California officials have urged residents to prepare for a third year of drought and urged people to conserve water.
“With only one month left in California’s wet season and no major storms in the forecast, Californians should plan for a third year of drought conditions,” said California Department of Water Resources Director Karla Nemeth. “A significantly below-average snowpack combined with already low reservoir levels make it critical that all Californians step up and conserve water every day to help the state meet the challenges of severe drought.”
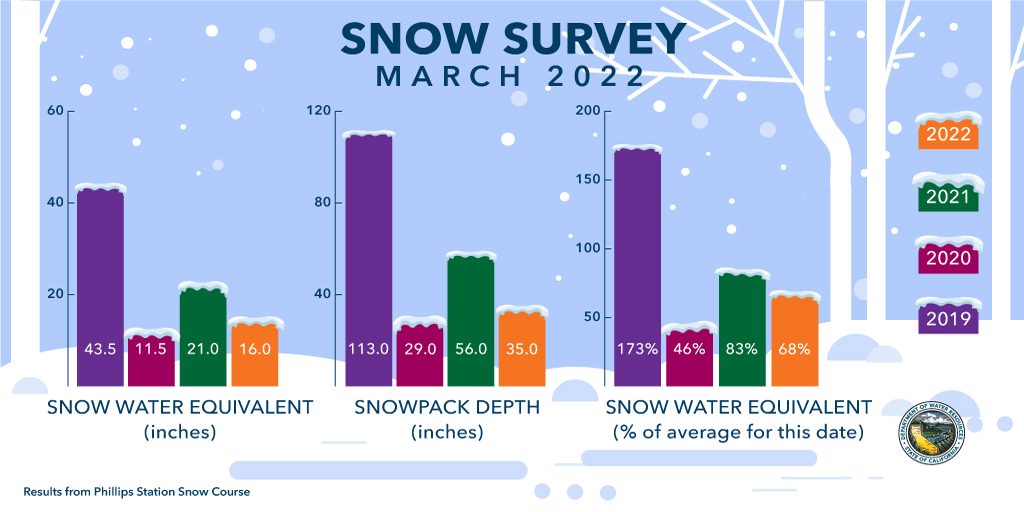
The DWR conducted the third snow survey of the season March 1 at Phillips Station.
Following a January and February that will enter records as the driest documented in state history, the manual survey recorded 35 inches of snow depth and a snow water equivalent of 16 inches, which is 68% of average for this location for March, according to the DWR. The snow water equivalent measures the amount of water contained in the snowpack and is a key component of DWR’s water supply forecast. Statewide, the snowpack is 63% of average for this date.
Water conservation “a way of life” in San Diego County
“As we enter a third year of drought, we encourage residents and businesses in San Diego County to increase their water conservation efforts,” said Jeff Stephenson, water resources manager with the San Diego County Water Authority. “While the Water Authority and its 24 member agencies have worked to create multiple sources of water supply for the region, there are still opportunities, including rebates, to save more water.”
In San Diego County, the website, watersmartsd.org, provides sources of residential and business rebates, including indoor and outdoor incentives, agricultural programs, and free landscape makeover classes.
Stephenson added that the region has reduced its reliance on imported water supplies, including from the Sacramento-San Joaquin Bay Delta, which means more of that source is available for other parts of California.
Governor Gavin Newsom has asked all Californians to cut back water use at least 15% compared to 2020 levels. Regionally, the Northern, Central, and Southern Sierra snowpacks are all standing just above 59% to 66% of average for this date, impacting watersheds across the state, according to the DWR.
“As the world continues to warm, precipitation is pushing toward extremes,” said Jeremy Hill, Manager of DWR’s Hydrology and Flood Operations Branch. “Even when we see large storms producing a lot of snow early in the season, all it takes is a few dry weeks to put us below average. This new pattern challenges forecasting efforts that have relied on historical patterns, so DWR has led the charge to adopt new technologies and utilize the best available science to manage water in real time and use forecasts that give us time to make decisions to get the most benefits and minimize the hazards.”
California Drought
An extremely dry January and February have wiped out an early season surplus and brought the February snowpack below average. With no storm relief in sight, Californians should prepare for drought conditions to continue, the DWR tweeted March 1. Graphic: California Department of Water Resources
Dry times in the Golden State
Although early season storms helped alleviate some drought impacts, a lack of storms in January and February heightens the need for conservation. The Governor has asked all Californians to cut back water use at least 15 percent compared to 2020 levels. Regionally, the Northern, Central, and Southern Sierra snowpacks are all standing just above 59 percent to 66 percent of average for this date, impacting watersheds across the state.
“With below average precipitation and snowpack up until this point, our latest statewide snowmelt forecasts are only 66 percent of average,” said Sean de Guzman, Manager of DWR’s Snow Surveys and Water Supply Forecasting Unit. “That is not enough to fill up our reservoirs. Without any significant storms on the horizon, it’s safe to say we’ll end this year dry and extend this drought a third year.”




