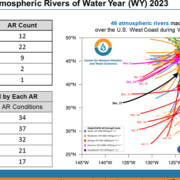
For insight into the numerous atmospheric rivers that brought impressive precipitation accumulations to California this Water Year and how it compares to previous years, the Scripps Institution of Oceanography Center for Western Weather and Water Extremes provides this end of water year 2023 summary.
Water Year 2023 and Atmospheric Rivers
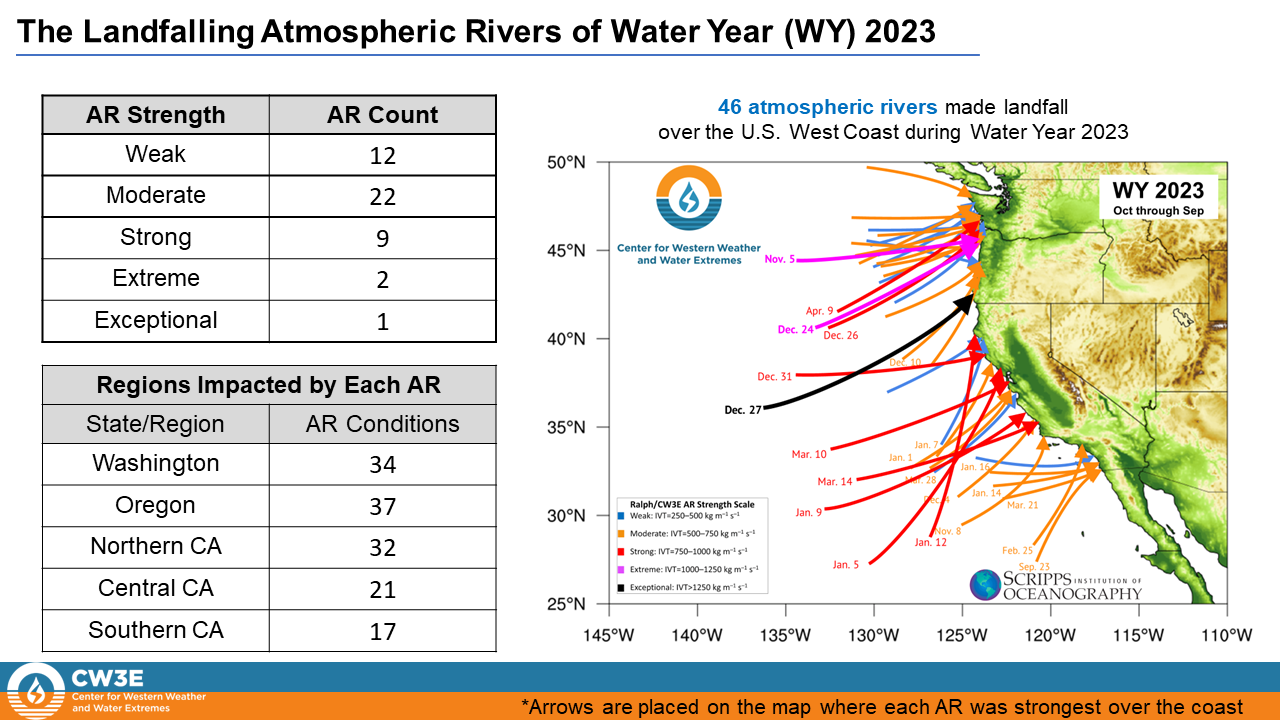
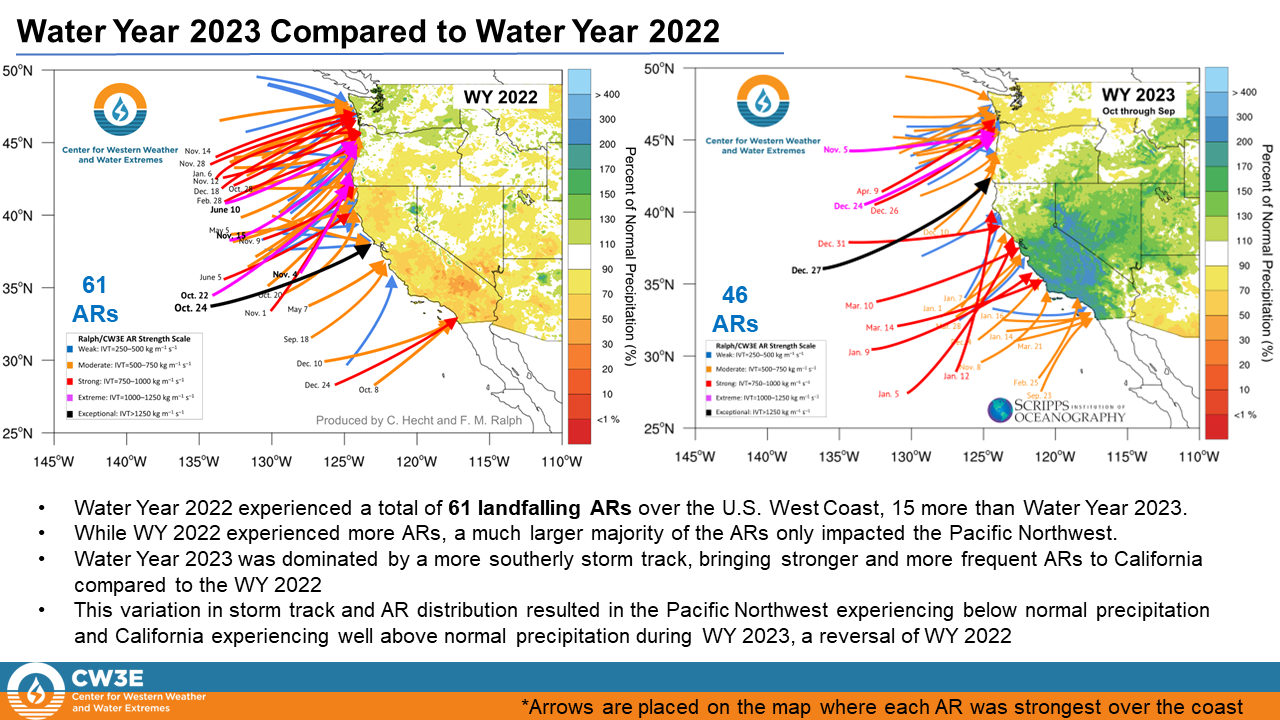
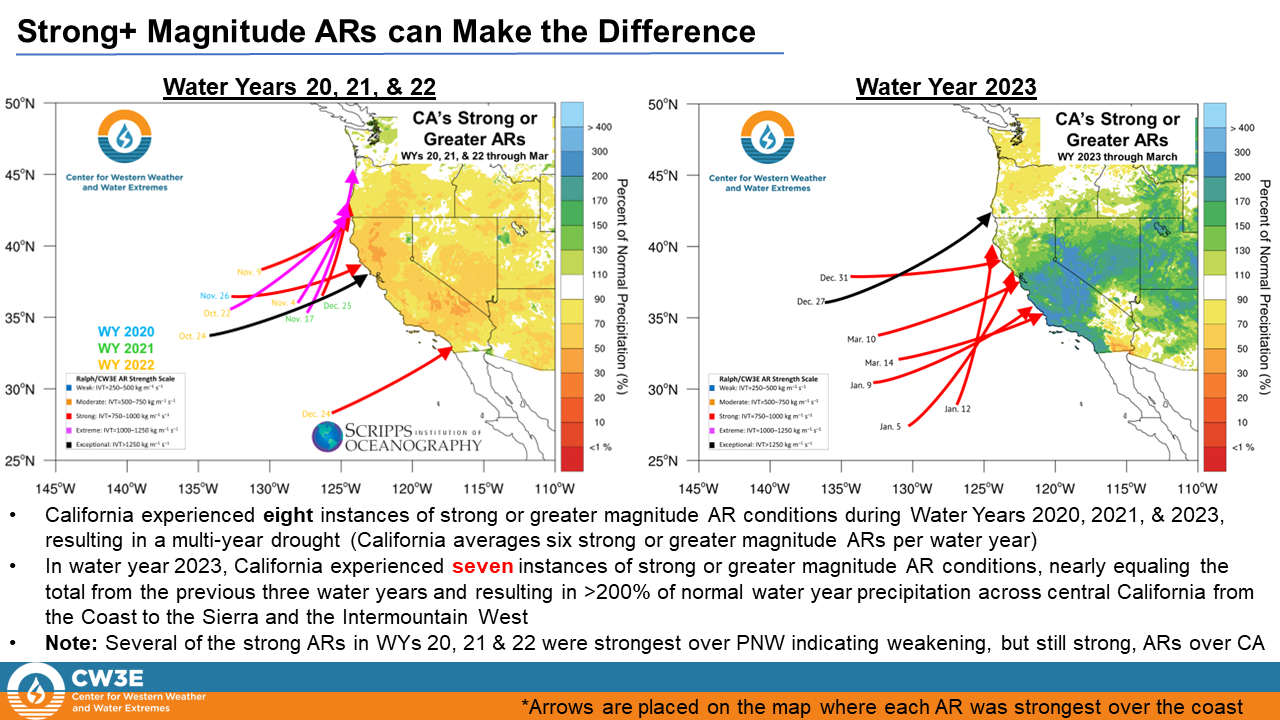
• Water Year 2022 experienced a total of 61 landfalling ARs over the U.S. West Coast, 15 more than Water Year 2023.
• While WY 2022 experienced more ARs, a much larger majority of the ARs only impacted the Pacific Northwest.
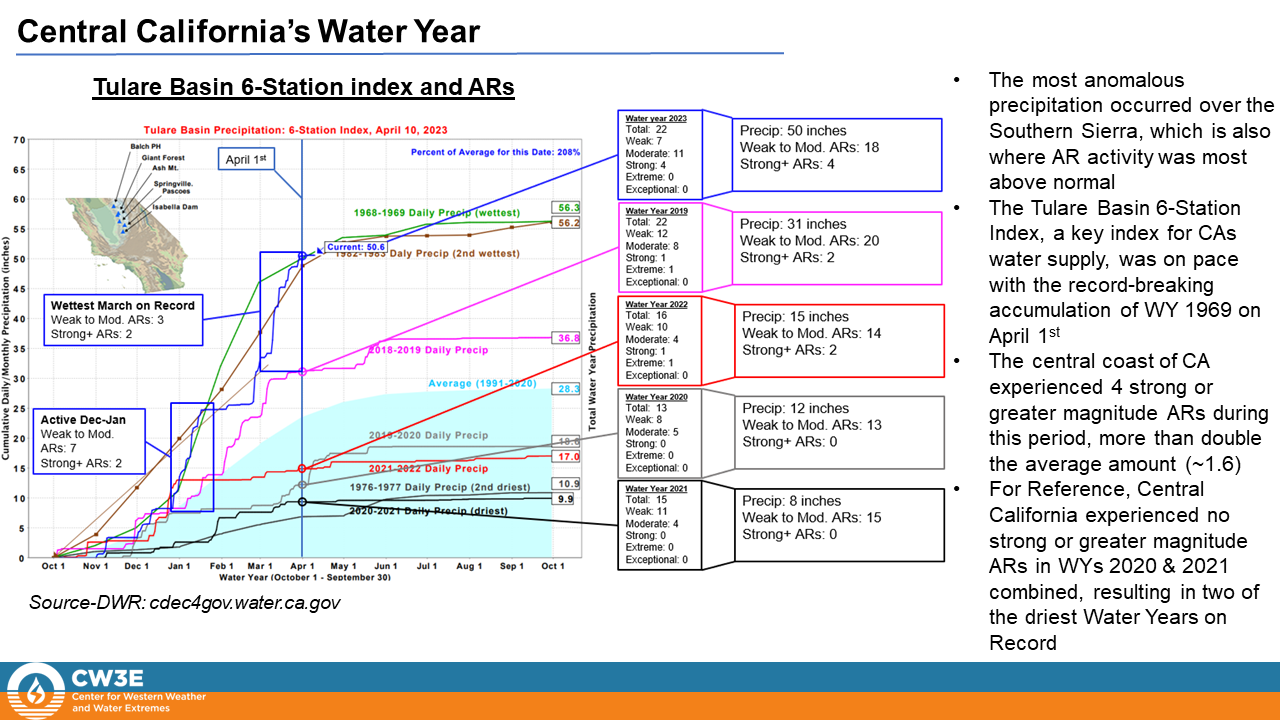
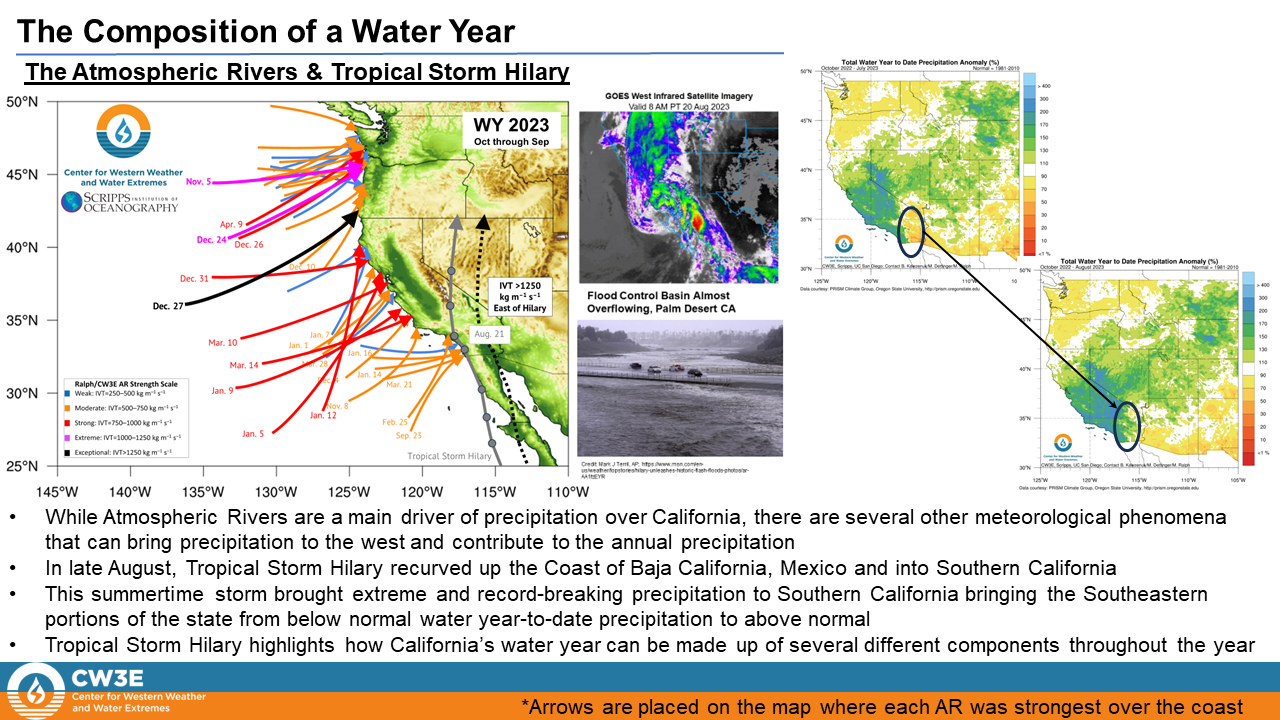
• Water Year 2023 was dominated by a more southerly storm track, bringing stronger and more frequent ARs to California compared to the WY 2022
• This variation in storm track and AR distribution resulted in the Pacific Northwest experiencing below normal precipitation and California experiencing well above normal precipitation during WY 2023, a reversal of WY 2022
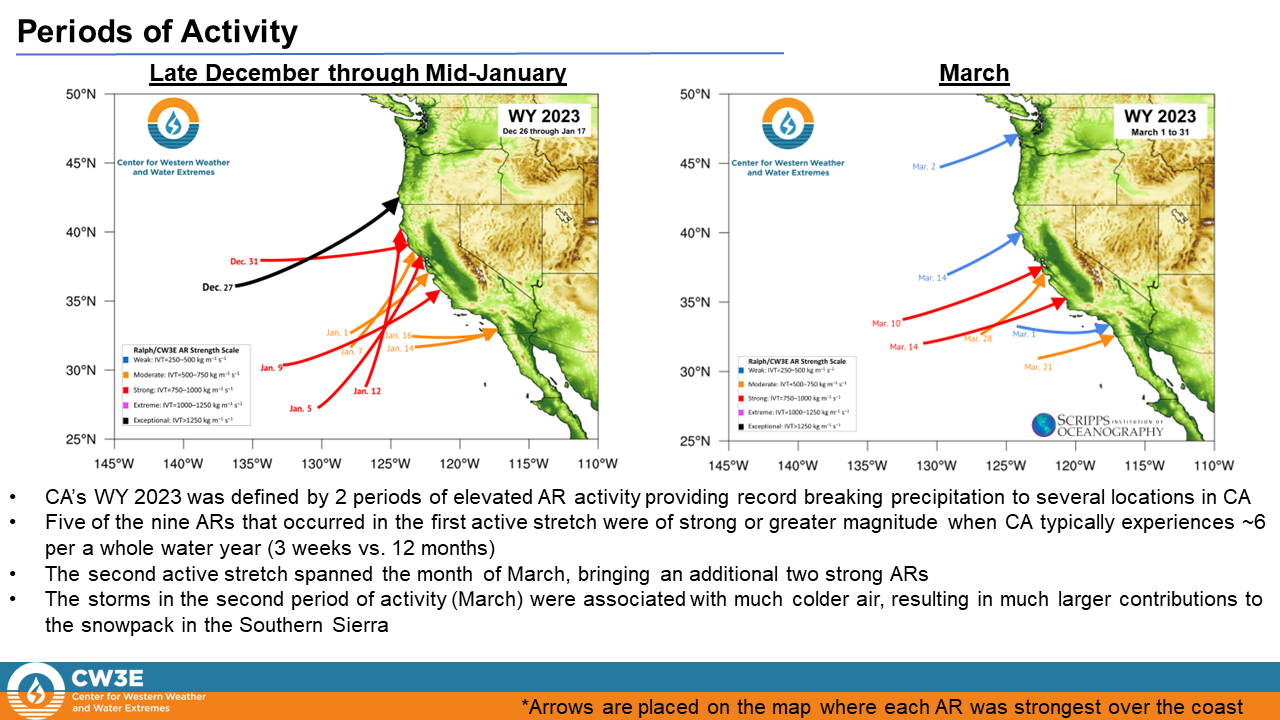
Analysis by Chad Hecht, Julie Kalansky, & F. Martin Ralph. This analysis is considered experimental.
Legislation signed into law by California Governor Gavin Newsom earlier this year ensures the state has the science and weather forecasting tools it needs for more flexible reservoir operations. The bill, AB 30, makes breakthrough water management technology standard for the California Department of Water Resources.
The legislation was introduced by San Diego Assemblymember Chris Ward and co-sponsored by the Sonoma County Water Agency and the San Diego County Water Authority. The bill was supported by the Water Authority’s partner, UC San Diego’s Scripps Institution of Oceanography.
Forecast-Informed Reservoir Operations strategy will help deal with drought and flood
The strategy is called forecast-informed reservoir operations, or FIRO, and it complements Gov. Newsom’s California Water Supply strategy released in August 2022 calling for more reservoir storage capacity to capture runoff from big storms, often fueled by atmospheric rivers. The governor and Legislature have already provided funding for state water managers to integrate the strategy.
(Editor’s Note: The San Diego County Water Authority has partnered with the Scripps Institution of Oceanography at UC San Diego to better predict atmospheric rivers and improve water management before, during, and after those seasonal storms.)