Horticulture director embraces educational mission
WaterSmart landscapes are transforming San Diego County’s neighborhoods in part due to the work of Paul Redeker and his colleagues at The Water Conservation Garden in El Cajon.
“We’re a learning center, not just a place where you’re surrounded by beautiful plants,” said Redeker, who recently returned for a second run as director of horticulture and facilities the garden. “All of our exhibits are geared toward teaching. We are all about educating the public to be inspired to make changes in their lives because we’re literally at the end of the water pipeline.”
Driving that point home is a giant pipe protruding from a landscaped embankment with water trickling from its opening into a lily pond near the entrance to this one-of-a-kind, six-acre conservation showcase on the campus of Cuyamaca College.
“I love the educational element,” Redeker said. “The learning that goes on in this garden regarding low-water options is wonderful.”
‘Wonderful’ low-water options
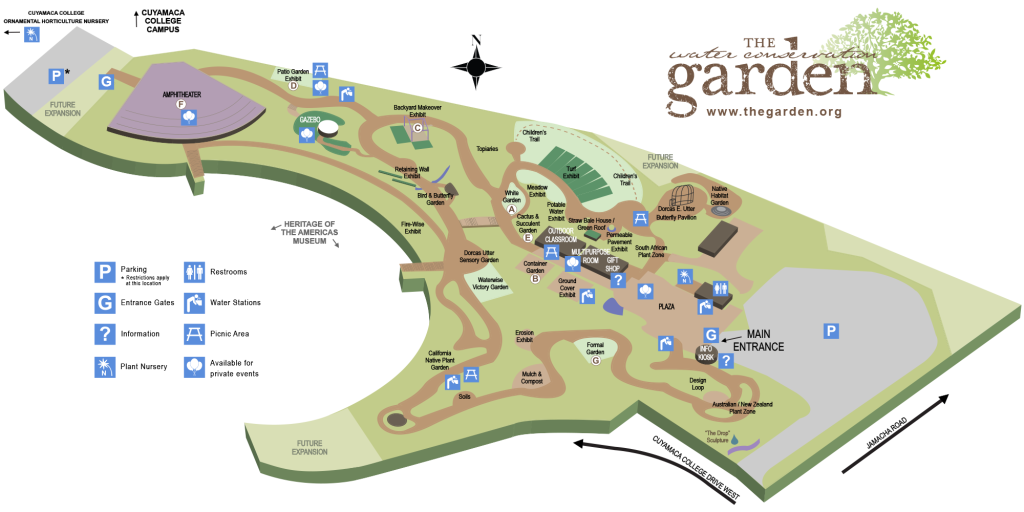
The Water Conservation Garden feature a Native Habitat Garden, the Compost Exhibit, the Veggie Garden and the Succulent Garden. Take a free, docent-led tour the first Saturday of each month at 10 a.m. Illustration: The Garden
Opened in 1999, The Water Conservation Garden is owned by a joint powers agency comprising the San Diego County Water Authority, the Otay Water District, the Helix Water District, the Sweetwater Authority, the City of San Diego Public Utilities and Cuyamaca College. From the start, the garden was seen as an important conservation tool in a region with few natural water resources.
More than 30,000 people visit each year, and the garden’s programs reach an additional 80,000. It is the educational element that lured Redeker back. “The learning that goes on in this garden regarding low-water options is wonderful,” he said.
Born and raised on a Sonoma County ranch, Redeker earned his bachelor’s degree in ornamental horticulture, with a focus on landscape design, from Cal Polytechnic State University at San Luis Obispo. He worked at several Northern California nurseries before exploring other career interests overseas.
Redeker returned to California and was designing landscapes for a San Diego company when he fell in love with public gardens and landed a position as The Water Conservation Garden’s director of horticulture more than 10 years ago.
After five years in El Cajon, he expanded his professional expertise at the San Diego Botanic Garden, another regional showcase garden in Encinitas. “It gave me a wonderful understanding of how larger gardens operate,” said Redeker.
A constantly evolving gem of a garden

Plans are underway for new displays including an interactive irrigation exhibit, watershed exhibit, and a new outdoor classroom. Photo: David Ogul, Water Authority
Redeker returned to his “little gem of a garden” last fall, and he is thrilled with the opportunities to innovate. “We are always looking to improve the experience so that when people come back, they can see something new and fresh,” he said.
Projects under way or in the planning stages at The Water Conservation Garden include:
- An interactive irrigation exhibit to help visitors understand and appreciate different types of water-saving technologies.
- A watershed exhibit with a “follow the raindrop” feature that illustrates the benefits of strategic stormwater management.
- More than a dozen strategically placed, drought-tolerant trees – including the Silk Oak , Blue Atlas Cedar, Sweetshade, and the Variegated Brisbane box – have been planted throughout the garden to help keep summertime temperatures in check.
- An expanded indoor classroom that will more than triple capacity to nearly 100.
- A new outdoor classroom, covered with a shade structure, will replace the current outdoor class space.
“The new classroom is going to be huge for us,” said Pam Meisner, the garden’s director of operations and programs. “We simply don’t have the room to accommodate demand for all of our adult-education landscaping and gardening classes.”
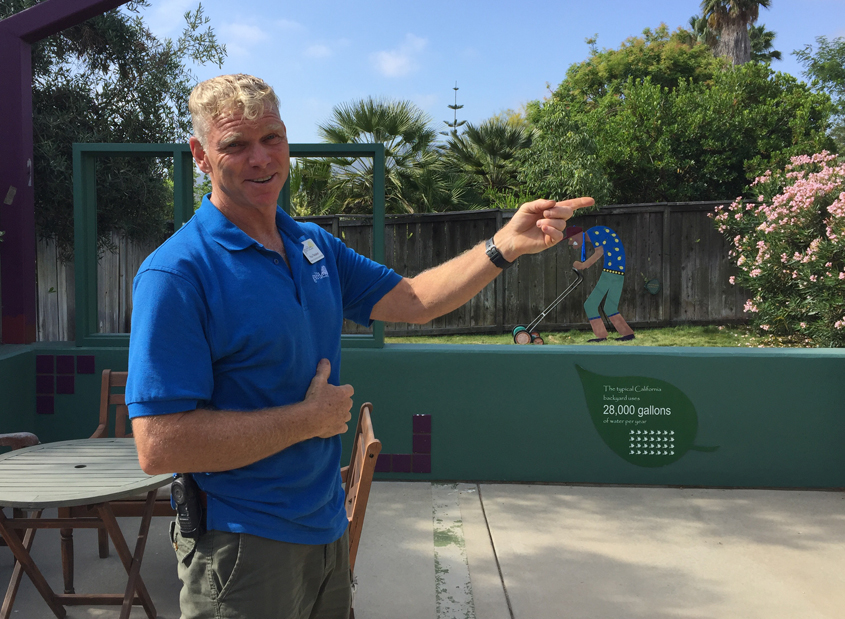
Among the permanent features is a Retrofit Backyard Exhibit that includes a traditional backyard lawn – complete with a depiction of a homeowner struggling to mow a greenbelt that drinks some 28,000 gallons of water annually – adjacent to a more visually appealing, and less labor-intensive garden featuring drought-tolerant plants that uses just 6,000 gallons of water each year.
“People are being smarter and much more creative with what they’re doing with their landscape,” said Redeker. “We’re seeing smarter plant choices, more hardscape, more patios, more mulch, dry streambeds and the like, and it’s making a difference.”











