12 Grand Groundcovers to Use as Lawn Substitutes
You’ve decided to eliminate the thirsty turf areas in your current landscaping when planning your new sustainable landscape. It’s tempting to install hardscape. It needs no water at all. It might seem like a smart idea, but it creates a new problem: stormwater runoff. It can also increase temperatures and add in its own small way to global warming.
Finding alternatives to cover the area with plants instead of hardscaping will help prevent too much stormwater runoff and capture rainfall.
Consider replacing your lawn with groundcovers. There are many good choices of groundcover plants that make good lawn substitutes. Many species grow well in San Diego County’s six climate zones and the Mediterranean climate natives fall into the very low or low Plant Factor categories. They won’t use as much water than the same amount of grass.
Very Low Plant Factor groundcover choices include:
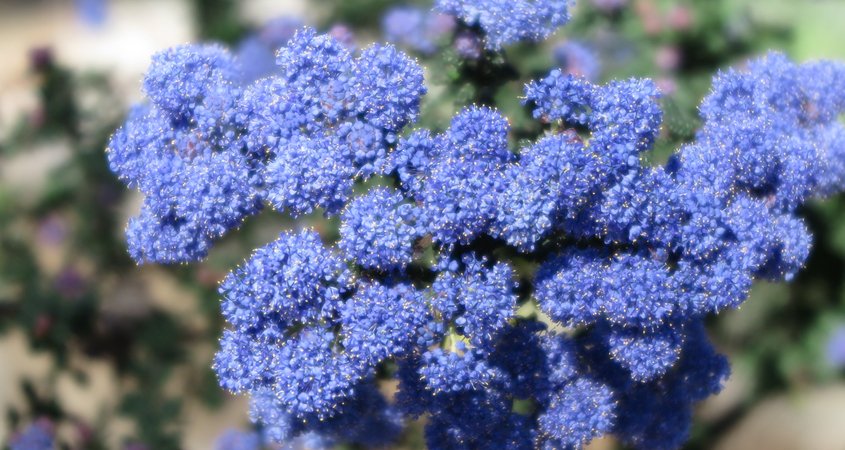

California lilac (Ceanothus) is a native plant to San Diego County and produces spectacular blooms in early spring. Photo: Wikimedia
Silver Carpet (Dymondia margaretae)
Bluff California Lilac (Ceanothus maritimus)
Low Plant Factor groundcover choices include:
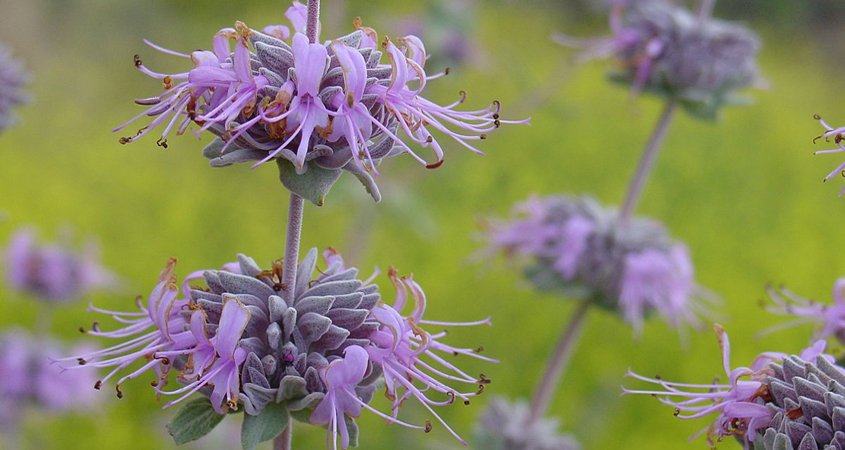

Bee’s Bliss Sage (Salvia leucophylla) attracts pollinators including bees and butterflies to your landscaping. Photo: Wikipedia
Pink Yarrow (Achillea millefolium rosea)
Gold Coin Plant (Asteriscus maritumus)
Sundrops (Calylophus hartwegii)
Carmel Mountain ceanothus
Dwarf Mat Rush (Lomandra longfolia)
Bee’s Bliss Sage (Salvia)
Wooly Thyme (Thymus pseudolanguinosus)
Blue Chalksticks (Senecio serpens)
Moderate Plant Factor groundcover choices include:
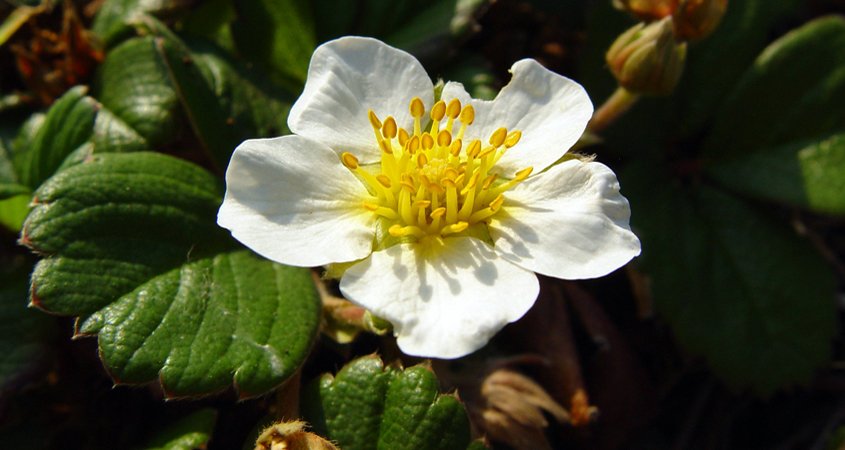

The Beach Strawberry (Fragaria chiloensis) provides a display of white flowers. Photo: Wikimedia
Creeping Manzanita ‘Carmel Sur’ (Arctostaphylos edmunsii)
Beach Strawberry (Fragaria chiloensis)
Pink yarrow, sages, and lilacs also support the lifecycle of butterflies, which are important pollinators.
This article is part of a year-long series inspired by the 71-page Sustainable Landscapes Program guidebook. The Water Authority and its partners also offer other great resources for landscaping upgrades, including free WaterSmart classes at WaterSmartSD.org.