When the Helix Water District received contractor estimates as high as $3.5 million to upgrade the R.M. Levy Water Treatment Plant’s ozone power supply units and generators, it decided to perform the upgrade in-house.
With Suez Water Technologies provided engineering and equipment, Helix employees incorporated new technology and innovative installation practices. The proof of concept pilot project proved the feasibility of the new approach, and a full retrofit is now planned. The estimated upgrade costs to complete the full project is $1.1 million – an approximately 70% cost savings. The upgrade will extend the life of the power supply units and generators at least 15 years.
Reducing upgrade costs saves ratepayers
“The ozone project is our latest example of cost-effective local government,” said Brian Olney, Helix Water District director of water quality and system operations. “In early 2020, Helix staff also standardized the design, hardware, and software of the motor control centers in the district’s 25 pump stations, and that project also saved our customers money, and created long-term operating, maintenance and purchasing efficiencies.”
Ozone treatment provides safe and reliable water to East County
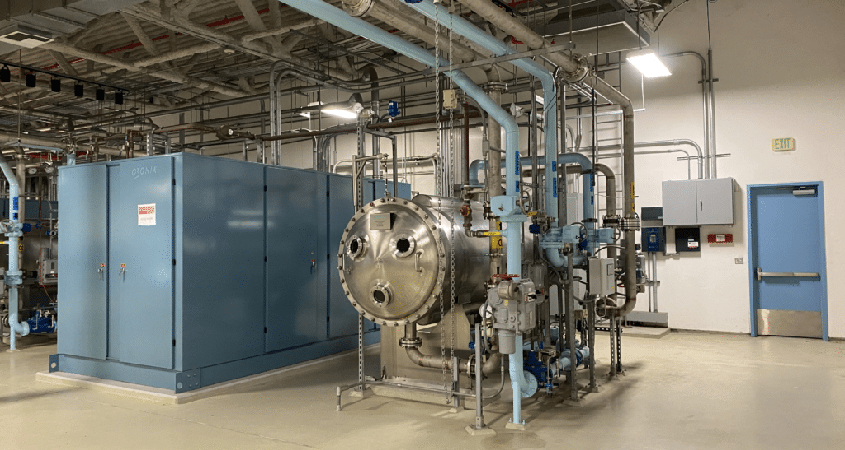
The ozone generator at Helix Water District’s R.M. Levy Water Treatment Plant in Lakeside. Photo: Helix Water District
The water treatment process at the R.M. Levy Water Treatment plant begins with the removal of dirt and other material suspended in the water. Ozone is then used to inactivate or destroy any organisms in the water. Ozone offers important advantages over chlorine:
- Ozone destroys or inactivates a wide range of organisms in the water
- Ozone needs little contact time with the water to be effective
- Ozone produces fewer potentially harmful disinfection byproducts than other disinfectants
- Ozone removes most of the smell and taste issues people associate with tap water
Helix Water District’s ozone project team (pre-pandemic) in front of the rebuilt power supply unit. Photo: Helix Water District
Ozone is naturally unstable at normal atmospheric conditions, which is why Helix needs ozone generators to produce it on site. The high voltage generators break down oxygen molecules (O2) and form ozone (O3). The ozone molecules are then diffused in a contact chamber and bubble up through the water to destroy any organisms present.
After ozonation, Helix Water District filters the water and adds a dose of chloramines — chlorine and ammonia — to maintain water quality throughout its 737 miles of water distribution pipelines. The treatment process is managed by a team of highly trained plant operators who conduct 200 water quality tests per day. Chemists and biologists test water samples from both the plant and the distribution system as well.




 Sweetwater Authority Logo 2019
Sweetwater Authority Logo 2019
