June Marked by Record U.S. Heat Waves, Severe Weather
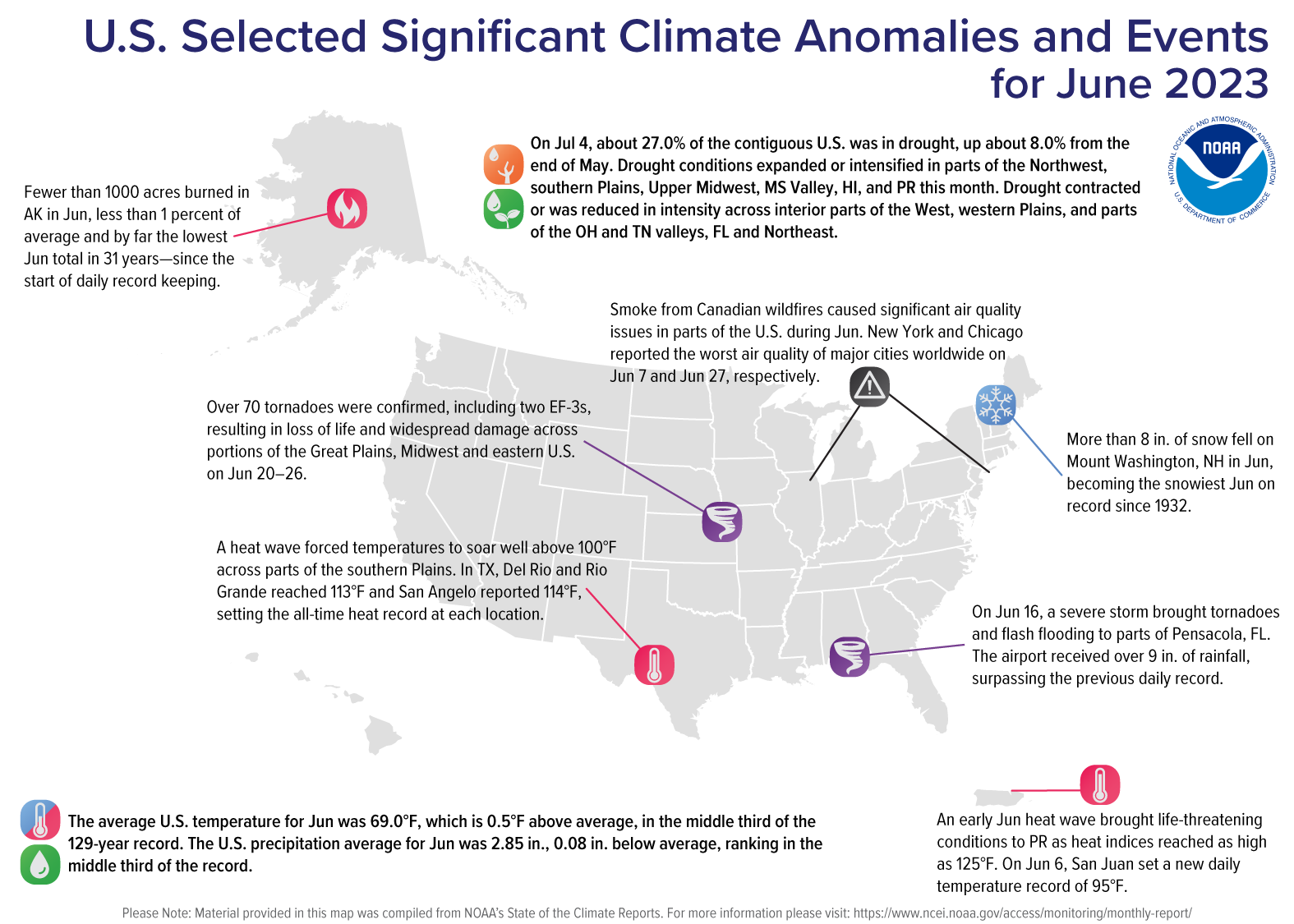
June 2023 was record hot for some parts of the U.S., while other locations were roiled by severe weather and poor air quality, according to NOAA’s National Centers for Environmental Information. Heat waves led to record high temperatures in Puerto Rico, the Northeast, Mid-Atlantic, Great Lakes, Texas, and Louisiana.
Thick smoke from Canadian wildfires created air quality issues for millions of people in portions of the Northeast and Great Lakes this June. On June 7, around 100 million people across 16 states were under air quality alerts while New York City reported the worst air quality of major cities worldwide. According to the July 4 U.S. Drought Monitor report, about 27.0% of the contiguous U.S. was in drought, up about 8.0% from the end of May. Most of the drought expansion took place in the Midwest, Texas, and the South.
Highlights from “Assessing the U.S. Climate in June 2023” from NOAA National Centers for Environmental Information
- Heat waves impacted the southern Plains, Northeast and Puerto Rico this month, breaking temperature records and creating life-threatening conditions.
- In June, the average temperature and precipitation for the contiguous U.S. ranked in the middle third of the historical record.
- A total of 12 billion-dollar weather and climate disasters have been confirmed this year. These disasters consisted of 10 severe storm events, one winter storm and one flooding event.
- Thick smoke from Canadian wildfires created air quality issues for millions in portions of the Northeast and Great Lakes this June.
- Portions of the Midwest experienced dry soils, low streamflows and distressed crops in June. Missouri, Illinois, Wisconsin and Michigan each ranked in the top-10 driest June on record.
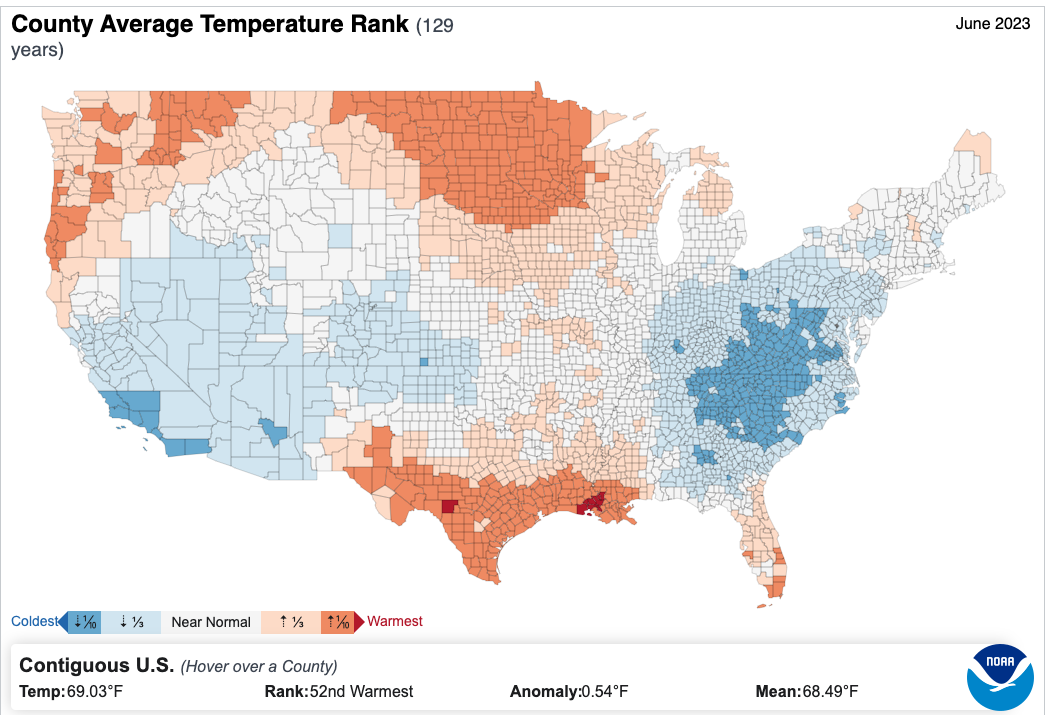
Temperature – ‘Record Hot’
The average temperature of the contiguous U.S. in June was 69.0°F, 0.5°F above average, ranking in the middle third of the 129-year record. Generally, June temperatures were below average from California to the central Plains and across much of the Mid-Atlantic and Southeast. 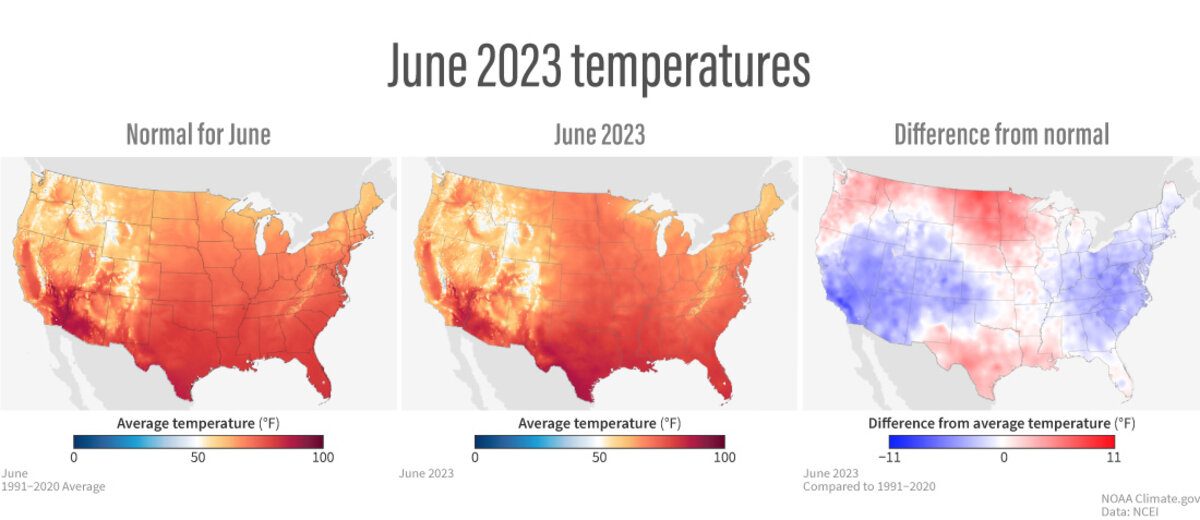
Temperatures were above average from the Northwest to the northern Plains, as well as in the southern Plains and Florida Peninsula. North Dakota ranked third warmest on record for June while two additional states ranked among their top-10 warmest on record. Conversely, West Virginia and Virginia had their ninth- and 10th-coldest June on record, respectively.
The Alaska statewide June temperature was 50.0°F, 0.8°F above the long-term average, ranking in the middle third of the 99-year period of record for the state. Above-normal temperatures were observed across the Aleutians and in parts of the North Slope and the Southeast during the month while small pockets of below-average temperatures were observed in interior portions of the state.
Precipitation
June precipitation for the contiguous U.S. was 2.85 inches, 0.08 inch below average, ranking in the middle third of the historical record. Precipitation was above average across much of the West and in parts of the Southeast and New England.
Precipitation was below average across much of the Midwest and in parts of the Northwest, Southwest, southern Plains, Mid-Atlantic and southern New England. Wisconsin and Michigan each had their fifth-driest June on record, while two additional states had their top-10 driest June on record. Conversely, Wyoming ranked third wettest with two additional states ranking among their top-10 wettest June on record.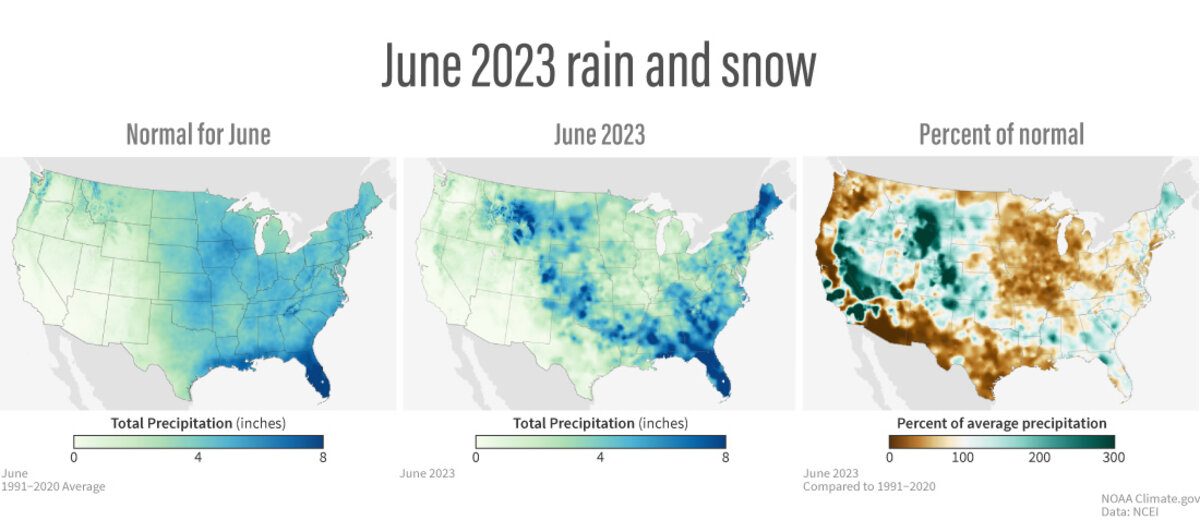
Across the state of Alaska, the average monthly precipitation was 2.85 inches, making last month the 19th-wettest June in the 99-year record. Conditions were wetter than average across most of the state while parts of the Northeast, Southwest and Panhandle were near normal and parts of the Southeast Interior and Aleutians observed below-normal precipitation during the month.
Billion-Dollar Disasters
Three new billion-dollar weather and climate disasters were confirmed this month, two of which occurred during the month of May. All of these disasters were severe storm events.
For 2023 to-date, 12 weather and climate disasters have losses exceeding $1 billion. These disasters consisted of 10 severe storm events, one winter storm and one flooding event. The total cost of these events exceeds $32.7 billion (CPI-adjusted), and they have resulted in 100 direct and indirect fatalities. For this year-to-date period, the first six months of 2023 rank second-highest for disaster count, behind 2017 with 14 disasters and behind 2021 which had $42.5 billion in terms of total cost.