Making smart decisions about your landscape design and your plant choices relies in large part on your climate zone. San Diego County’s six different climate zones vary in their average conditions. By choosing wisely, you can minimize the need for artificial irrigation and still create a beautiful, sustainable landscape.
The California Irrigation Management Information System (CIMIS) divides San Diego County into these six climate zones: Coastal, Coastal Inland, Upland Central, Transition, Mountain, and Desert.
This climate system provides you factors to help you understand which plants will thrive in your landscaping under its native conditions. Gardening in harmony with your local climate zone and your microclimate helps you use resources, including water, most efficiently.
Descriptions of San Diego’s six climate zones
Which CIMIS climate zone are you in?
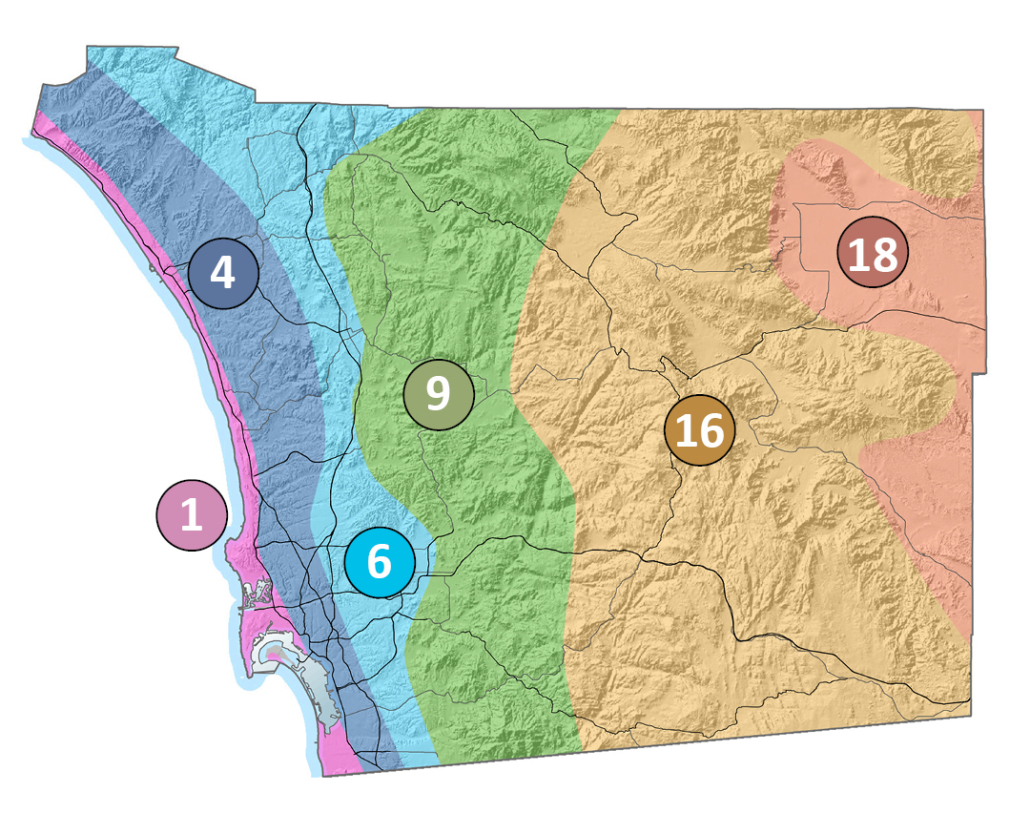
San Diego County’s geography falls within six of the 24 CIMIS climate zones. Photo: CIMIS
Zone 1: Coastal Prairie
The Coastal Prairie zone hugs our county’s coastline. It is the zone most strongly influenced by the ocean, with a mild marine climate resulting from the warm Pacific Ocean. Winters are mild, summers are cool, and there is almost always moisture in the air.
Zone 4: South Coast Inland
South Coastal Inland areas are just inland from the beach, or on high bluffs above the coastline. You can feel the ocean breeze, but you can’t taste the salt in the air. There is less fog and humidity than the immediate coastal area, and higher temperatures.
Zone 6: Upland Central
The higher elevation Upland Central areas are influenced both by moist coastal air and dry interior air. Humidity, morning fog, and wind are moderate, with low annual rainfall.
Zone 9: Transition
This marine-to-desert transition climate is farther inland. It features a combination of warmer thermal belts and cold-air basins and hilltops, with an occasional marine influence. The climate can vary from heavy fog to dry Santa Ana winds.
Zone 16: Mountain
Steep slopes, variation in sun and wind exposure, shallow soils and heavier rainfall affect plants in the Mountain regions. Average annual rainfall is 30 inches, and wet years can bring 45 inches or more.
Zone 18: Desert
Dry and hot daytime conditions combine with cold nighttime temperatures in the Desert zone. Humidity is very low, and water is scarce. Average annual rainfall can be as low as 2.5 inches, with an average of just 6 inches.
Learn more about the specifics of your climate and microclimate on the California Irrigation Management Information System website.
This article is part of a year-long series inspired by the 71-page Sustainable Landscapes Program guidebook. The Water Authority and its partners also offer other great resources for landscaping upgrades, including free WaterSmart classes at WaterSmartSD.org.




