New California Law Taps Science to Improve Water Management
Legislation signed into law by California Governor Gavin Newsom ensures the state has the science and weather forecasting tools it needs for more flexible reservoir operations. The bill, AB 30, makes breakthrough water management technology standard for the California Department of Water Resources.
The legislation was introduced by San Diego Assemblymember Chris Ward and co-sponsored by the Sonoma County Water Agency and the San Diego County Water Authority. The bill was supported by the Water Authority’s partner, UC San Diego’s Scripps Institution of Oceanography.
Forecast-Informed Reservoir Operations strategy will help deal with drought and flood
The strategy is called forecast-informed reservoir operations, or FIRO, and it complements Gov. Newsom’s California Water Supply strategy released in August 2022 calling for more reservoir storage capacity to capture runoff from big storms, often fueled by atmospheric rivers. The governor and Legislature have already provided funding for state water managers to integrate the strategy.
“We thank Assemblymember Chris Ward for his leadership and vision in supporting next-gen water management and flood reduction efforts that will benefit residents statewide,” said Mel Katz, chair of the San Diego County Water Authority Board of Directors. “The legislation provides an innovative approach to help San Diego County and California thrive in the changing climate.”
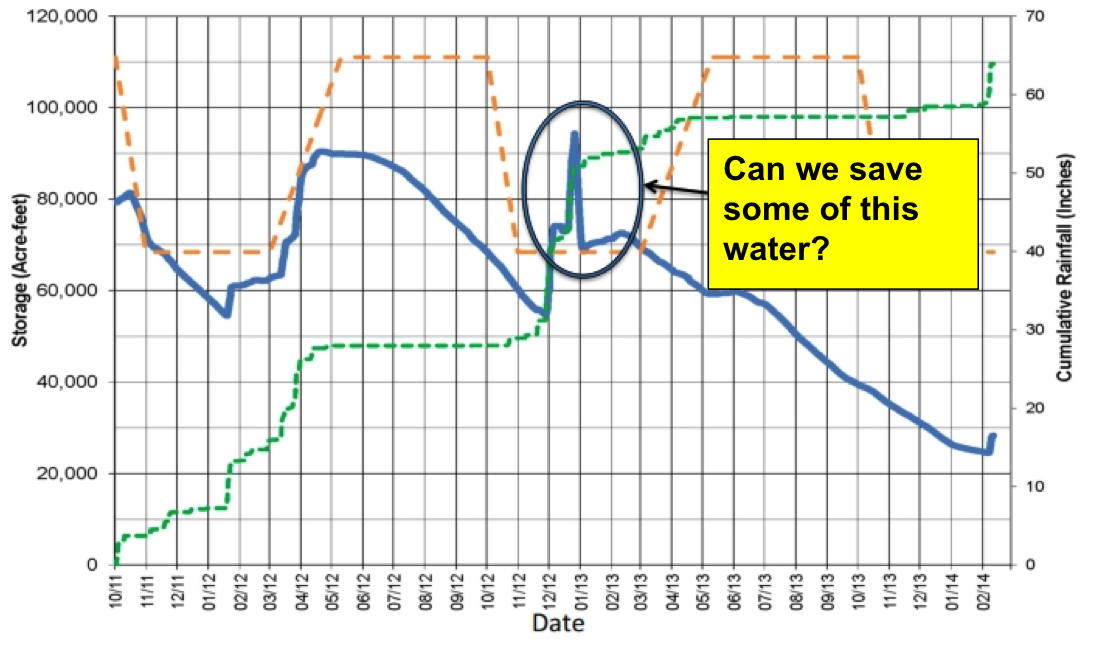
Forecast-informed reservoir operations use weather predictions to advise dam operators about how much water to retain or release from reservoirs, enhancing their ability to handle whatever nature serves up while retaining as much water as possible in storage.
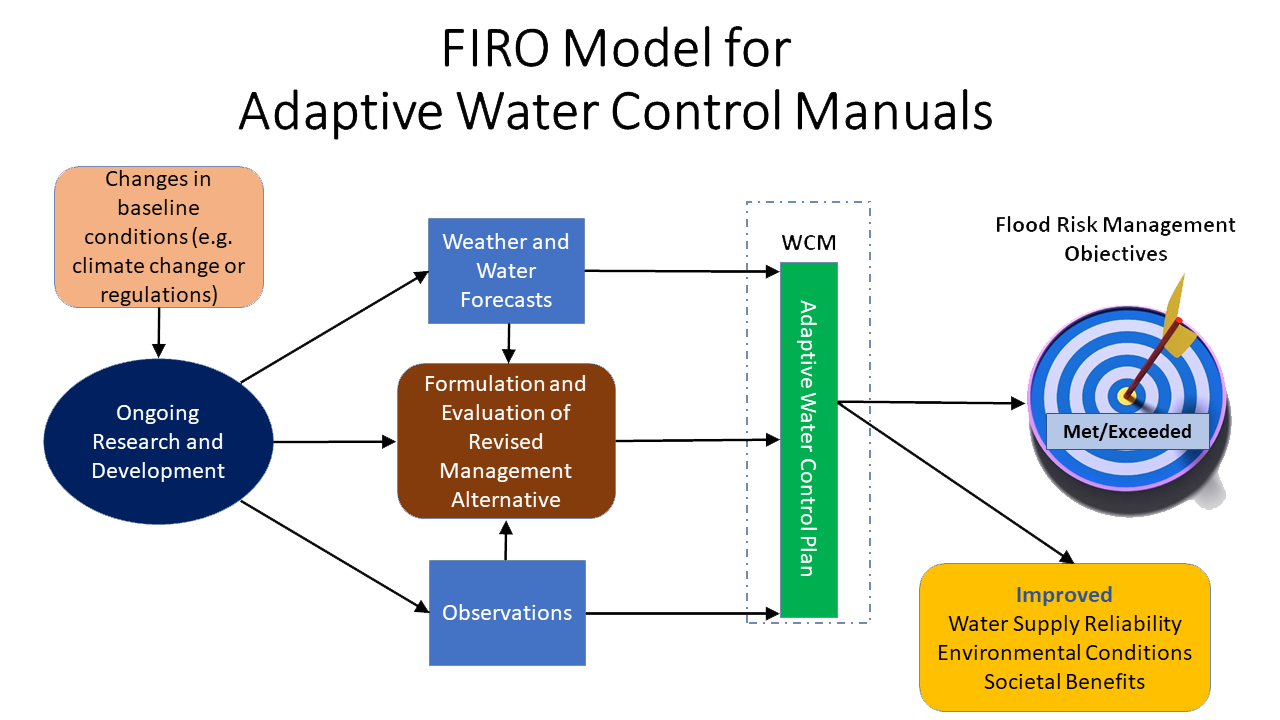
Diagram illustrating the FIRO process to develop an adaptive water control manual. Graphic courtesy Scripps Institution of Oceanography Center for Western Weather and Water Extremes
Many reservoirs in the West are strictly regulated based on historical averages of winter storms and spring runoff. Under existing rules, the highly variable rainfall from year to year is not directly considered. Complicating the problem, many current guidelines and practices were developed before satellites, radar and advanced numerical models significantly improved weather forecasts.
To address these challenges, researchers at Scripps Institution of Oceanography and elsewhere developed tools that provide weather forecasters with reliable notice of atmospheric rivers a week in advance. Advancing this research could have taken decades, but sophisticated prediction products have evolved in less than 10 years with funding by the San Diego County Water Authority and other water agencies statewide, along with state and federal support.
The Water Authority has partnered with SIO and the Scripps Center for Western Weather and Water Extremes at UC San Diego, to share and support best practices in FIRO, to increase research around atmospheric rivers and droughts, and develop strategies for mitigating flood risk and increasing water supply reliability.