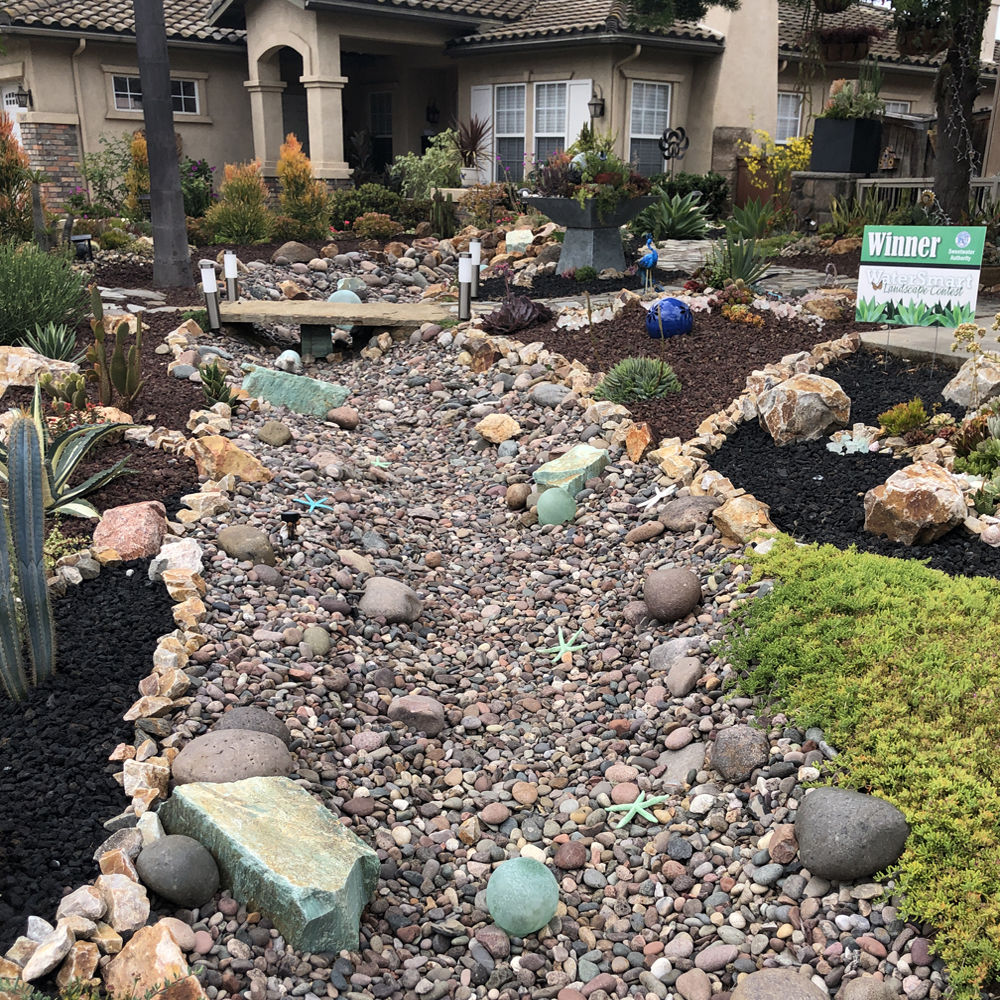
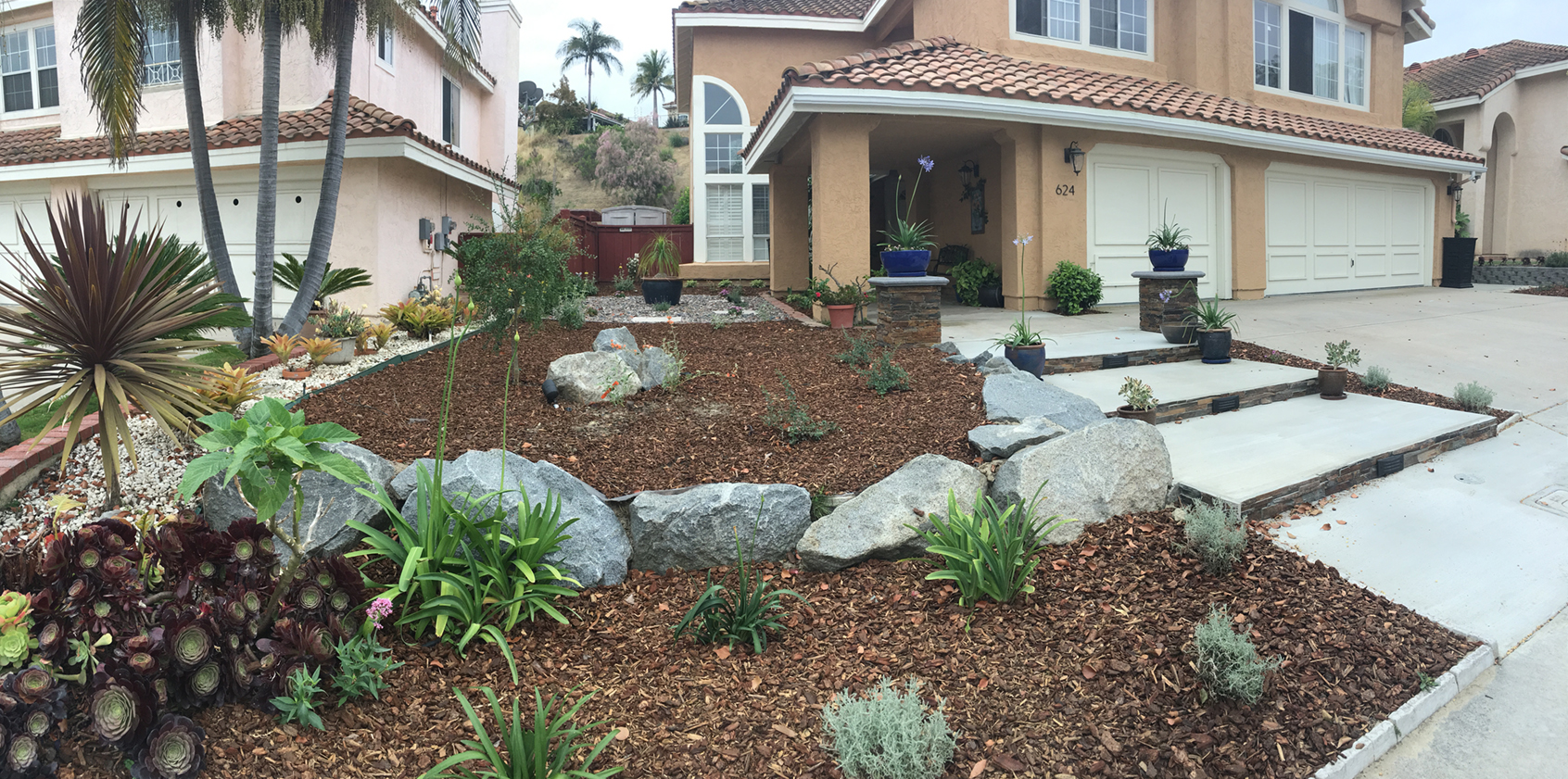
Tree Care Tips Preserve Benefits During Drought
Trees are among the most valuable investment in San Diego County’s landscape – including your own waterwise landscaping. Trees stand out as key performers in your landscape design for multiple reasons. No other landscape plant offers greater benefits to your landscape and the greater environment.
Investing in tree maintenance is vital to keep them healthy. As you reassess your landscaping’s irrigation needs during extended periods of drought, allocate sufficient water to your trees, which will in turn provide multiple benefits.
Trees need time to grow and reach maturity. Saving water in the short term during a drought could result in damaged or dead trees, which could take decades to restore. According to the San Diego Regional Urban Forest Council, the cost of watering a mature tree is less than $20 each year. It can cost $1,000 to remove a dead tree. Taking care of your trees during drought ensures a tremendous return on this investment.
Multiple long-term benefits from trees

Healthy trees fight climate change and cool our cities, provide habitat, and improve the health of our neighborhoods. Photo: Kampus Production / Pexels
In the region’s dry and increasingly warming Mediterranean climate, trees help fight climate change. Trees counteract the urban heat island effect, especially in areas dominated by hardscapes such as streets, sidewalks, and building roofs. The evapotranspiration from tree leaves cools the ambient temperature down, much as perspiration lowers a person’s body temperature. Watering your trees also reduces the water needs of plants growing in their shade.
Trees provide habitat for insects, pollinators, birds, and animals – and human beings with their welcoming shade and protection. Placed properly, shade trees can reduce the use of air conditioning from 20% to 50%. The evaporation from a single tree can produce the cooling effect of ten room-size residential air conditioners operating 20 hours a day. California street trees alone save the amount of electricity it would take to air condition 530,000 households every year.
Trees protect your property, and studies show the presence of trees improves property values. Neighborhoods with more trees have lower crime rates. In business districts, trees attract customers. People linger and shop longer when trees are present. Sales rise and benefit the entire economy.
Prevent wildfire risks with healthy trees
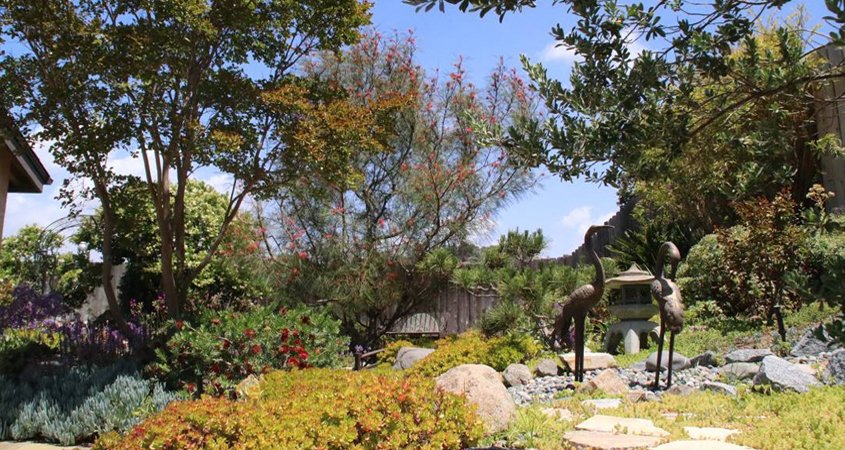

Even the strictest drought restrictions allow for watering trees on residential and commercial properties. Photo: Helix Water District
When trees die off due to drought, they become wildfire safety risks in addition to losing their many environmental and economic benefits. While any plant might die off without sufficient water, it may grow back within weeks. Drought stress can make living trees more susceptible to diseases and pests.
Even the strictest drought restrictions allow for watering trees on residential and commercial properties. The preferred method is to use a slow-release method such as a perforated bucket or low-volume non-spray irrigation.
Effective ways to water trees
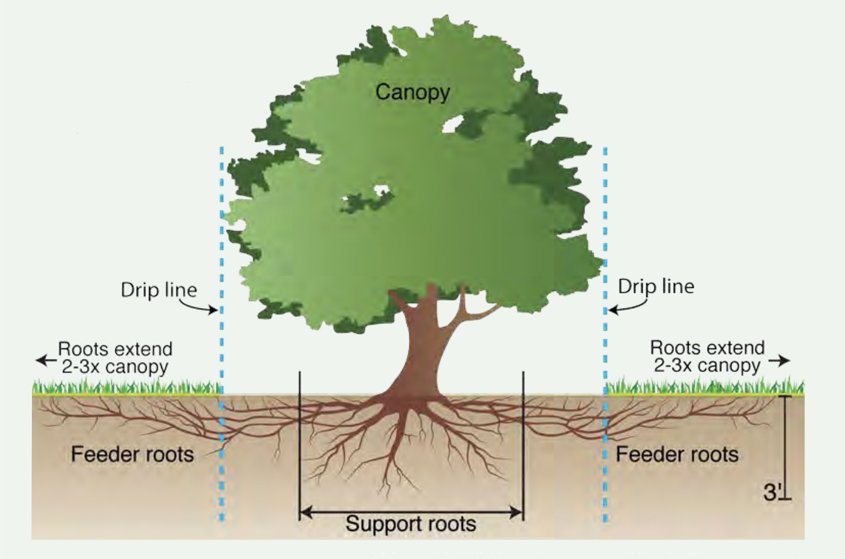
When watering your trees, water along the dripline below the canopy edge, not at the trunk. Graphic: San Diego Regional Urban Forestry Council
Trees need deep infrequent watering. Once established, once a month in the summer and during months without measurable rainfall is sufficient.
- Newly planted trees: For the first three years, water once weekly with up to five gallons of water.
- Small, established low water trees need only about 20 gallons a month. This is the same amount of water in a single average shower.
- Larger, mature low water trees need up to 200 gallons per month.
- Monitor the soil moisture under your tree and adjust amounts accordingly. You may want to use a soil probe to check at the roots.
- Apply water at the edge of the tree’s canopy, not at the trunk. This is where the roots absorb and bring water into the tree.
Trees create community. They provide inviting and cool areas for recreation and relaxation in our neighborhoods and contribute to playgrounds and parks. San Diego enjoys a perfect example right in the heart of the city. One of our greatest civic attractions is Balboa Park, full of beautiful trees planted by visionaries like Kate Sessions a century ago.














