a wildfire. Many of San Diego County’s native plant communities including chaparral can survive and recover from infrequent wildfires.
But the ability to survive is disrupted for even the most well-adapted plants when fires reoccur too frequently. Non-native, invasive plant species encourage more frequent, longer duration fires burning at a hotter intensity. It is critical to remove invasive plants in fire-prone areas.
Choose firefighting plants that resist ignition
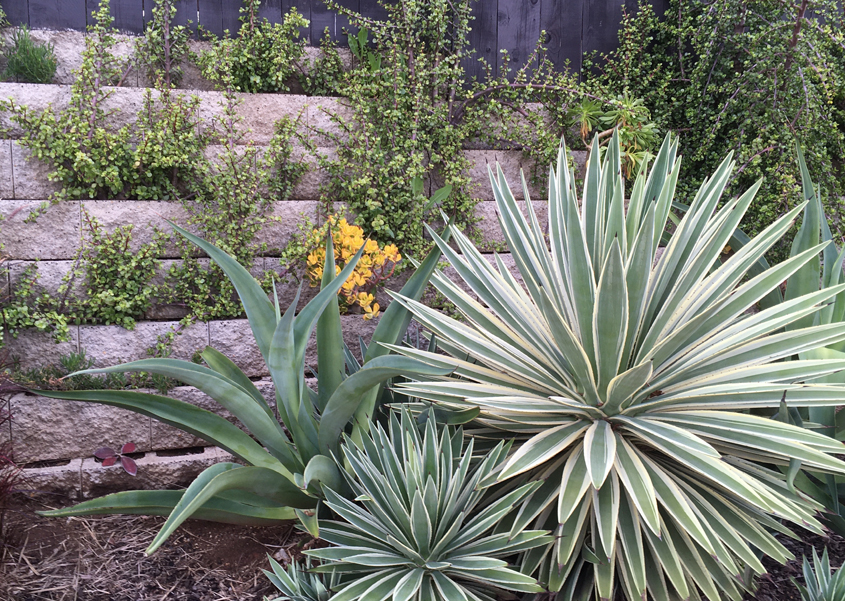

Firesafe plants like these succulents are a smart choice for your watersmart landscape plan. Photo: City of Escondido
Some native plants can prevent airborne plant embers due to high salt or water content and low volatile oil content in their leaves. Succulents such as agaves, aloes and crassulas store extra water in their fleshy leaves guarding against drought, and they will help guard your property from wildfire.
Five exceptional firefighting plant choices include:
- Daylily hybrids
- Coral Aloe
- Bush Morning Glory
- California Sycamore trees
- Indian Mallow
Rob wildfires of the fuel they need
Messy, oily trees and shrubs like eucalyptus trees and junipers may flourish in Southern California, but they aren’t natives, and they provide ready fuel for wildfires. They ignite quickly, burning hot and long, releasing embers into the air which causes flames to spread.
Preventative maintenance includes removing dry grass, brush, weeds, litter, waste, and dead and dying vegetation. Trees should be regularly pruned. Shrubs should be thinned, with dead branches and leaves removed. Leave root structures intact to avoid erosion.
Dead leaves and branches are especially flammable on evergreen shrubs and vines like bougainvillea. Avoid planting these close to homes or other structures.
This article is part of a year-long series inspired by the 71-page Sustainable Landscapes Program guidebook. The Water Authority and its partners also offer other great resources for landscaping upgrades, including free WaterSmart classes at WaterSmartSD.org.






