San Diego Region is Drought-Safe This Summer
The San Diego County Water Authority announced June 21 that the region is protected from drought impacts this summer, and through 2045, despite continued hot and dry conditions.
Statewide drought conditions are highlighting the value of regionally and locally controlled water supplies in San Diego County. No shortages or regional water-use mandates are in the forecast, the result of three decades of strategic investments that create an aquatic safety net for San Diego County’s $253 billion economy and quality of life for 3.3 million residents.
WaterSmart San Diego
At the same time, Water Authority Board Chair Gary Croucher asked residents to continue embracing water-use efficiency practices that have become part of the regional ethic. Simple but important steps include turning off the faucet while brushing teeth, fixing irrigation system leaks, and using hoses with automatic shut-off nozzles.
“Thank you San Diegans for everything you have done to make sure that we have enough water to meet the region’s needs now and for decades into the future,” said Croucher. “You have invested through your water bills and your water-smart practices, and those efforts are paying off in tangible ways. The key this summer is to stay water-smart.”
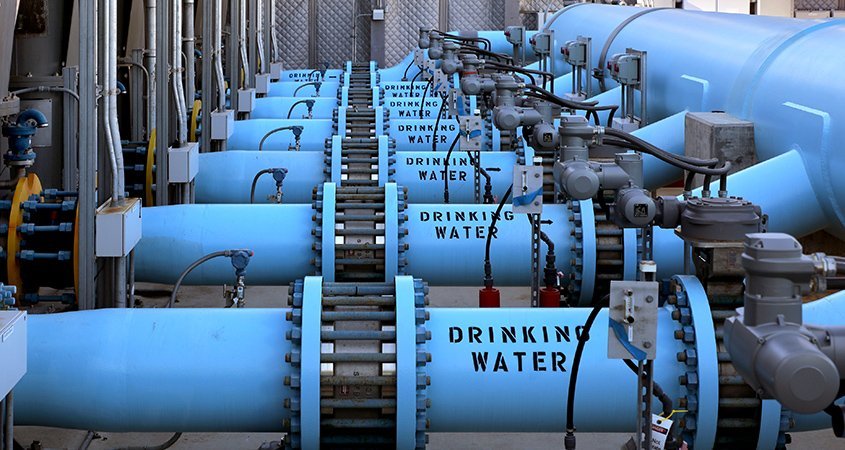

The San Diego region’s diversified water supply portfolio includes highly reliable, locally controlled and drought-proof supplies from the Claude “Bud” Lewis Carlsbad Desalination Plant. Photo: San Diego County Water Authority
Diversified water supply portfolio
Key government, agriculture, business, and science leaders joined Croucher in thanking residents for their efforts, encouraging continued water-use efficiency, and marking the region’s progress over the past 30 years.
In the early 1990s, the county’s economy was crippled by drought, suffering 13 straight months of 31% supply cutbacks from the Water Authority’s wholesale water provider, the Los Angeles-based Metropolitan Water District of Southern California, which controlled almost all of San Diego County’s water.
Today, the picture is much different: The region’s diversified water supply portfolio includes highly reliable, locally controlled and drought-proof supplies from the Claude “Bud” Lewis Carlsbad Desalination Plant and the nation’s largest conservation-and-transfer agreement, which provides high-priority, low-cost water from the Colorado River. The combination offers significant protection against droughts and other emergencies so that the Water Authority’s newly adopted 2020 Urban Water Management Plan shows San Diego County will continue to have sufficient water supplies through the 2045 planning horizon, even during multiple dry years.
Drought-Safe “for the long haul”
“There’s no way around it: Our region’s economy runs on water – brewing, tourism, biotech, defense, farming and so many other key pieces of our economic engine require safe, reliable water supplies to function,” said Jerry Sanders, president and CEO of the San Diego Regional Chamber of Commerce. “We look to the Water Authority and its 24 member agencies to provide the fundamental water resources that keep us strong – not just for today, but for the long-haul.”
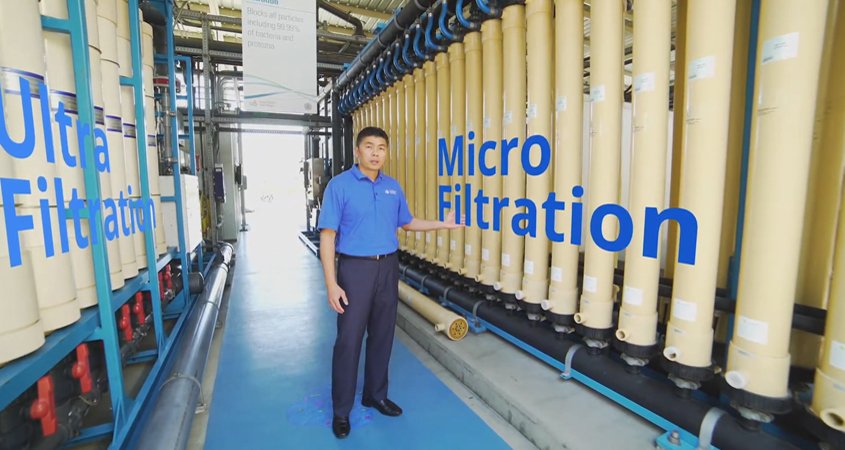

By 2035, Pure Water San Diego will provide nearly half of the City of San Diego’s water supply using proven water purification technology to clean recycled water and produce safe, high-quality drinking water. Photo: City of San Diego
Pure Water San Diego
The region’s multi-faceted water portfolio strategy includes local projects such as Pure Water San Diego, the next major increment of water supply for the county. The City of San Diego expects its project to start producing 30 million gallons per day of drinking water in the next few years. By 2035, Pure Water will provide nearly half of the City of San Diego’s water supply using proven water purification technology to clean recycled water and produce safe, high-quality drinking water.
“By helping reduce the impacts of statewide drought on our communities and ensuring supply reliability, Pure Water is an investment that will create a more sustainable future for all of us,” said San Diego Mayor Todd Gloria. “Our changing climate is challenging us to develop new, creative solutions. Thanks to our long history of regional collaboration and innovation, we can say with confidence that San Diego is up to the test.”
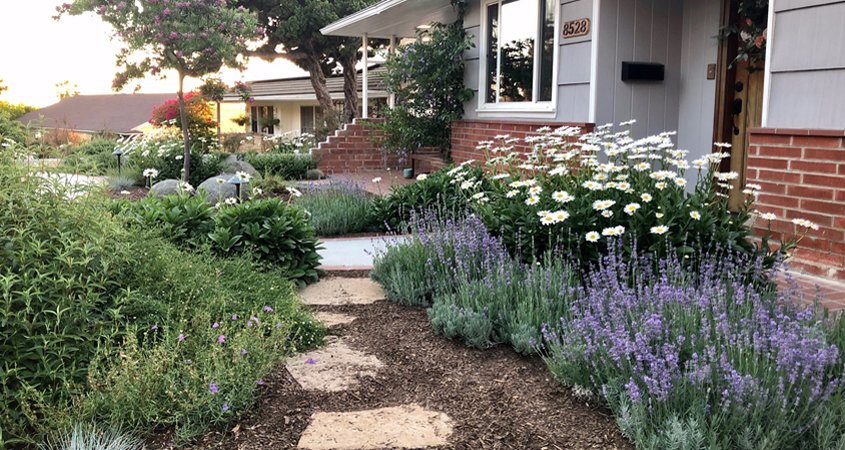

San Diego County ratepayers have conserved more than 1 million acre-feet of water over the past three decades, and per capita water use across the region has decreased nearly 50% since the devastating drought of the early 1990s. Residents have saved water by converting landscapes to drought-tolerant and native plants. Photo: Helix Water District
Regional water use cut by 50% since 1990s
San Diego County ratepayers have conserved more than 1 million acre-feet of water over the past three decades, and per capita water use across the region has decreased nearly 50% since the devastating drought of the early 1990s.
Widespread adoption of water-efficiency measures were not the only result of that drought. In fact, the biotech industry advocacy group Biocom California was founded in San Diego to help ensure that the Water Authority would never again risk the region’s economy by over-dependence on a single source of water. Today, Biocom California works on behalf of more than 1,400 members to drive public policy, build a network of industry leaders, create access to capital, introduce cutting-edge workforce development and STEM education programs, and create robust value-driven purchasing programs.
“Biocom California was founded on the issue of access to water – our members depend on reliable, constant access for sensitive research and manufacturing processes,” said Joe Panetta, president and CEO of Biocom California. “Water supply reliability and diversification in our region has given the life science industry a firm foundation and the confidence to grow and thrive.”
Agriculture industry makes “the most of every drop”
The San Diego region’s multibillion-dollar farming industry also has flourished thanks to a reliable water supply. Today, the county is among the most productive in the nation with more than 5,000 family farms, the most of any county in the United States. Innovative practices – including water-use efficiency measures – allow local farms to be productive by focusing on high-value crops such as ornamental trees and shrubs, bedding plants, succulents, and indoor plants.
“San Diego County farmers have done their part by investing heavily in water efficiency so that they can produce an amazing cornucopia of products,” said Hannah Gbeh, executive director of the San Diego County Farm Bureau. “Our members are stewards not just of the land, but of the water as well. They make the most of every drop through high-efficiency irrigation systems and other strategies.”
Climate Change and water supply
The changing climate means that San Diego County will need to continue to evolve to meet the water needs of the future through continued efficiency efforts, strategic investments, and scientific advances. That’s why the Water Authority and the City of San Diego are partnering with the Scripps Institution of Oceanography at UC San Diego to better predict atmospheric rivers and improve water management before, during and after those seasonal storms. Scripps’ Center for Western Weather and Water Extremes (CW3E) last year launched the Water Affiliates Group, which brings together cutting-edge science and hands-on water industry experience to enhance reservoir operations in light of the changing climate.
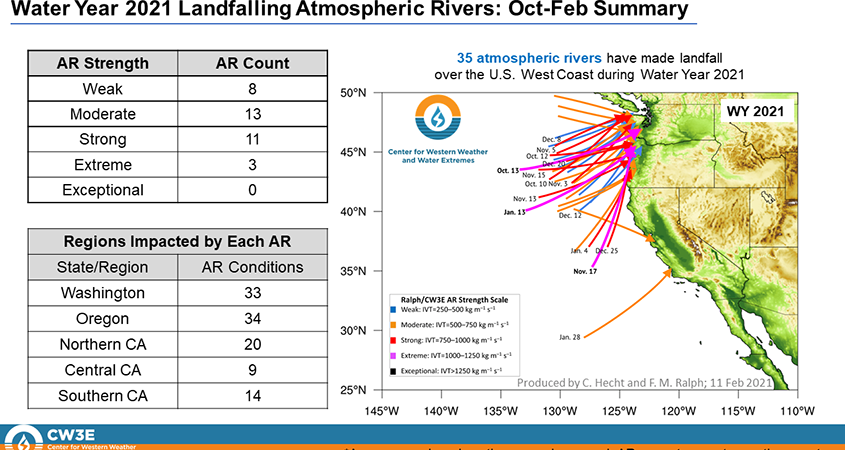
Scripps Center for Western Weather and Water Extremes reports that more atmospheric rivers have made landfall on the U.S. West Coast in the first four months of Water Year 2021 compared to Water Year 2020. Graphic: Scripps Center for Western Weather and Water Extremes.
“It is vital that the Water Authority, the City of San Diego and our other affiliates are helping to improve modeling in ways that will continue to produce practical, real-world benefits for water managers statewide,” said Margaret Leinen, vice chancellor for marine sciences at UC San Diego and director of Scripps Institution of Oceanography. “With continued research we can utilize the latest science to develop strategies for mitigating flood risk and increasing water resilience through improved reservoir management. This will aim to decrease the impact of dry years by improving forecasts that lead to capturing more water produced by atmospheric rivers. Applying science to action will help protect San Diego County and the rest of California from droughts, as California’s climate becomes increasingly volatile in the future.”
For more information about water supplies in the San Diego region, go to www.sdcwa.org/investments-protect-san-diego-region-from-drought/.
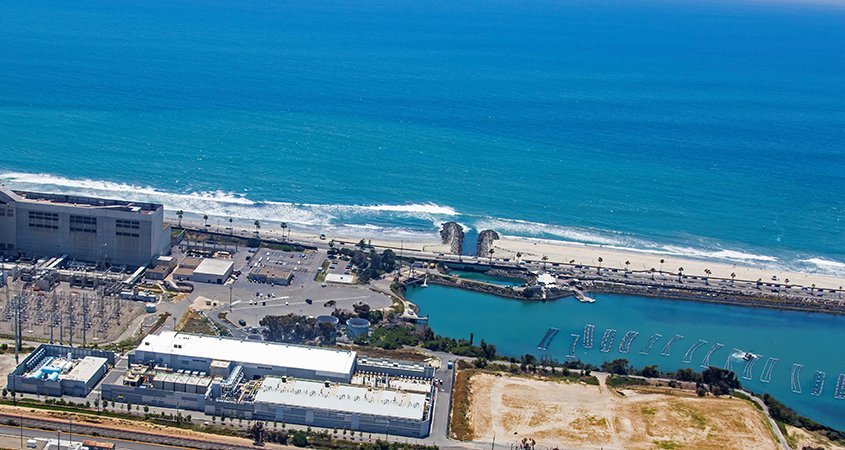

The Water Authority added desalinated seawater to its supply portfolio in 2015 with the start of commercial operations at the nation’s largest seawater desalination plant – the result of a public-private partnership in northern San Diego County. Photo: San Diego County Water Authority




