Following three consecutive years of drought in California, the Sierra Nevada snowpack is one of the most bountiful in more than 40 years. While the snowpack and snow water equivalent is great news for water supply, there are concerns the record snowpack could create flooding issues.
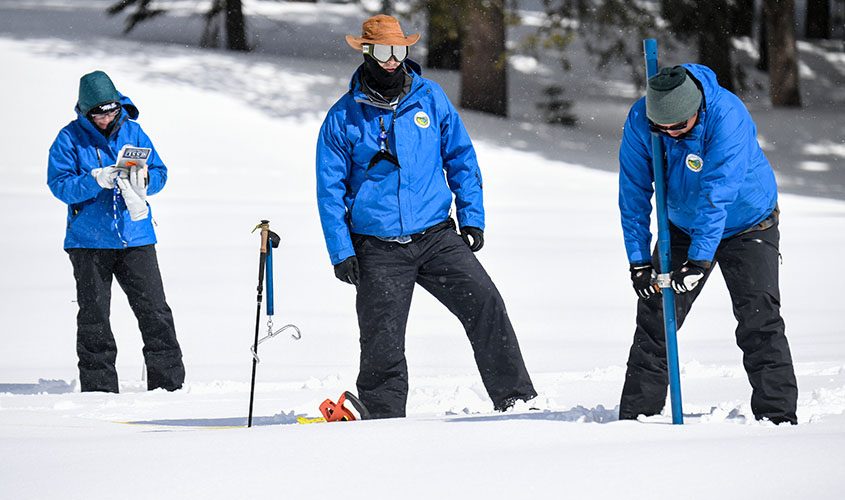
The California Department of Water Resources electronic readings from 130 snow sensors placed throughout the state indicate the statewide Sierra Nevada snowpack’s snow water equivalent is 61.1 inches, or 237% of average for April 3. The snow water equivalent measures the amount of water contained in the snowpack and is a key component of DWR’s water supply forecast.
Sierra Nevada snowpack
This year’s April result from the statewide snow sensor network is higher than any other reading since the snow sensor network was established in the mid-1980s. Before the network was established, the 1983 April 1 statewide summary from manual snow course measurements was 227% of average. The 1952 April 1 statewide summary for snow course measurements was 237% of average.

“This year’s severe storms and flooding is the latest example that California’s climate is becoming more extreme,” said DWR Director Karla Nemeth after the April 3 snow survey at Phillips Station in the Sierra Nevada. Photo: Fred Greaves/California DWR
“California’s climate is becoming more extreme”
“This year’s severe storms and flooding is the latest example that California’s climate is becoming more extreme,” said DWR Director Karla Nemeth. “After the driest three years on record and devastating drought impacts to communities across the state, DWR has rapidly shifted to flood response and forecasting for the upcoming snowmelt. We have provided flood assistance to many communities who just a few months ago were facing severe drought impacts.”
Just as the drought years demonstrated that California’s water system is facing new climate challenges, this year is showing how the state’s flood infrastructure will continue to face climate-driven challenges for moving and storing as much of these flood water as possible.

“This year’s result will go down as one of the largest snowpack years on record in California,” said Sean de Guzman, manager of DWR’s Snow Surveys and Water Supply Forecasting Unit. (R-to-L: de Guzman, Jacob Kollen, Water Resources Engineer in Snow Surveys and Water Supply Forecasting Unit, and Jordan Thoennes, Water Resources Engineer in Snow Surveys and Water Supply Forecasting Unit.) Photo: Kenneth James/California DWR
“One of the largest snowpack years on record”
“This year’s result will go down as one of the largest snowpack years on record in California,” said Sean de Guzman, manager of DWR’s Snow Surveys and Water Supply Forecasting Unit. “While 1952’s snow course measurements showed a similar result, there were fewer snow courses at that time, making it difficult to compare to today’s results. Because additional snow courses were added over the years, it is difficult to compare results accurately across the decades with precision, but this year’s snowpack is definitely one of the biggest the state has seen since the 1950s.”
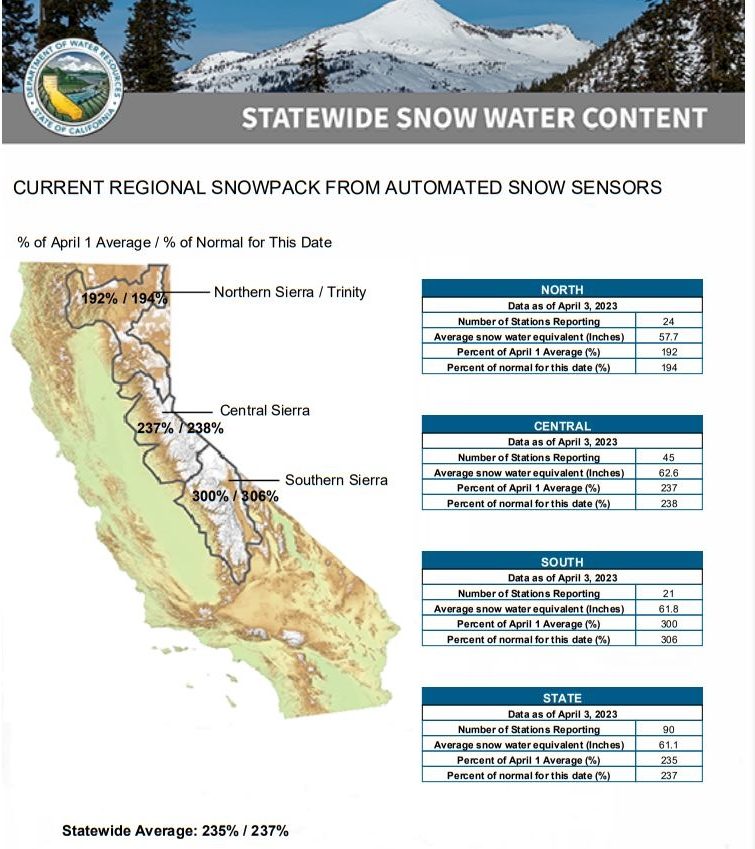
Snowpack varies by region
For California’s snow course measurements, only 1952, 1969 and 1983 recorded statewide results above 200% of the April 1 average. While above average across the state this year, snowpack varies considerably by region. The Southern Sierra snowpack is currently 300% of its April 1 average and the Central Sierra is at 237% of its April 1 average. However, the critical Northern Sierra, where the state’s largest surface water reservoirs are located, is at 192% of its April 1 average.
Flooding and spring snowmelt
The size and distribution of this year’s snowpack is also posing severe flood risk to areas of the state, especially the Southern San Joaquin Valley. DWR’s State-Federal Flood Operations Center (FOC) is supporting emergency response in the Tulare Lake Basin and Lower San Joaquin River by providing flood fight specialists to support ongoing flood response activities and by providing longer-term advanced planning activities.
The FOC and DWR’s Snow Surveys and Water Supply Forecasting Unit are helping local agencies plan for the spring snowmelt season by providing hydraulic and hydrologic modeling and snowmelt forecasts specific to the Tulare Lake Basin that are informed by DWR’s snowmelt forecasting tools, including Airborne Snow Observatory (ASO) surveys.
Storms this year have caused impacts across the state including flooding in the community of Pajaro and communities in Sacramento, Tulare, and Merced counties. The FOC has helped Californians by providing over 1.4 million sandbags, over 1 million square feet of plastic sheeting, and over 9,000 feet of reinforcing muscle wall, across the state since January.
State Water Project deliveries increased
On March 24, DWR announced an increase in the forecasted State Water Project deliveries to 75%, up from 35% announced in February, due to the improvement in the state’s water supplies. Governor Gavin Newsom has rolled back some drought emergency provisions that are no longer needed due to improved water conditions, while maintaining other measures that continue building up long-term water resilience and that support regions and communities still facing water supply challenges.
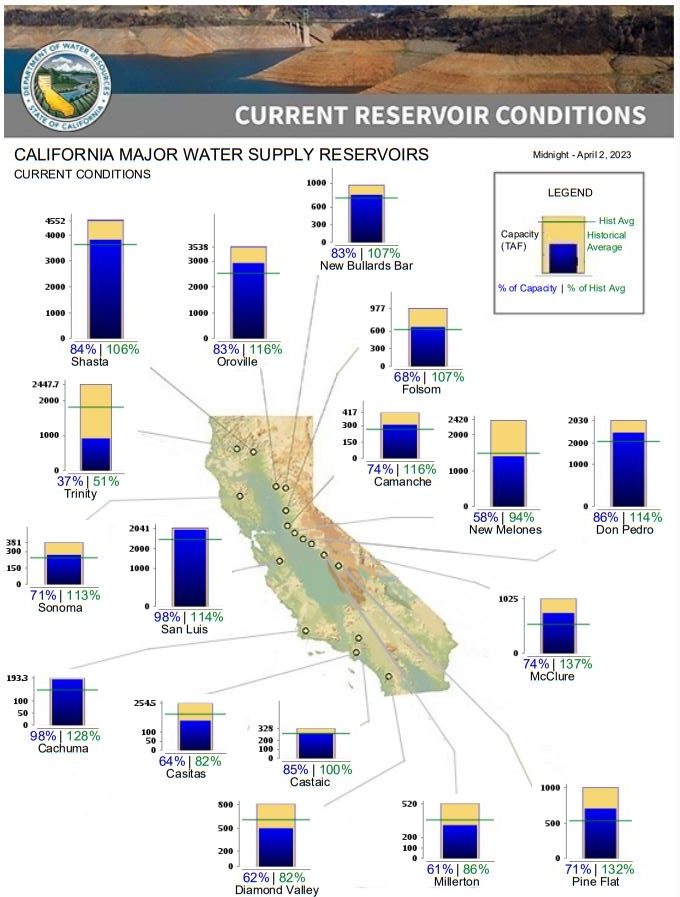
Water supply challenges
While winter storms have helped the snowpack and reservoirs, groundwater basins are much slower to recover. Many rural areas are still experiencing water supply challenges, especially communities that rely on groundwater supplies which have been depleted due to prolonged drought.
Water conservation ‘a way of life’
Long-term drought conditions in the Colorado River Basin will also continue to impact the water supply for millions of Californians. The state continues to encourage Californians to make water conservation a way of life as more swings between wet and dry conditions will continue in the future. The San Diego County Water Authority and its 24 member agencies provide rebates and programs to encourage water conservation.
Given the size of this year’s snowpack with more snow in the forecast, DWR anticipates conducting a May snow survey at Phillips Station. That is tentatively scheduled for May 1.