WaterSmart: Weathering Dry Times in San Diego County
News stories by national and regional media outlets highlighted the investments by the San Diego County Water Authority and its 24 member agencies to create a plentiful water supply for the region, helping to weather dry times like the current drought.
The New York Times, Spectrum News 1, The Wall Street Journal and Wired Magazine are among several news organizations that have reported on the region’s water supply projects, current and future, that ensure the 3.3 million residents of San Diego County won’t be left high and dry during times of drought. The news stories also recognize the successful efforts by the region’s residents to significantly reduce water-wasting practices by embracing a “conservation ethic.”
Water supply in dry times
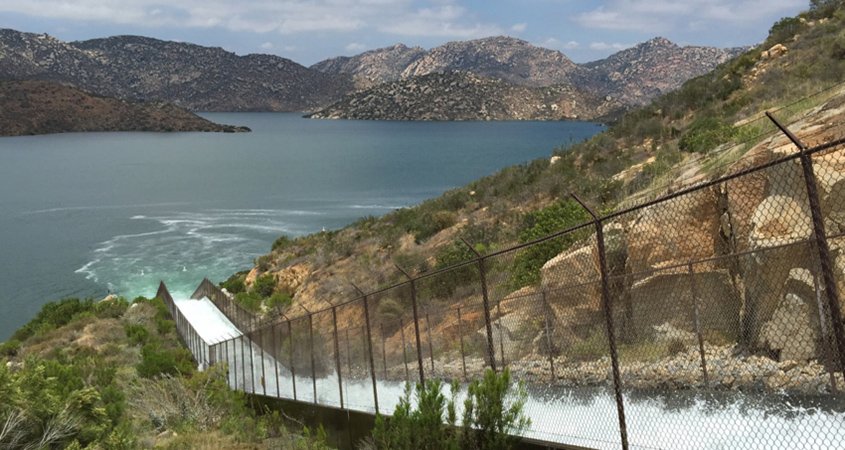
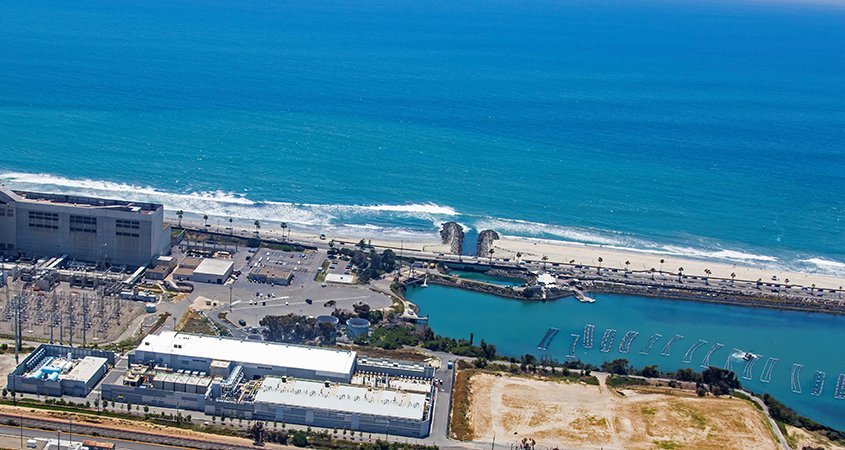
California-based reporter Jill Cowan visited the Claude “Bud” Lewis Carlsbad Desalination Plant and the San Vicente Reservoir, among other locations, for her article in The New York Times. The story covers regional water supply projects and investments made by the Water Authority and its member agencies to ensure San Diego County would not be stuck “at the end of the pipe” during periods of drought.
“There are no silver bullets anywhere,” said Jeffrey Mount, a senior fellow with the Public Policy Institute of California’s Water Policy Center, who noted San Diego’s strides. “They’re definitely in the upper echelon of these creative approaches.”
Chula Vista resident and Sweetwater Authority customer Paul Rodriquez was highlighed in the story as one of many county homeowners who are WaterSmart: Conserving water by yanking out turf for drought-tolerant landscaping and using water-efficient fixtures indoors.
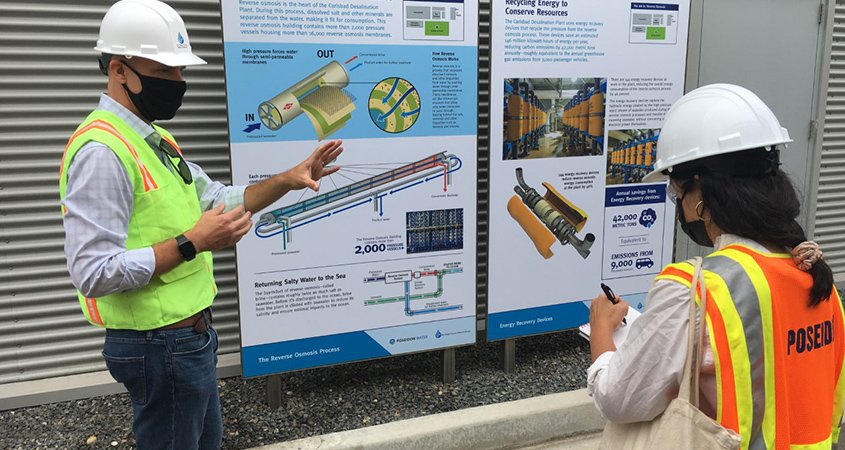

San Diego County Water Authority Water Resources Manager Jeremy Crutchfield (L) explains the reverse osmosis process to The New York Times Reporter Jill Cowan (R) at the Carlsbad Desalination Plant. Photo: San Diego County Water Authority
“Let’s Diversify”
Spectrum News 1 Reporter Sarah Pilla wrote about the region’s water supply history and how an historic drought led to investments that created a diverse water supply portfolio:
Back in the drought of the ’90s, 95% of San Diego’s water came from one source, and they faced 30% cuts for 13 months.
“Of course being at the end of a pipeline, when there’s little water available, you are at high risk. So, our community came together and said let’s diversify,” Kerl said.
Fast-forward 30 years later, and the San Diego County Water Authority has multiple streams of water sources in its portfolio, including the groundbreaking Carlsbad Desalination Plant that utilizes ocean water to provide the region with about 10% of its drinking water.
Video and story: https://bit.ly/3DWFM1F
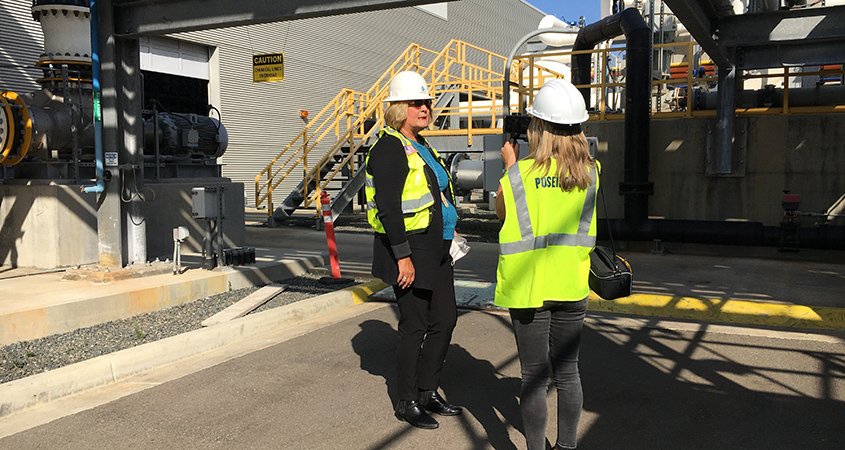

San Diego County Water Authority General Manager Sandra L. Kerl (L) talks with Spectrum News 1 (LA) Reporter Sarah Pilla, at the Carlsbad Desalination Plant. Photo: San Diego County Water Authority
Diverse portfolio of resources
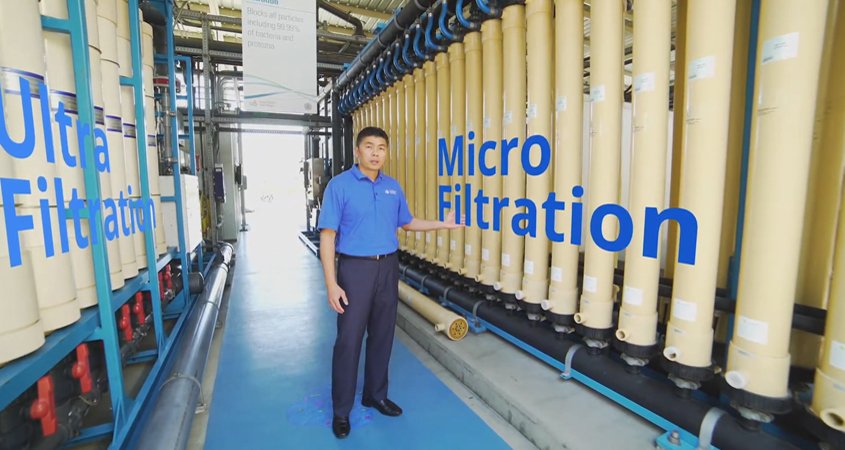
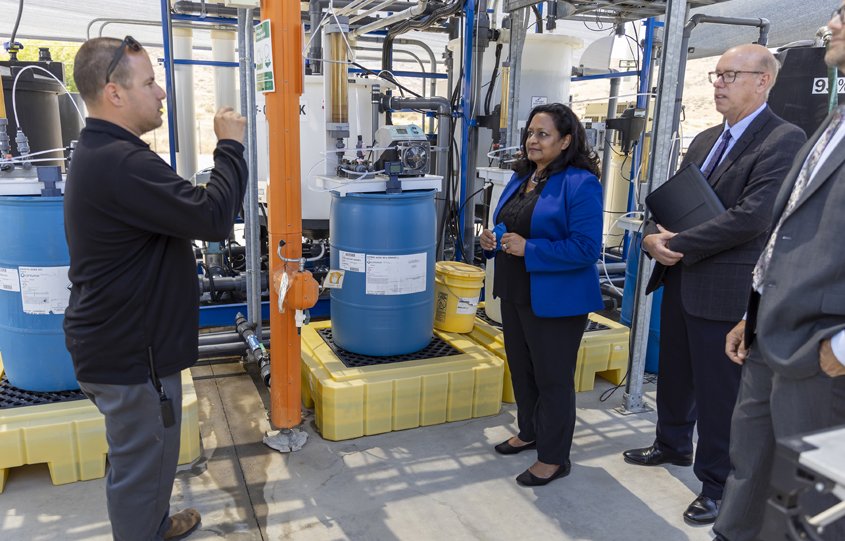
Wired Magazine writer Matt Simon focused on the science of water recycling and the Pure Water San Diego project.
If that all sounds like a rather convoluted way to get drinking water, that’s because the American West is facing a rather convoluted climate crisis. San Diego—and the rest of Southern California—have historically relied on water from Northern California and the Colorado River. But they’ve always been at the end of the line. The river hydrates 40 million other people in Colorado, Wyoming, Utah, Arizona, Nevada, and New Mexico, and it is withering under a historic drought, a harbinger of even worse water scarcity to come as the climate warms.
So San Diego has to figure out how to do more with less water. The Pure Water program aims to provide more than 40 percent of the city’s water from local sources by the year 2035 by reusing water recycled from homes and businesses. (That means water that has flowed through sinks, showers, toilets, and washing machines.) “We’re diversifying the portfolio,” says Todd Gloria, San Diego’s mayor. “We’re heavily dependent upon water that comes from very far away, and that’s a problem that we have to address.”
Read more: https://bit.ly/30xU8qF
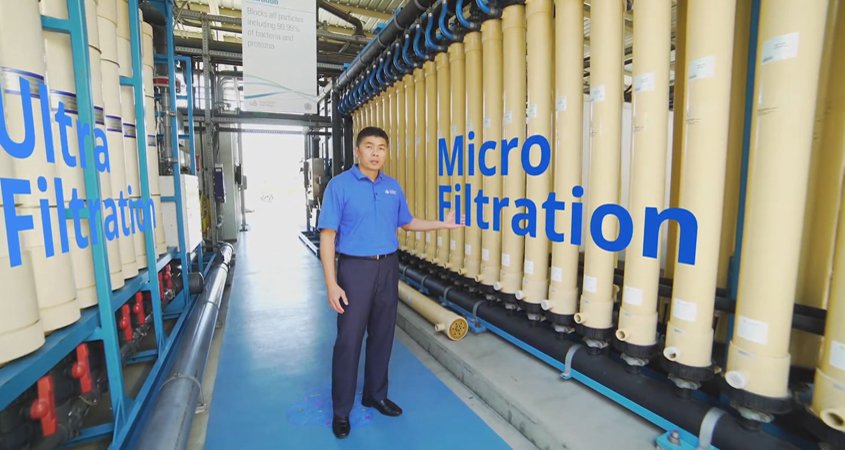

Pure Water San Diego Associate Engineer Anthony Van guides a virtual tour of the demonstration facility. Photo: City of San Diego
If you're able to recycle water on a large scale, you’ve got a powerful hedge against drought.
“That's an extraordinarily reliable supply, being able to access that flow of wastewater, clean it up, and then use it to offset the need for other supplies." https://t.co/huni1ygAsN
— WIRED (@WIRED) October 18, 2021
Dry Times and Cutbacks
Reporter Jim Carlton, with The Wall Street Journal, visited San Diego County In June 2021, reporting on the differences in water supply and drought conditions in California: “California’s Drought Leads to Cutbacks in Marin County but Not in San Diego”
The pain of a two-year drought drying up the American West isn’t being felt evenly across the country’s most populous state.
That is because Southern California water agencies have for decades invested in new ways to diversify their supplies and recycle what they get, say people who study and work with water in the West. In Northern California, meanwhile, a history of more plentiful rain and snow meant many communities were less prepared for the latest drought and now more homes and businesses must cut back.

Jim Carlton, reporter with The Wall Street Journal (L) listens as San Diego County Water Authority Principal Engineer Jeff Shoaf describes the San Vicente Dam raise during Carlton’s visit to the San Vicente Reservoir in June 2021. Photo: San Diego County Water Authority
“Plenty of water”
The Southern California News Group published an editorial, “SoCal’s water planning offers lesson for state” on October 19:
It’s beyond ironic that the driest, most-populated parts of California are in reasonably good shape whereas the less-populated rainiest parts of the state are in dire straits. San Diego, for instance, had so much water during the last drought that it had to release some of it from its reservoirs. It has plenty of water during this current drought.
Statewide Drought Emergency Declared
California extended its drought emergency statewide on Tuesday.
“It’s critical that Californians across the state redouble our efforts to save water in every way possible,” Gov. Gavin Newsom said.https://t.co/6t7X3rzeen
— The New York Times (@nytimes) October 20, 2021
Water Shortage Contingency Plan Level 1
Following Gov. Gavin Newsom’s Oct. 19 extension of the statewide drought emergency to all counties in California, the San Diego County Water Authority Board of Directors voted unanimously to activate the agency’s Water Shortage Contingency Plan. That plan includes a call for increased voluntary conservation by San Diego residents. CBS 8 Reporter Heather Hope reported on the Board action and tips for how people can reduce water use.
In support of Gov. Gavin Newsom’s water conservation efforts following California’s two record-dry years, the San Diego County Water Authority activated its “Level 1,” or Voluntary Conservation of its Water Shortage Contingency Plan.
“We’re trying to achieve 15% to be consistent with the governor’s request of 15% voluntary conservation. It’s using what you have efficiently and not wasting,” said San Diego County Water Authority Water Resources Manager Jeff Stephenson.
San Diegans are urged to use less water💧 as the @sdcwa activated Level 1 of its #Water shortage contingency plan. We went to @cuyamacacollege to hear from The Water Conservation Garden Director of Horticulture Paul Redeker explain a water reduction tip🚿 @CBS8 pic.twitter.com/rU2ylw9Hjd
— Heather HOPE (@HopeNEWS8) October 30, 2021
How San Diego Gets Its Drinking Water
Reporter Jill Cowan with The New York Times, provided a tour of the Carlsbad Desalination Plant, in a story published October 29, 2021.
Whenever California is pummeled by drought — as is still very much the case despite recent rain — a lot of people find themselves asking, “What if we got water from the ocean?”
In San Diego County, it’s already happening at a $1 billion facility by the beach.
Recently, as I reported on San Diego’s decades-long quest for water stability, I visited the Carlsbad Desalination Plant, the largest such facility in the country, to see how it works.
Pure Water Oceanside
Reporter Leah Pezzetti, with ABC 10 News San Diego, visited the City of Oceanside’s Pure Water Oceanside project on Oct. 29 for a look at the process to purify wastewater into drinking water.
San Diego County has been planning ways to increase its sustainable water supply and one of the planned methods is through turning wastewater into potable water. There are three sites planned in the county and the first one, Pure Water Oceanside, is set to open before the end of 2021.
Thank you to @LeahPezzetti and @10News for stopping by to interview #Oceanside Water Utilities Director Cari Dale about Pure Water Oceanside and the expansion of the City's existing recycled water system. Look for the piece on tonight's news.
Learn more > https://t.co/jBC4ONBBtQ pic.twitter.com/nL1RdEczQI
— City of Oceanside (@CityofOceanside) October 29, 2021
(Editor’s note: This story was updated on October 30. The Sweetwater Authority, the City of San Diego, and the City of Oceanside are three of the San Diego County Water Authority’s 24 member agencies that deliver water across the metropolitan San Diego region.)