Few landfalling atmospheric rivers in the current water year have reached California, now in the third year of a statewide drought.
The latest update from the Center for Western Weather and Water Extremes, Scripps Institution of Oceanography at UC San Diego, shows that Water Year 2022 started strong in October, but weaker storms did not ease dry conditions.
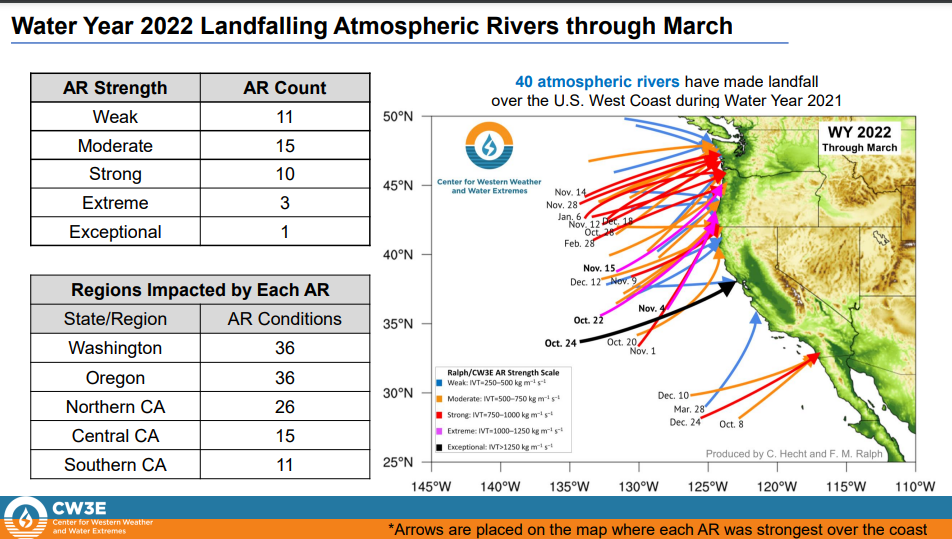
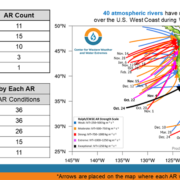
Landfalling atmospheric rivers
The CW3E report, Distribution of Landfalling Atmospheric Rivers over the U.S. West Coast During Water Year 2022: Summary Through March, was published April 7.
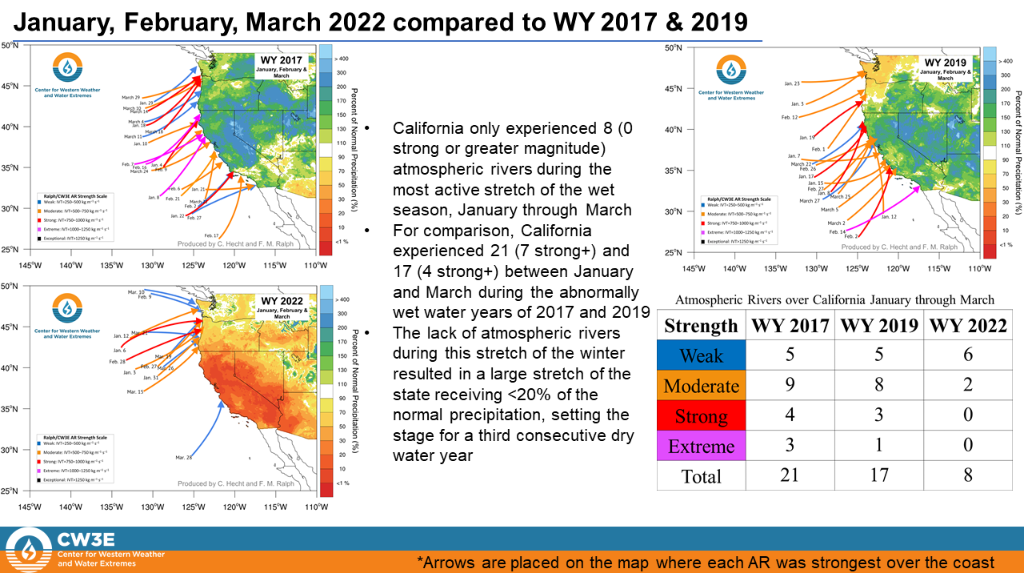
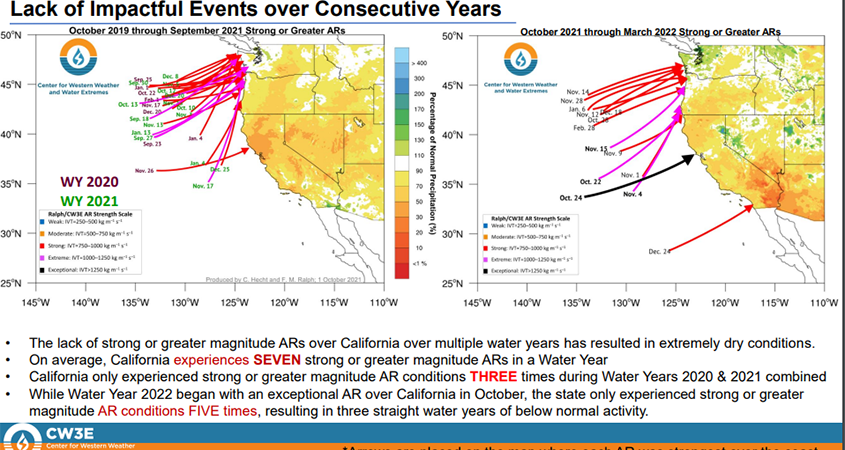
“While Water Year 2022 began with an exceptional AR over California in October, the state only experienced strong or greater magnitude AR conditions FIVE times, resulting in three straight water years of below normal activity,” according the report.
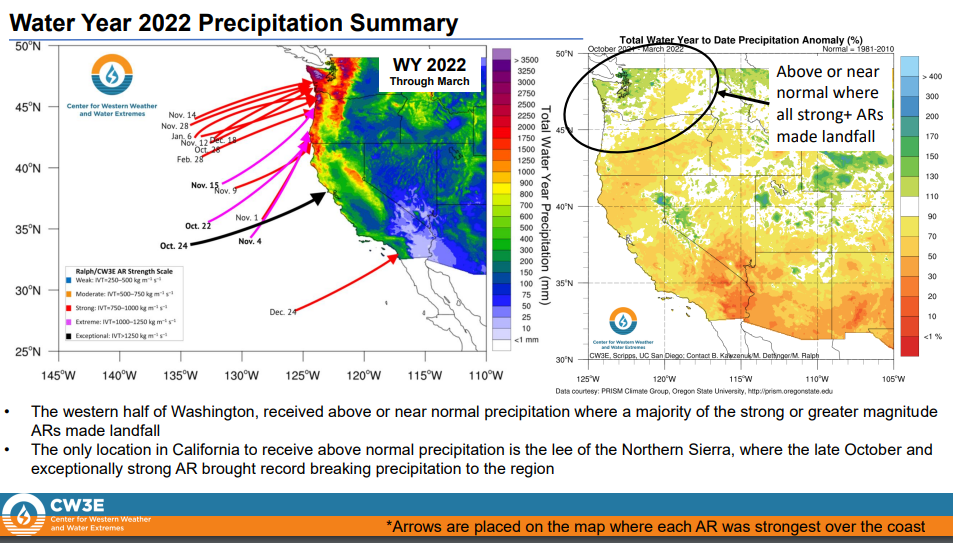
The report shows that the “lack of impactful events over consecutive years” – water year 2021 and water year 2020, combined with the current water year, has resulted in three straight years of below normal activity. Bottom line: If California hoped strong atmospheric rivers would end the current drought this water year, that’s not happening, at least so far. And the two previous years were a bust, creating extremely dry conditions across the state.
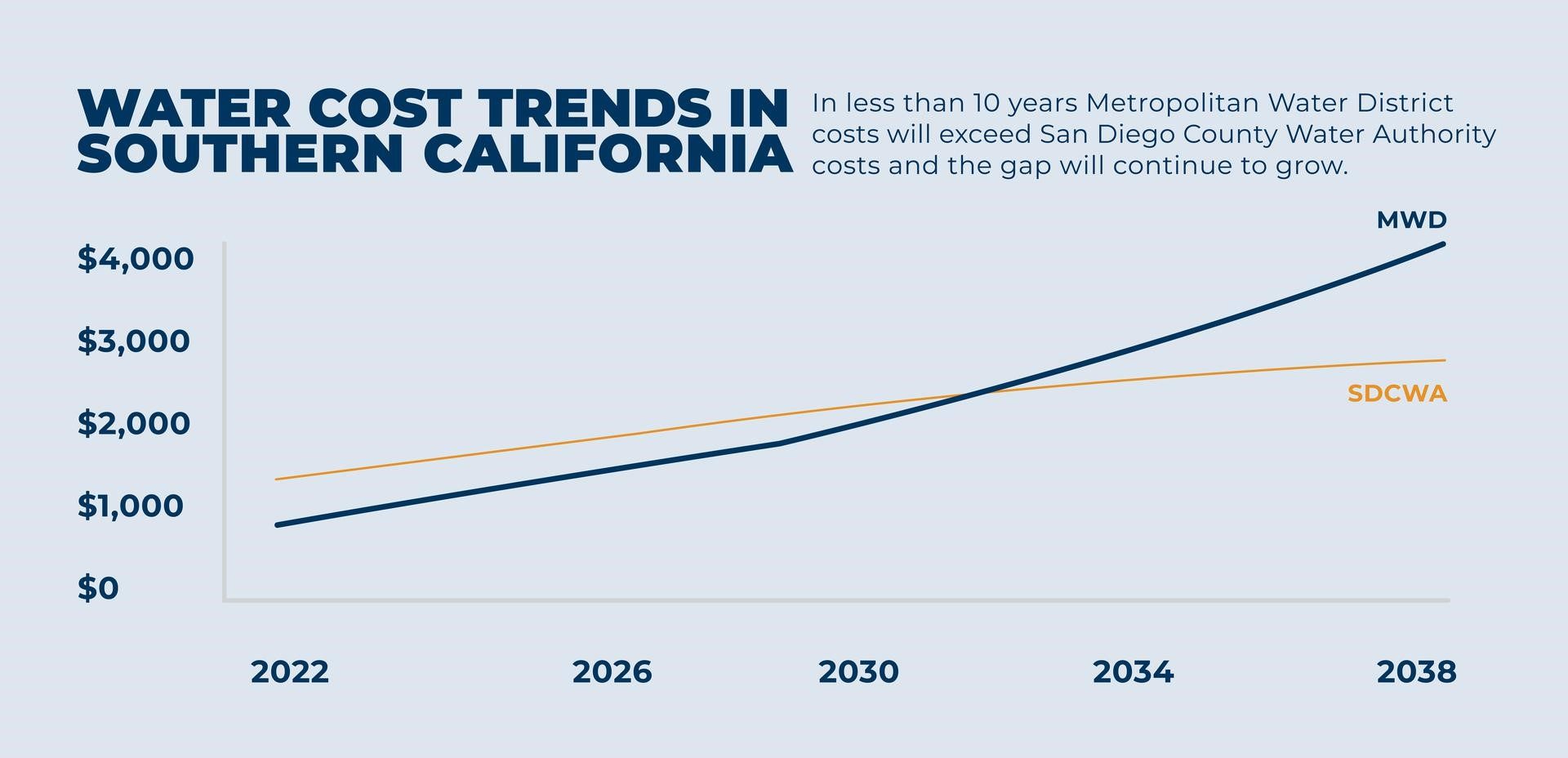
CW3E and Water Authority partnership
The San Diego County Water Authority partnered with the Scripps Institution of Oceanography, Center for Western Weather and Water Extremes, at UC San Diego in 2020 to better predict atmospheric rivers and improve water management before, during, and after those seasonal storms. The Center and its partners share best practices in forecast-informed reservoir operations, increased research around atmospheric rivers and droughts, and develop strategies for mitigating flood risk and increasing water supply reliability.
“Through our partnership with CW3E and the AR forecasting tools they’ve developed, it better prepares us in management of our water resources using regional storage,” said Jeff Stephenson, Water Resources Manager with the San Diego County Water Authority, in 2021. “This storage, in conjunction with developing multiple water supply sources in the San Diego region, has prepared us for years when rainfall levels are below normal in the region.”
For additional details and graphics go to: https://bit.ly/38rSTNE.
(Editor’s Note: Atmospheric river analysis by Chad Hecht, Julie Kalansky, & F. Martin Ralph. This analysis is considered experimental.)