San Vicente Energy Storage Facility Powers Ahead with $18M Boost
A large-scale renewable energy project proposed jointly by the City of San Diego and the San Diego County Water Authority received $18 million in the state budget signed this week by Gov. Gavin Newsom, enough to advance the San Vicente Energy Storage Facility through initial design, environmental reviews, and the federal licensing process.
The San Vicente energy project is one of the most promising pumped energy storage solutions in California and it would be a major asset to help avoid rolling blackouts through on-demand energy production while helping to meet state climate goals. It also could mitigate costs for water ratepayers across the San Diego region by generating additional revenue to help offset the cost of water purchases, storage, and treatment. The City and the Water Authority are developing the project together, just like they did to raise the height of the city-owned San Vicente Dam 117 feet in the 2010s.
Energy for 135,000 households
Upon completion, the San Vicente energy project would provide up to 500 megawatts of long-duration stored energy, which will assist in meeting peak electrical demand periods throughout Southern California and help meet the goals of Senate Bill 100, which requires 60% renewable energy by 2030 and 100% zero-carbon energy resources statewide by 2045. The project will provide enough energy for about 135,000 households when operating.
Construction jobs
“I want to thank Governor Newsom, Senate President pro Tempore Toni G. Atkins, Assembly Speaker Anthony Rendon and all the members of the Legislature for funding a vital San Diego project that will help us provide reliable, clean energy,” said San Diego Mayor Todd Gloria. “This innovative partnership with the San Diego County Water Authority will help our City meet its climate goals while building sustainable infrastructure and supporting good-paying local jobs.”
Water Authority Board Chair Gary Croucher also highlighted the work of state leaders and staff at both agencies who have been collaborating on project plans for years.
“The San Vicente Energy Storage Facility will reduce the chances for rolling blackouts by storing renewable energy for use when it’s needed most,” Croucher said. “We owe a debt of gratitude to Gov. Gavin Newsom and Senate President pro Tempore Toni G. Atkins for ensuring funding for this critical infrastructure project, which will create more than 1,000 construction-related jobs in addition to its other benefits.”
Environmental reviews, licensing
With state funding in place, the Water Authority and the City are preparing to launch federal and state environmental reviews, seek a project license from the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission, and issue a Request for Proposals for a full-service private partner to help develop the project. Those complex components are expected to take at least four years, with construction completion forecast for 2030.
“California has a proud history of adopting forward-thinking solutions to our biggest challenges, and the San Vicente Energy Storage Project is no exception,” said Sen. Atkins of San Diego. “This may well be a pivotal moment in our statewide efforts to meet peak power needs and maximize our use of renewable energy.”
Pumped energy storage
California sources nearly one-third of its power from renewables, mainly solar and wind. The target for renewable energy in California is 60% by 2030. Such a major shift to renewables will require new kinds of investments, markets, and business practices. Electric grids need to be more flexible; new kinds of power supplies will help deliver energy flexibility when needed; and new pricing systems are needed to send clear signals to developers and financial markets that these projects need to move forward.
Pumped energy storage projects are a major piece of the solution. They are designed to store excess renewable energy from solar and wind during the day, and then discharge that energy when energy use increases in the evening and renewable energy is not available.
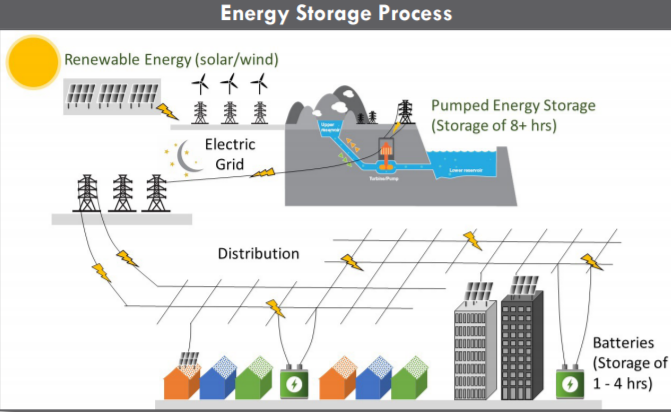
The San Diego County Water Authority and the City of San Diego are partners in developing the San Vicente Energy Storage Facility. The pumped storage energy project at San Vicente Reservoir could store 4,000 megawatt-hours per day of energy, or 500 megawatts of capacity for eight hours.
The San Vicente project would create a small upper reservoir above the existing San Vicente Reservoir in Lakeside, along with a tunnel system and an underground powerhouse to connect the two reservoirs. The powerhouse would contain four reversible pump turbines.
During off-peak periods – when power is inexpensive and renewable supplies from wind and solar facilities exceed demand – turbines would pump water to the upper reservoir where it would act as a battery of stored potential energy. During high energy use, the system would discharge water from the upper reservoir downhill through the turbines, producing energy. The exchange between the two reservoirs would not consume water.
San Vicente Reservoir is near major electricity transmission interconnection facilities, which would allow the project to play a central role in integrating solar and wind energy from across the Southwest for use in San Diego County. The San Vicente project is largely immune to the challenges faced by some conventional hydropower facilities because it is a closed-loop system that mainly holds imported water and is not reliant on runoff that can fluctuate significantly from year to year and hamper power production.
For more details about the San Vicente Energy Storage Facility go to: www.sdcwa.org/projects/san-vicente-pumping-facilities/




