Much like your body, public infrastructure needs constant care and attention. Check-ups, tests, and consistent monitoring help you stay on top of your health. It’s similar with the regional water infrastructure, with 1,400 structures, 308 miles of large pipelines, a dam, a water treatment plant, as well as pump stations and hydroelectric facilities. All pieces working together as one integrated system, much like your body, yet all of it aging, day by day.
Monitoring and assessing the condition of the regional water infrastructure is the responsibility of the “doctor” of asset management, Martin Coghill, Operations and Maintenance Manager at the Water Authority, and his staff.
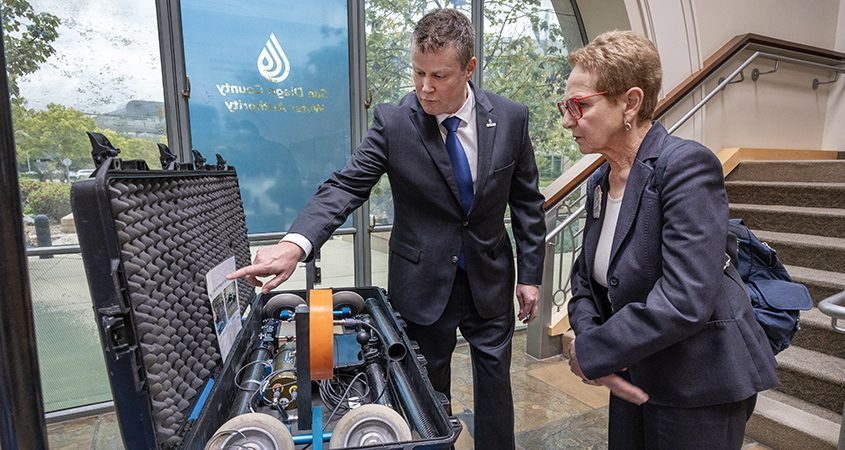
During the last week of May, members of the Water Authority’s Board of Directors were treated to a showcase of technologies, as well as incredible stories from Coghill and his staff about their use – and how they help the organization save time and money.
A history of innovation
The Water Authority has long been on the cutting edge of testing and utilizing the latest technology to help assess the condition of its system. This is important because Water Authority pipelines no longer traverse formerly agricultural and rural settings. San Diego County has urbanized quite a bit over the last half-century, and a ruptured pipeline in a now urban setting is likely to threaten property and the livelihoods of those living nearby.
In 2006, a large-diameter pipeline ruptured in the western portion of Mission Trails Regional Park. Thankfully, damage wasn’t worse, not only because of the remote location, but also thanks to the rapid response of Water Authority staff that closed valves to stop the flow of water.
Though the break was unfortunate, it provided critical data to the Water Authority, who had recently installed a new technology inside the pipe – an acoustic fiber optic cable. That AFO cable heard pings as the pipeline started to fail and recorded that data. As a result, that type of cable has been installed in other pipelines throughout San Diego County to help monitor their health.
Now, Coghill and his team know what it sounds like when a section of pipe is in distress. That technology works alongside other technologies to provide critical data about the condition of the pipe, which then helps Coghill and his staff develop a recommendation for repair before the pipe fails.
In the 1980’s, Water Authority staff thought up an ingenious solution to reline a certain kind of pipe called Prestressed Concrete Cylinder Pipe with new steel liners. That repair solution continues to be the preferred solution by the Water Authority and other water agencies around the world to repair those sorts of pipes. The bonus is that this method of repair saves the agency millions of dollars each year and is less intrusive than digging up and replacing those sections of pipelines.
An eye to the future
This innovative culture continues to breed new, cost-effective solutions.
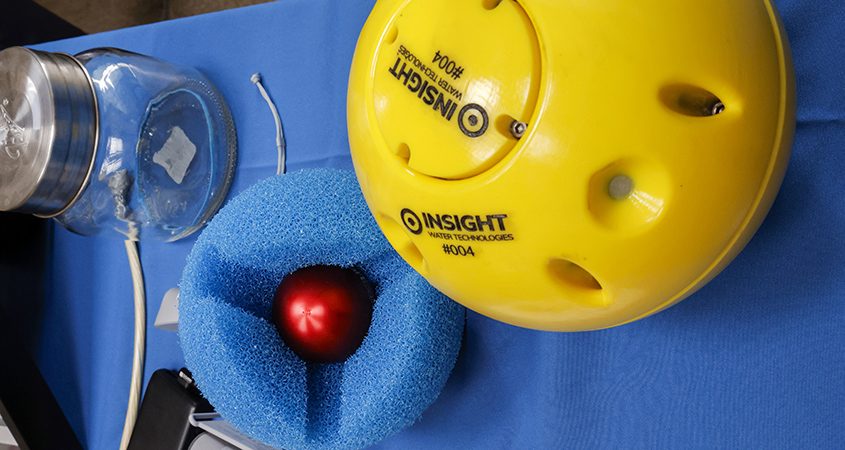
One historical challenge has been assessing the condition of the pipe while it’s in service. In the past, pipelines had to be dewatered before crews could enter them to deploy tools and assess their condition. One fairly new technology that allows the pipelines to stay in service – saving water and money – are acoustic leak detection devices. These tools are inserted into a live pipe and travel with the flow of water. They can detect sounds of active leaks.

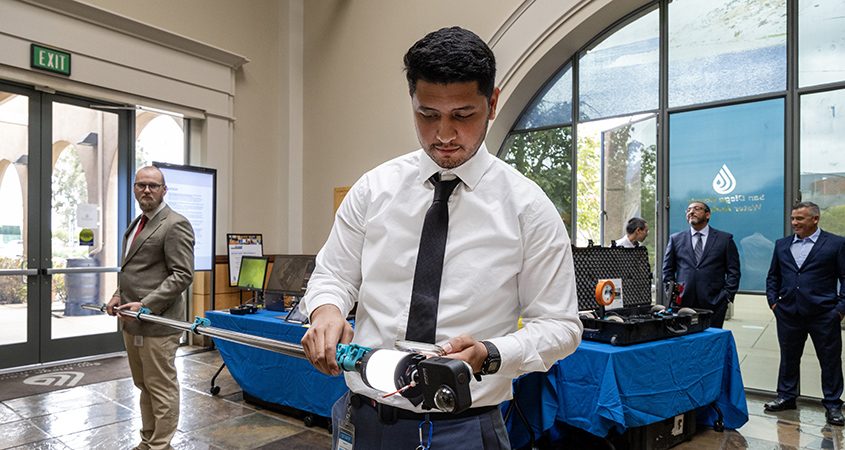
Another challenge has been “getting eyes” on the inside of the approximately 1,400 structures along the pipelines. In order to inspect them on a routine basis, staff have had to climb down into the structures and take photos. The confined space makes this task hazardous and difficult. Recently, one of Coghill’s staff developed a tool using a 360-degree action camera mounted on a telescopic pole. Staff was able to save the organization money by purchasing the components separately and assembling them. This innovative solution saved the Water Authority nearly $9,000, which does not include the staff time saved from having to climb in and out of each structure to take the same photos.

These new technologies and tools produce large amounts of very important data. It takes Coghill and his team many hours to comb through it, crunch the numbers, and analyze it to develop recommendations for repairs or replacement. His team is considering other data storage and reporting options, including use of artificial intelligence and/or other software that could streamline efforts to analyze the data.
While the technology showcase was just a one-day event, the use of the featured technologies, along with monitoring and condition assessment efforts, continue, 24 hours a day, 7 days a week. At the heart of it all lies a team and their tools embedded in a culture of innovation – an investment for the future that helps safeguard our region’s long-term sustainability.