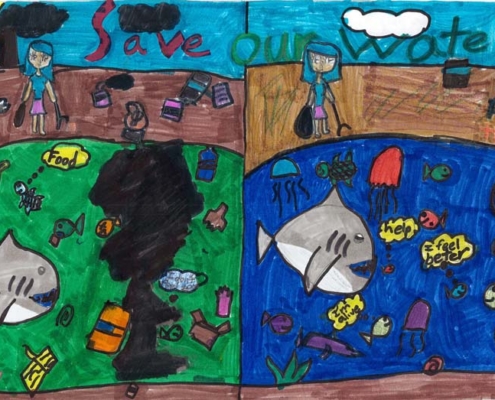
Residents, volunteers, and officials gathered June 1 at the Elfin Forest Recreational Reserve in Escondido to celebrate the 10th anniversary of its Interpretive Center honoring Susan J. Varty.
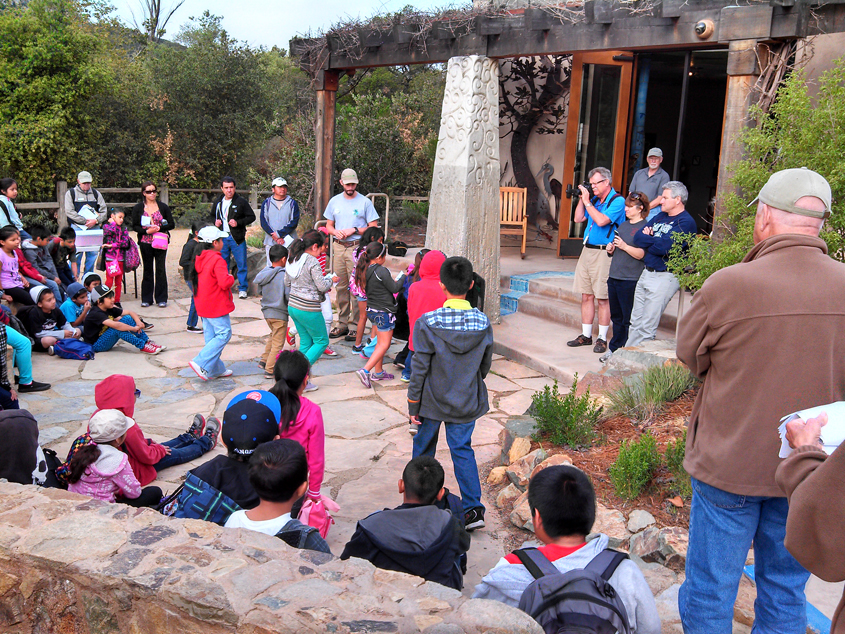

Visitors explore the Interpretive Center on its opening day June 1. Photo: Olivenhain Municipal Water District
Located at OMWD’s Elfin Forest Recreational Reserve, the center was constructed as a centerpiece of environmental education through a cooperative effort between OMWD and the Escondido Creek Conservancy.
“As we celebrate ten years of operation, we couldn’t be more proud of what we have accomplished by working together,” said OMWD Board Secretary Robert Kephart. “Yet, without the dedicated support of docents and donors, this one-of-a-kind facility with its many successful education programs would not have been possible. We also honor their efforts today.”
The Center’s namesake, Susan J. Varty, served as an OMWD board director from 1994 until her death in 2009. She exhibited a passion and tenacity for water issues and environmental preservation.
Reserve provides regional resource for outdoor education, and environmental appreciation
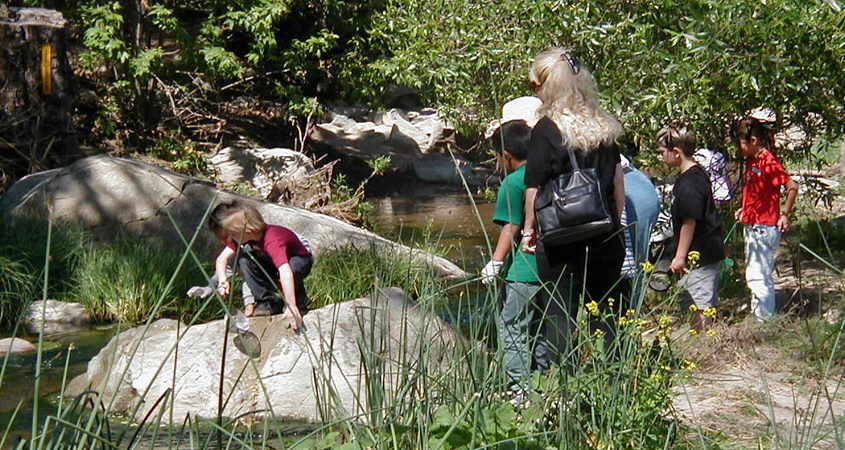

The Elfin Forest Recreational Reserve provides a wealth of opportunities for recreation, outdoor education, and environmental appreciation for all ages. Photo: Olivenhain Municipal Water District
The Elfin Forest Recreational Reserve provides a wealth of opportunities for recreation, outdoor education, and environmental appreciation.
Olivenhain partnered with the San Diego County Water Authority and the Bureau of Land Management to develop the 784-acre Elfin Forest Recreational Reserve as part of the regional Emergency Storage Project. The reserve opened in 1992. Currently, the reserve offers approximately 11 miles of hiking, mountain biking, and equestrian trails, as well as picnic areas and scenic mountain viewing points.
The Escondido Creek Conservancy has formed alliances with landowners, government agencies, and education and community groups to increase awareness of the invaluable resources intrinsic to the Escondido Creek watershed.
Originally, Olivenhain planned to construct a cinder block building with the assistance of a $68,500 grant from California’s Department of Parks and Recreation. The Conservancy sought at the same time to establish a location close to Escondido Creek for hosting educational programs. The timing allowed the organizations to form a mutually beneficial partnership.
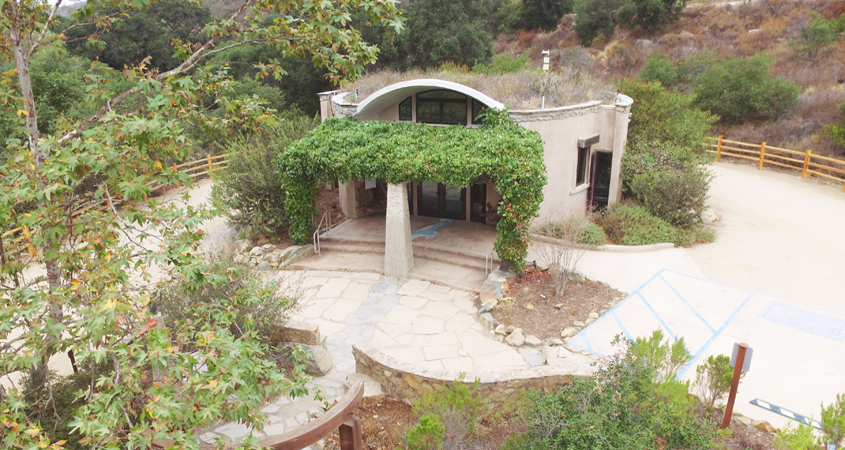

The new Elfin Forest Recreational Reserve’s Interpretive Center features green design elements such as recycled building materials, solar panels powered by photovoltaic cells, and a green roof. Photo: Olivenhain Municipal Water District
The Conservancy raised over $565,000 from individual donors to complete the enhanced design and center construction. Another $200,000 was raised for educational programs, including wildlife displays and nature activities.
Renowned local artist James T. Hubbell designed the center and several original works by Hubbell and his collaborations with other artists are on display. The building also features green design elements such as recycled building materials, solar panels powered by photovoltaic cells, and a green roof.
New grant funding provides educational field trips
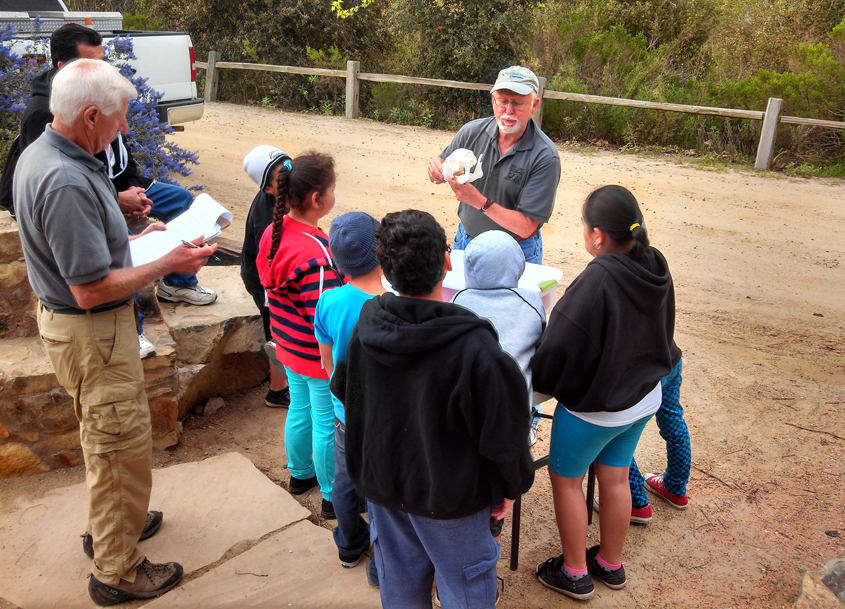

The new Escondido Creek Eichen Education Fund will continue the joint education programs held at the Elfin Forest’s interpretive center in perpetuity. Photo: Olivenhain Municipal Water District
More than 3,650 students visited the reserve on field trips during the 2018-2019 school year. The Conservancy provides the opportunity for students in disadvantaged communities to attend field trips through grant funding. Additional education partners are the Nature Collective and San Diego Zoo.
At the event, the Conservancy announced the creation of the Escondido Creek Eichen Education Fund. The new fund will continue the joint education programs held at the center in perpetuity.
“The Escondido Creek Conservancy’s education department helps bring thousands of underserved, urban-based students from Escondido out to the Elfin Forest every year so they can experience the outdoors, many for the first time in their lives,“ said Conservancy board member Jeff Swenerton. “This is vitally important because we can’t expect the next generation to value nature if they’ve never been exposed to it.
“We’re reaching more children now than in any other time in our organization’s history,” added Swenerton. “It’s very exciting to see the impact we’re making, but we’ve reached a point where we need to launch the Escondido Creek Eichen Education Fund campaign to sustain our success and enable us to continue connecting children with nature.”
The center is open seven days a week, from 8 a.m. to 3 p.m., depending on the availability of the reserve’s 65 docents. View the current docent schedule on the center’s website.

 Compost can be beneficial in many ways, including functioning as mulch to prevent erosion and help soil filter pollution. Photo: Ben Kerckx/Pixabay
Compost can be beneficial in many ways, including functioning as mulch to prevent erosion and help soil filter pollution. Photo: Ben Kerckx/Pixabay