NOAA’s U.S. Spring Outlook indicates the abnormally wet winter will further improve drought across much of the western U.S. as the snowpack melts in the coming months. Winter precipitation, combined with recent storms, wiped out exceptional and extreme drought in California for the first time since 2020, and is expected to further improve drought conditions this spring.
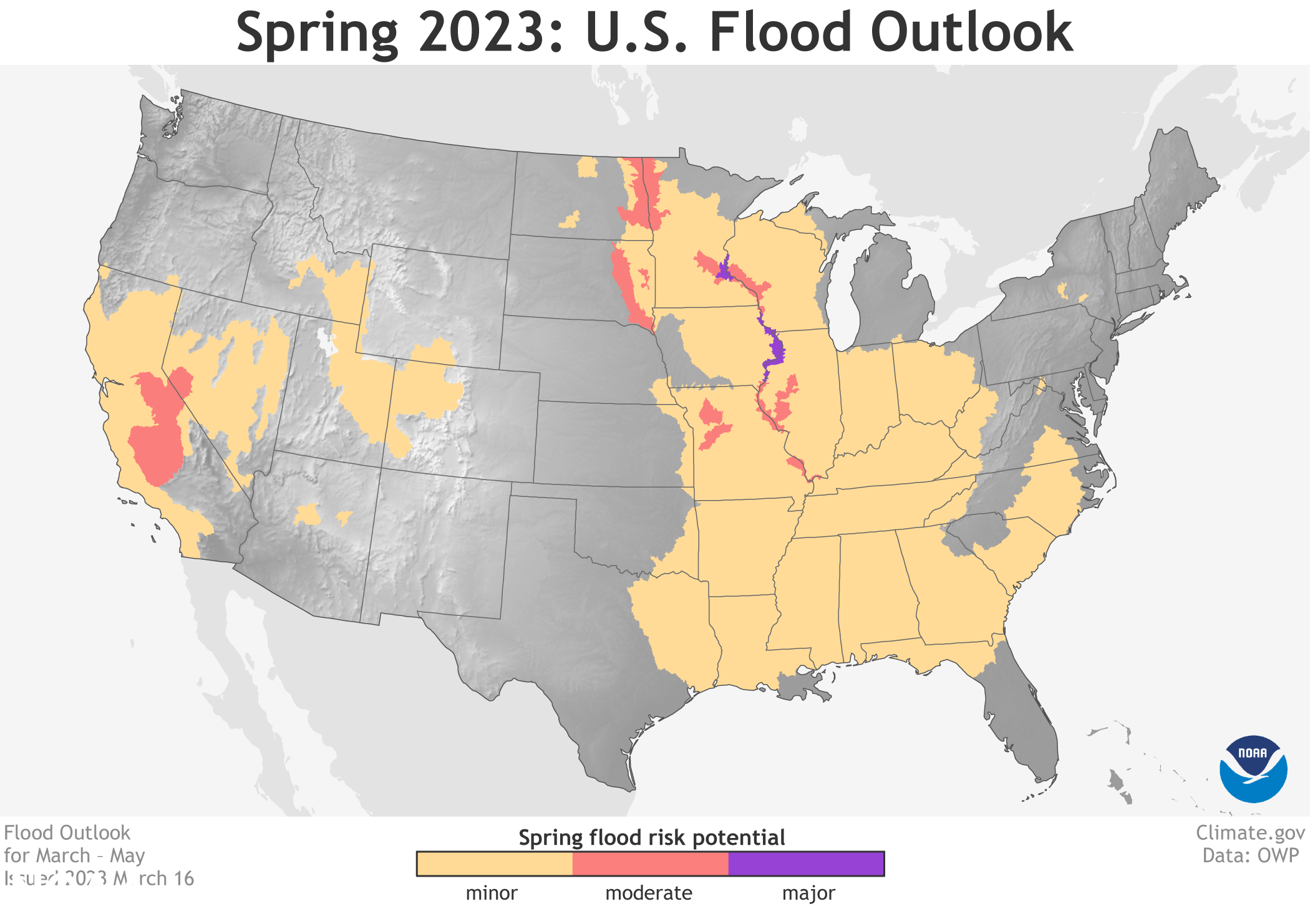
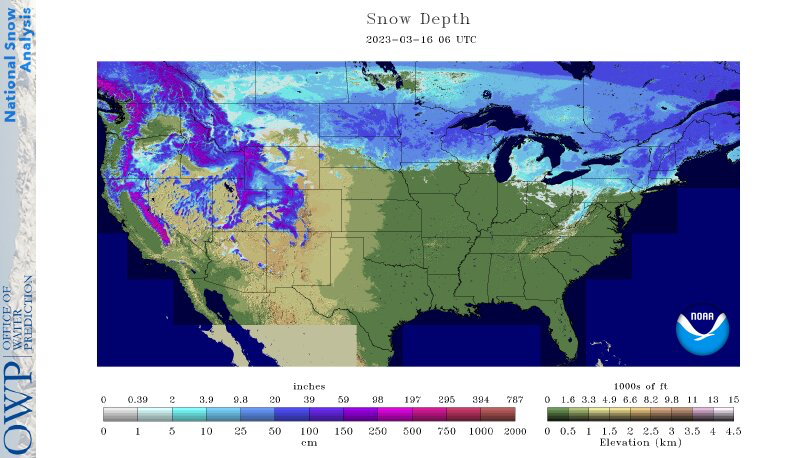
Significant flooding in the western U.S., especially in California, followed another series of strong Pacific storms that battered the region in March, and piled on to an already historic snowpack.
NOAA’s U.S. Spring Outlook highlights temperature, precipitation, drought and flood predictions for April through June to help the nation prepare for potential weather and climate threats to lives and livelihoods.
Climate change – wet and dry extremes
“Climate change is driving both wet and dry extremes, as illustrated by NOAA’s observations and data that inform this seasonal outlook,” said NOAA Administrator Rick Spinrad, Ph.D. “Under the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law and Inflation Reduction Act, and in support of the Biden Administration’s priority to tackle the climate crisis, NOAA will invest significant resources to build a Climate-Ready Nation that gives communities tailored information about changing conditions so that residents and economies are protected.”
Spring Outlook for drought, temperature and precipitation
On March 9, NOAA forecasters declared La Niña over. The El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) is a climate pattern, based on changes in rainfall and sea surface temperatures across the equatorial Pacific Ocean, that influences temperature and precipitation around the world. La Niña occurs when ocean temperatures are cooler than normal and rainfall is reduced in the eastern to central Pacific Ocean.
El Niño and La Niña
“La Niña has finally ended after being in place nearly continuously for more than two years,” said Jon Gottschalck, chief of the operational prediction branch at NOAA’s Climate Prediction Center, a division of the National Weather Service. “ENSO-neutral — the transition period between El Niño and La Niña — is likely to continue into the early summer with elevated chances of El Niño developing thereafter. ENSO-neutral is factored into NOAA’s Spring Outlook.”
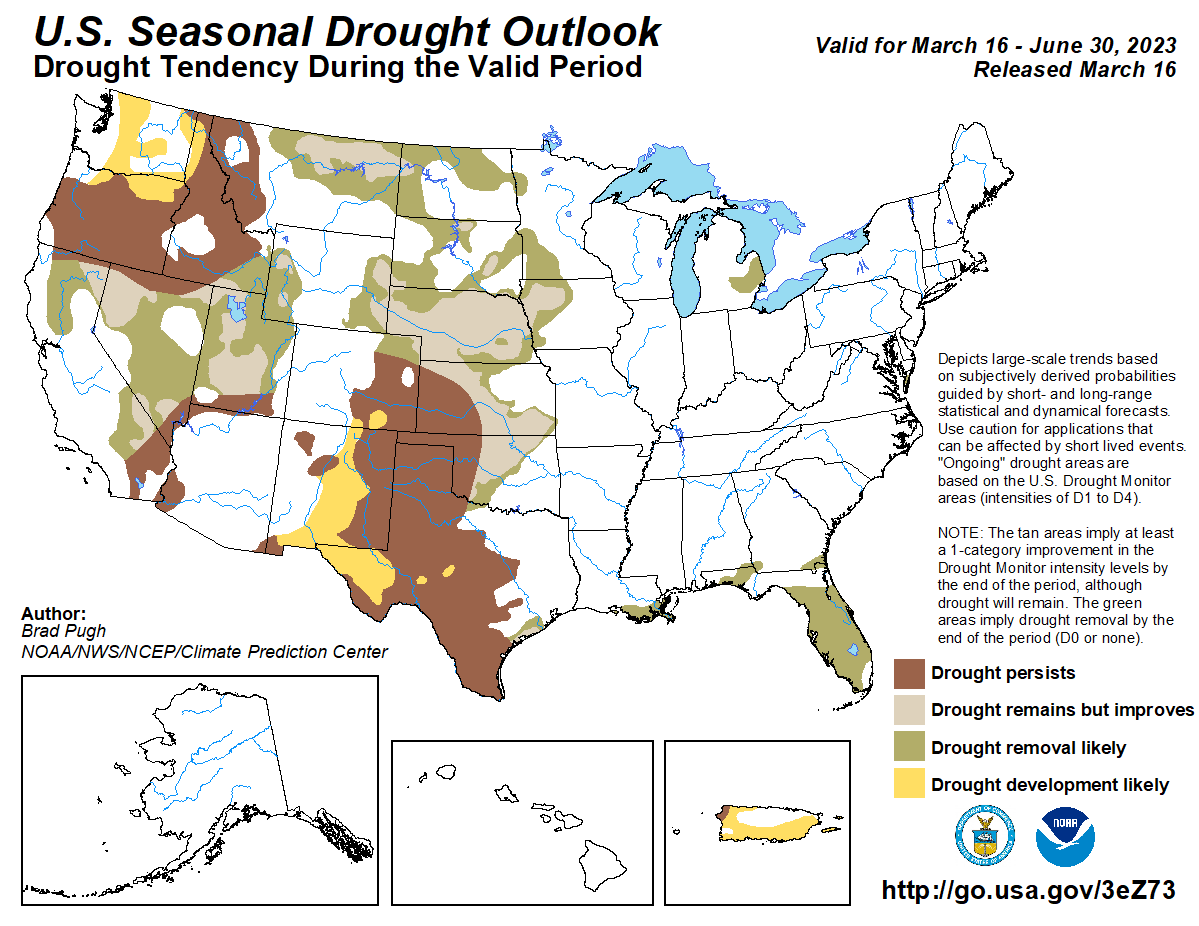
Moderate to exceptional drought coverage across the U.S. is at its lowest since August 2020 and is likely to continue improving, or end entirely, across much of California and the Great Basin. The spring wet season is expected to improve drought conditions across parts of the northern and central Plains. Current drought conditions in Florida are expected to improve or go away during the next three months.
Areas of extreme to exceptional drought across parts of the southern High Plains are likely to persist through the spring season, with drought also expected to develop into parts of New Mexico. Across parts of the Northwest U.S. and northern Rockies, drought conditions are also expected to continue. Drought may develop into parts of Washington state.
Above-average temperatures are favored for much of the southern and eastern half of the U.S. For April through June, the greatest chance for above-average temperatures exists from the southern High Plains eastward to Florida, and northward along the East Coast. Above-average temperatures are also likely for Hawaii and northern parts of Alaska. Below-average temperatures are predicted for the central Great Basin and the northern Plains.
California endures flooding, landslides, and evacuations
Parts of central and southern California that were still reeling from heavy snowfall earlier this month received yet another powerful atmospheric river which exited the region on March 15. Flooding, landslides, power outages, and evacuations are among the many impacts residents faced from the recent storm. The above graphic depicts most of the state receiving between 300-600% of normal precipitation over the last seven days. — USDA Water and Climate Update
Below-average precipitation like for the Southwest
NOAA forecasters predict above-average precipitation this spring across the Great Lakes, Ohio Valley, and into parts of the mid-Atlantic and Northeast. Below-average precipitation is most likely for the Southwest and parts of the Pacific Northwest.