San Diego County Quality of Life Indicators Mostly Positive in 2018
A report released today showed improvement in 2018 for the majority of 15 indicators used to measure San Diego County’s quality of life. The Equinox Project Quality of Life Dashboard measures and benchmarks several environmental and economic trends throughout the region.
The analysis highlighted the San Diego County Water Authority for developing water solutions for San Diego and the Southwest using a “portfolio approach.” One of the initiatives under that approach includes efforts to store water in Lake Mead on the Colorado River, which would benefit both San Diego County residents and many other river users.
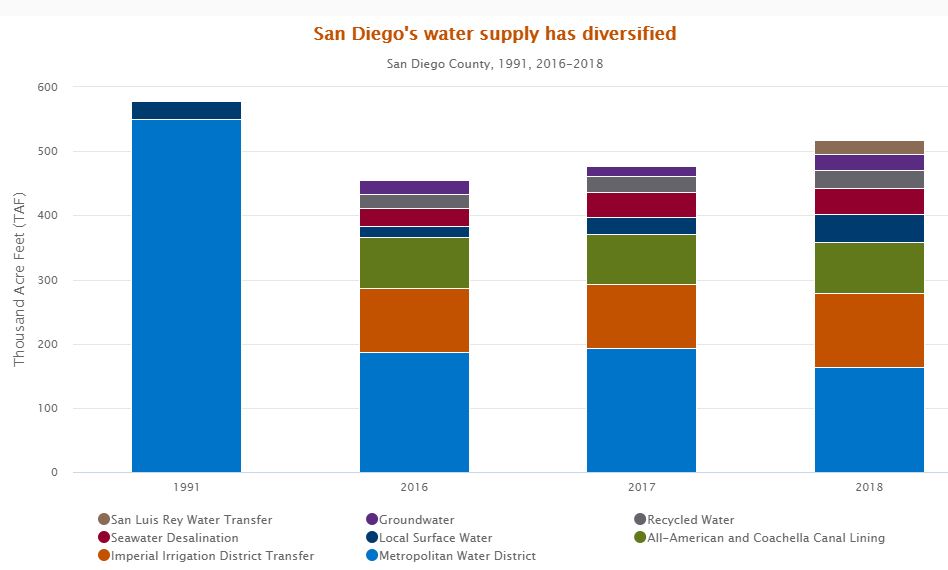
San Diego County’s water supply has diversified significantly over the last couple of decades. Source: San Diego County Water Authority
The nonpartisan Equinox Project report is a source of public policy research and analysis to guide policymakers, planners and other officials, said Emily Young, executive director of The Nonprofit Institute at the University of San Diego, where the project is based.
Carlsbad City Councilmember @CoriSchumacher says the nonpartisan 2018 Equinox Quality of Life Dashboard Indicators released today is a valuable tool for policymakers and other leaders in #SanDiegoCounty See it at #WaterNewsNetwork https://t.co/AYbo6Ds2hw #cawater #QofL pic.twitter.com/A5H9juUeat
— San Diego County Water Authority (@sdcwa) June 13, 2019
Water use increased in 2018
“There’s no one indicator when you’re talking our quality of life in the San Diego region,” Young said. “And in fact, the whole point is all of these things are connected. If you’re talking about air quality, you really can’t talk about that if you’re not also talking about our transportation systems and the pollution generated from them.
“Whether we’re looking at an issue like water, which is very precious to the San Diego region, or other issues around transportation or housing, all of these are things that we’re measuring our progress on,” said Young.
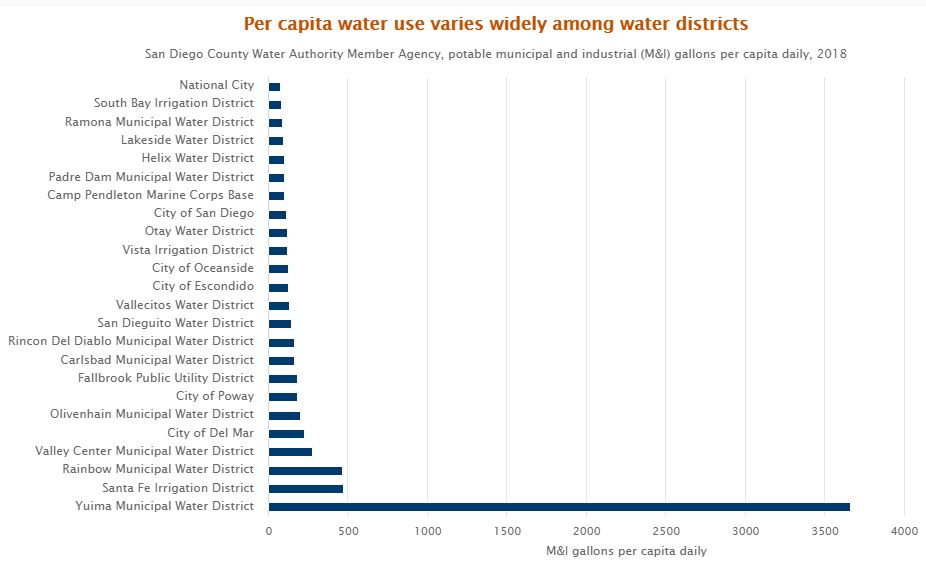
*This data includes agricultural water use served by local water agencies.
In 2018, National City had the lowest municipal and industrial (M&I) water use at 78 gallons per capita daily. Yuima’s high per capita M&I potable water use occurs because a large amount of water used for horticultural irrigation is classified as M&I, and the district services a small population (less than 2,000 people). Data Source: San Diego County Water Authority
Measuring quality of life
Six of the 15 indicators received a “thumbs-up” in the report, including air quality, electricity use and renewable energy. Four indicators, including water use, received a “thumbs-down.”
“Daily residential water consumption in San Diego County increased by 8.3% from 84 gallons per capita in 2017 to 91 gallons in 2018,” according to the report. “Water use has increased since the statewide water restrictions were lifted in 2017, though below pre-drought levels.”
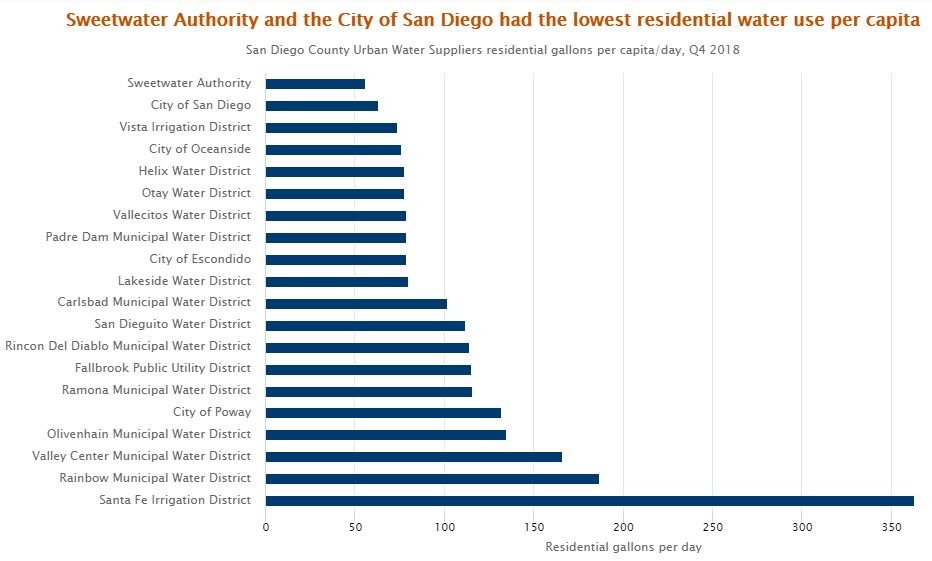
*Sweetwater Authority is comprised of the South Bay Irrigation District and National City. The dataset excludes the City of Del Mar, the City of Oceanside, Camp Pendleton Marine Corps Base and the Yuima Municipal Water District.
In Q4 of 2018, residents in the Sweetwater Authority area (National City and South Bay) had the lowest residential water use in San Diego County. Santa Fe Irrigation District used 363 gallons per capita/day, the most water per capita in San Diego County. Data Source: State Water Resources Control Board, Urban Water Supplier Report, 2019
Water use lower in 2019
Despite the slight increase in water use during 2018, residents continue to conserve compared to previous years.
“While extreme dry conditions contributed to increased residential water use in 2018, per capita water use was still lower than historical, pre-drought levels,” said Alexi Schnell, water resources specialist with the Water Authority. “Water use to date in 2019, a much wetter year, has been consistently lower than in 2018.
“There will always be fluctuations based on weather and other factors, but the San Diego region continues to embrace water-use efficiency, and per capita water use in the region is not forecasted to return to pre-drought levels for the foreseeable future,” Schnell added.
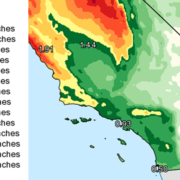
The report noted that “the San Diego region is making significant commitments to water efficiency and recycling” and has diversified local supply with the Claude “Bud” Lewis Desalination Plant in Carlsbad, the nation’s largest seawater desalination plant.