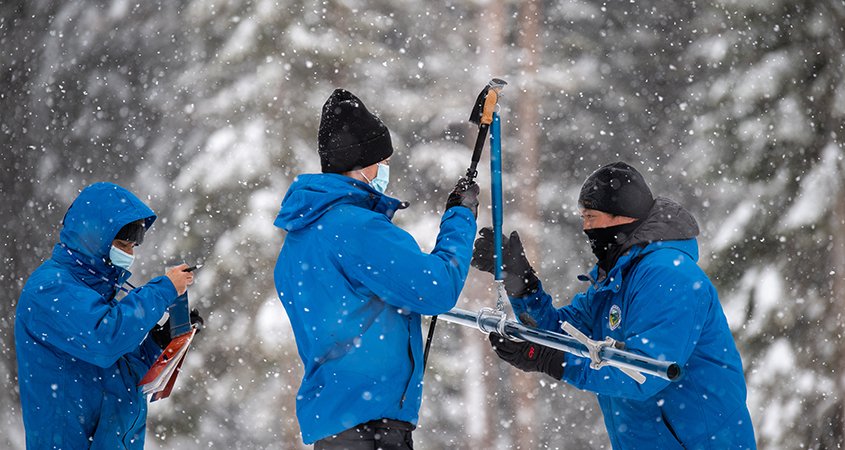
 (L-to-R) Ramesh Gautam, Chief of California Cooperative Snow Surveys Program, Nick Ellis, Electrical Engineer in Statewide Monitoring Network Section, and Sean de Guzman, Chief of the California Department of Water Resources Snow Surveys and Water Supply Forecasting Section, conduct the second media snow survey of the 2021 season Feb. 3 at Phillips Station in the Sierra Nevada. Photo: Florence Low / California Department of Water Resources
(L-to-R) Ramesh Gautam, Chief of California Cooperative Snow Surveys Program, Nick Ellis, Electrical Engineer in Statewide Monitoring Network Section, and Sean de Guzman, Chief of the California Department of Water Resources Snow Surveys and Water Supply Forecasting Section, conduct the second media snow survey of the 2021 season Feb. 3 at Phillips Station in the Sierra Nevada. Photo: Florence Low / California Department of Water ResourcesPrecipitation Below Average in California
Precipitation is below average in California for the current water year. Despite recent storms that increased the statewide Sierra Nevada snowpack to 70% of average to date, the state is experiencing its second consecutive below average year for rain and snow. The water year starts on October 1 and ends September 30.
The Department of Water Resources Feb. 3 conducted the second manual snow survey of the season at Phillips Station. The manual survey recorded 63 inches of snow depth and a snow water equivalent, or SWE, of 17 inches, which is 93% of average for that location, according to the DWR. The SWE measures the amount of water contained in the snowpack and is a key component of DWR’s water supply forecast.
“The recent blast of winter weather was a welcome sight, but it was not enough to offset this winter’s dry start,” said DWR Director Karla Nemeth. “While there is still a chance we will see additional storms in the coming weeks, the Department and other state agencies are preparing for the potential for a second consecutive year of dry conditions.”
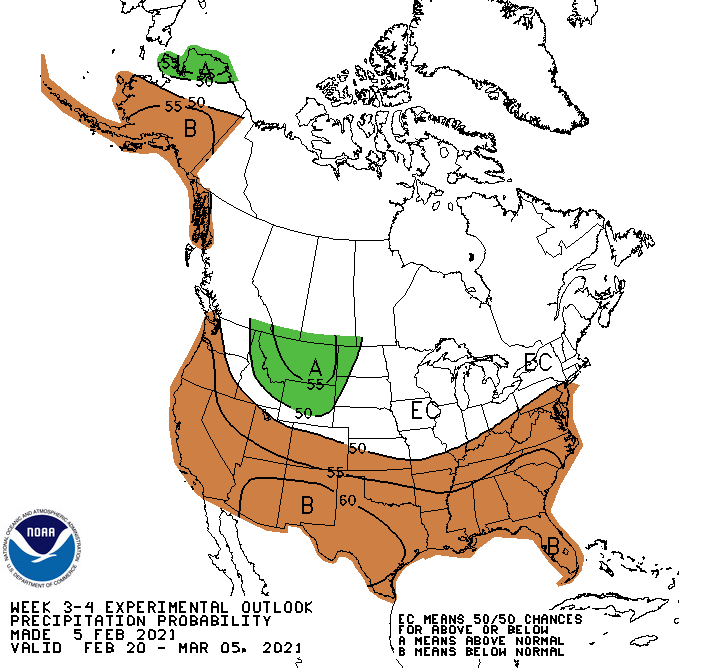
Below normal precipitation is favored throughout most of the southern tier of the United States in late February to early March, according to the National Weather Service Climate Prediction Center. La Niña conditions remain over the Pacific Ocean.
Precipitation below normal
Statewide snow survey measurements reflect those dry conditions. Measurements from DWR’s electronic snow survey stations indicate that statewide the snowpack’s SWE is 12.5 inches, or 70% of the February 3 average, and 45% of the April 1 average. April 1 is typically when California’s snowpack is the deepest and has the highest SWE.
“The recent atmospheric storms have brought rain and snow to the northern Sierra Nevada, but conditions are still well below normal,” said Goldy Herbon, San Diego County Water Authority senior resources specialist.
Following last year’s below average water year, northern California is now experiencing its second straight water year of below average precipitation.
How it started.
How it's going.Season-to-date snowfall through January 23 vs February 4.#CAwx #CAsnow ❄️☃️🏂🌨️ pic.twitter.com/UOvjEmxa5k
— NWS Sacramento (@NWSSacramento) February 4, 2021
Colorado River Basin
Another source of the state’s water supply, the Colorado River Basin, isn’t faring much better. The water year 2021 precipitation at the end of January for the Colorado River Basin is 66% of normal, according to the U.S. Bureau of Reclamation.
Precipitation totals to date are behind historical averages for two of the main sources of San Diego County’s supply, with two months to go in the winter season but, a couple of atmospheric rivers can change that quickly.
“The San Diego region will have a plentiful and reliable source of water due to actions taken by the Water Authority and its 24 member agencies to diversify the water supply,” said Herbon. “Continuing efforts to expand supply sources, including desalination, water reuse, and recycling, will ensure that the water needs are met for the region’s 3.3 million people and its $245 billion economy.”
Fall 2020 was extremely dry, especially in the Sierra Nevada, and follows last year’s below-average snow and precipitation, according to the DWR. With only a couple months remaining in California’s traditional wet season, DWR officials say Californians should look at ways to reduce water use at home.

Statewide Sierra Nevada snowpack is 71% of average for February 4, 2021. Graphic: California Department of Water Resources



