Sustainable Gardeners, Get Into Your Climate Zone
People around the world know San Diego for its beautiful, sunny, and mild weather. San Diego residents know our daily weather has more variety than visitors might imagine.
Climate is defined as the average weather conditions in an area over a long period, generally 30 years or more. German climate scientist Wladimir Koppen first divided the world’s climate into six regions in the early 1900s.
Since then, U.S. climate zones have been defined in more detail. The U.S. Department of Agriculture defines climate zones according to the lowest average temperature in the region. You may also be familiar with the 24 climate zones identified in Sunset Magazine’s iconic Sunset Western Garden Book. The book is now out of print, but is available online as an interactive edition. Existing print copies from the last edition printed in 2012 are prized heirlooms.
Devoted gardeners still follow the 24 climate zones featured in the guide. This is based on the California Irrigation Management Information System (CIMIS) adoption of a similar map identifying 24 climate zones.
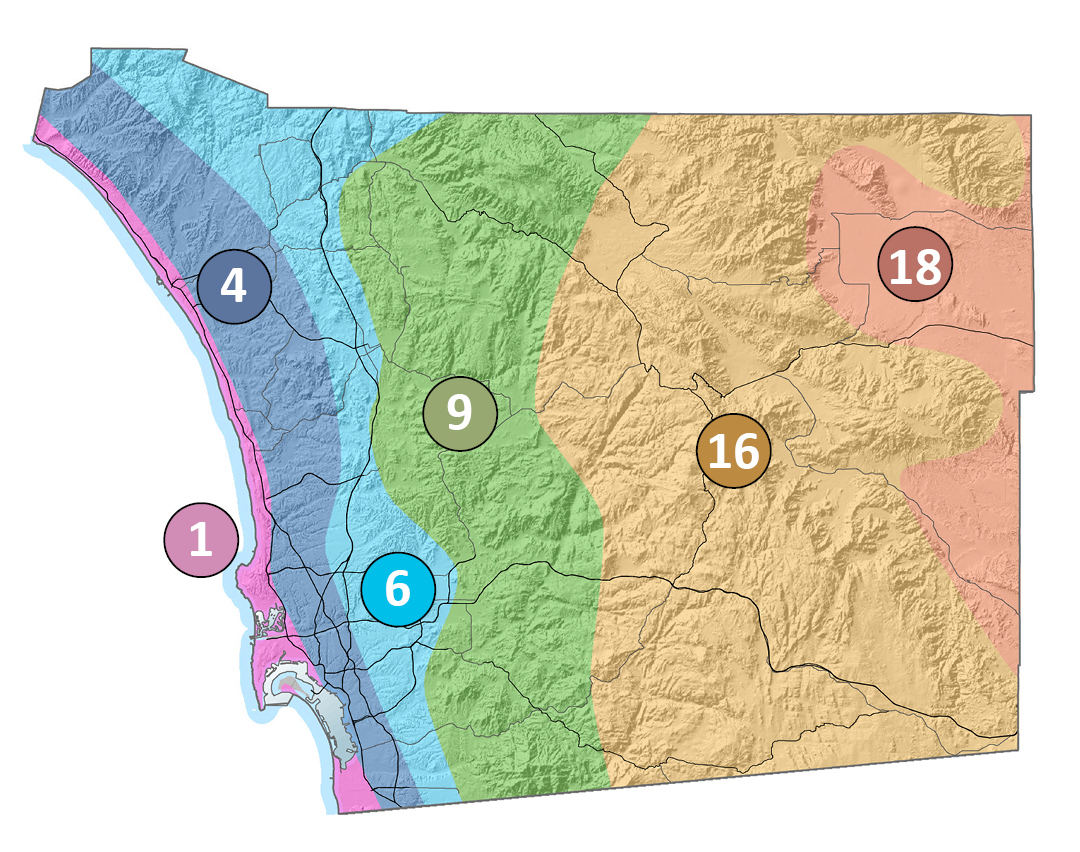
San Diego County’s geography falls within six of the 24 CIMIS climate zones. Photo: CIMIS
Evaporation + Transpiration = Evapotranspiration
Depending on the amount of rainfall, temperature, humidity, wind, shade, and the nature of the soil, water in the ground evaporates at different rates. When evaporation is higher, the soil becomes dry more quickly.
Evapotranspiration (ET) is the process by which water is transferred from the land to the atmosphere by evaporation from the soil and other surfaces, and by transpiration from plants.
Reference Evapotranspiration (ETo) is a baseline formula. All your plant water needs are measured against this baseline in a complex series of measurements and calculations.
Why is understanding evapotranspiration important?
In metropolitan San Diego County, our annual ETo rate increases as you move inland, meaning the soil becomes dry more quickly.
Fortunately, we don’t need to worry about making these calculations on our own. CIMIS maintains a statewide system of weather stations and reference plots. From these, it has identified the six main ET Zones in San Diego County.
Understanding your ETo zone and gardening climate zone are important first steps toward deciding how much water your landscaping will need. Working against the ETo and gardening climate zones can greatly increase your need for irrigation.
Learn more about your ETo climate zone’s specifics and gardening microclimate on the California Irrigation Management Information System website.
This article is part of a year-long series inspired by the 71-page Sustainable Landscapes Program guidebook available at SustainableLandscapesSD.org. The Water Authority and its partners also offer other great resources for landscaping upgrades, including free WaterSmart classes at WaterSmartSD.org.




