Water suppliers in San Diego County say future COVID-19 federal and state stimulus packages should include funding for shovel-ready projects that would create jobs in the region.
In a letter to members of California’s congressional delegation, a group of 13 agencies, including the San Diego County Water Authority and 10 of its member agencies, and the cities of Del Mar, Oceanside and Poway, say the region’s water utilities have dozens of infrastructure projects that could be launched with an infusion of state and federal stimulus funding.
“As the water suppliers throughout San Diego County, across the state, and around the nation are confronting the unprecedented impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic, there are several actions that the federal government could take to provide some much-needed relief,” according to the letter dated May 31.
From replacing valves in pipelines to building water purification facilities, to developing a major pumped hydropower energy storage project for the region, the funding boost would advance efforts to enhance water reliability and increase jobs across San Diego County.
Financial stress, economic fallout from pandemic
The letter requests the following action items be supported as Congress discusses additional legislative relief packages:
- Allow for use of federal funds to backfill for lost revenue: The largest issues that water suppliers are currently facing are the immediate budgetary impacts and the ongoing effects of lost revenues. Allowing water systems to use federal funds to fill the gap being created by lost revenue would provide significant assistance to prevent layoffs or furloughs, minimize project deferrals or delays, and help avoid other associated impacts that may have a lingering negative effect on regional economies. An analysis produced last month by the Association of American Metropolitan Water Agencies and the American Water Works Association estimated that drinking water utilities throughout the county are facing an annualized revenue loss of approximately $13.9 billion as a result of the pandemic – a sum equal to nearly 17% of the sector’s annual revenue. We strongly encourage Congress to set aside robust funding for water utilities to help offset these fiscal losses. Otherwise, ratepayers will face escalating costs and reduced economic activity related to delayed capital investments, which will only further hinder the nation’s, state’s, and region’s economic recovery.
- Extend the Emergency Payroll Tax Credit to Public Entities: The “Families First Coronavirus Response Act” required public employers to provide paid sick and family leave, yet the law excludes these same employers from receiving payroll tax credits made available to private employers. Extending this tax credit to local governments would help cover the costs associated with these programs.
- Restore advance refunding for tax-exempt bonds: This action would allow flexibility for local government entities to access billions of dollars to reallocate and spend on other projects and priorities, which would be much needed during this time.
- Aid to low-income ratepayers: COVID-19 response legislation should also include a separate component to ensure that low-income customers are able to afford to keep up with their utility bills throughout the pandemic. Without federal assistance targeted at these customers, some low-income households will fall even further behind on their bills, making it that much more difficult for them to catch up with their payments once the crisis ends.
San Vicente Energy Storage Facility
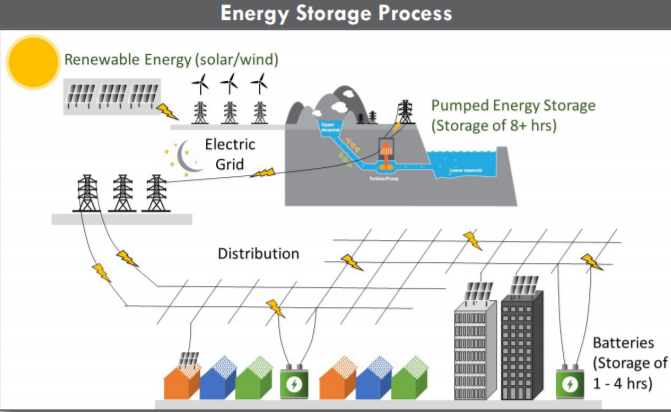
Pumped energy storage facilities are part of an integrated and sustainable energy system that includes the production, storage and distribution of clean energy.
Regional energy project needs regulatory path
One of those shovel-ready projects does not require any state investment or financial assistance to generate economic stimulus. But it needs a regulatory path forward, which could come in the form of state legislation or decisions by the California Public Utilities Commission.
The Water Authority and the City of San Diego have been working on the San Vicente Energy Storage Facility project for several years. All equity and debt financing would be provided by a private investor.
Generating renewable energy and jobs
The project would create a small upper reservoir above the existing San Vicente Reservoir, along with a tunnel system and an underground powerhouse to connect the two water bodies. The powerhouse would contain up to four reversible pump turbines.
During off-peak periods – when power is inexpensive and renewable supplies from wind and solar facilities exceed demand – turbines would pump water to the upper reservoir where it would act as a battery of stored energy. During peak energy use, the system would create clean energy as water from the upper reservoir flows downhill through the turbines.
“Our developer estimates the project could generate more than 50,000 hours of preconstruction work, followed by more than 1,000 jobs during a four-year construction period,” said Gary Bousquet, with the San Diego County Water Authority. “When it’s completed, the facility could store huge volumes of renewable energy and then use that energy when renewables are not available, such as nighttime.”
Bousquet said the project, when completed, would also generate additional revenue to offset water agency costs and help stabilize water rates.




