East County Advanced Water Project Fall Progress Report
Progress on the East County Advanced Water Purification Program (East County AWP) continues on schedule at multiple East County locations with significant milestones in recent months. Project construction is scheduled through 2025.
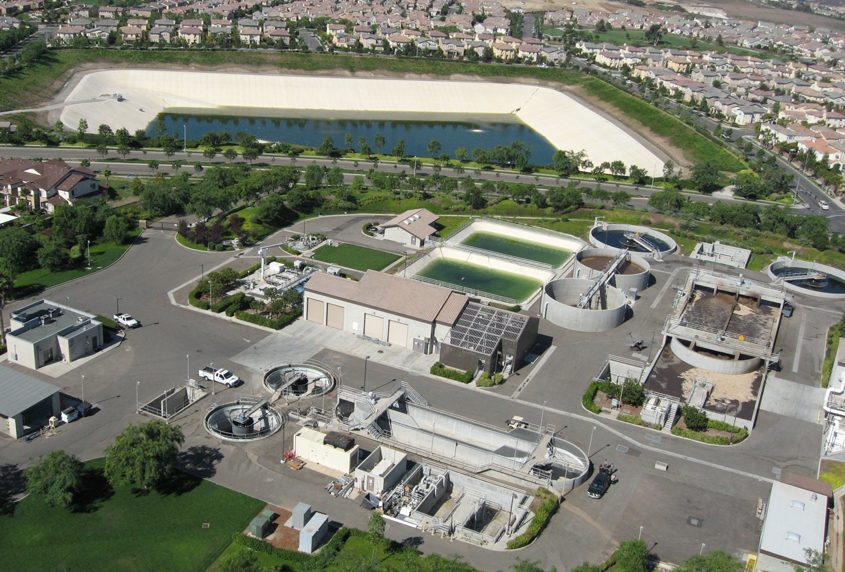
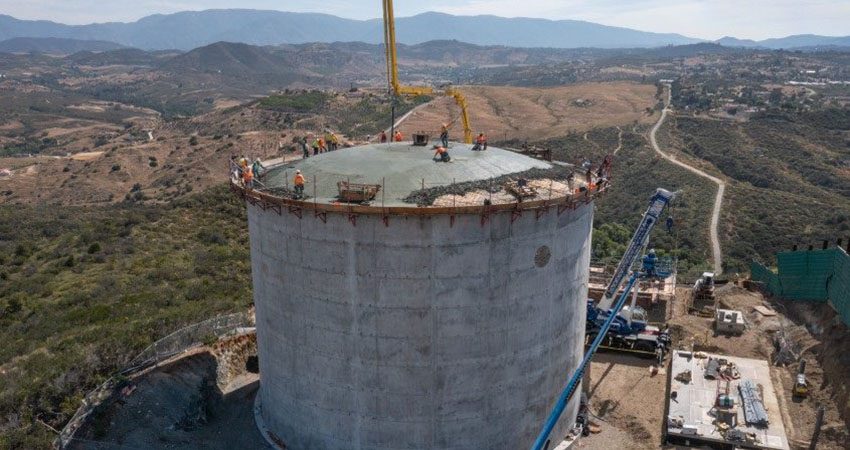
The main project site at the purification treatment facility is busy, with roughly 280 workers working on completion. Nearly 90% of the concrete is poured, and facility components are arriving from as far away as Japan and Canada.
The East County Advanced Water Purification Program is an important water project for East San Diego County. When complete, the Program will deliver a clean, reliable, and local water source.
See a video update on the progress of the East County Advanced Water Project here.
Roof Rising on the East County AWP Purification Treatment Facility
The building housing the advanced water purification treatment facility is taking shape as the roof is being added.
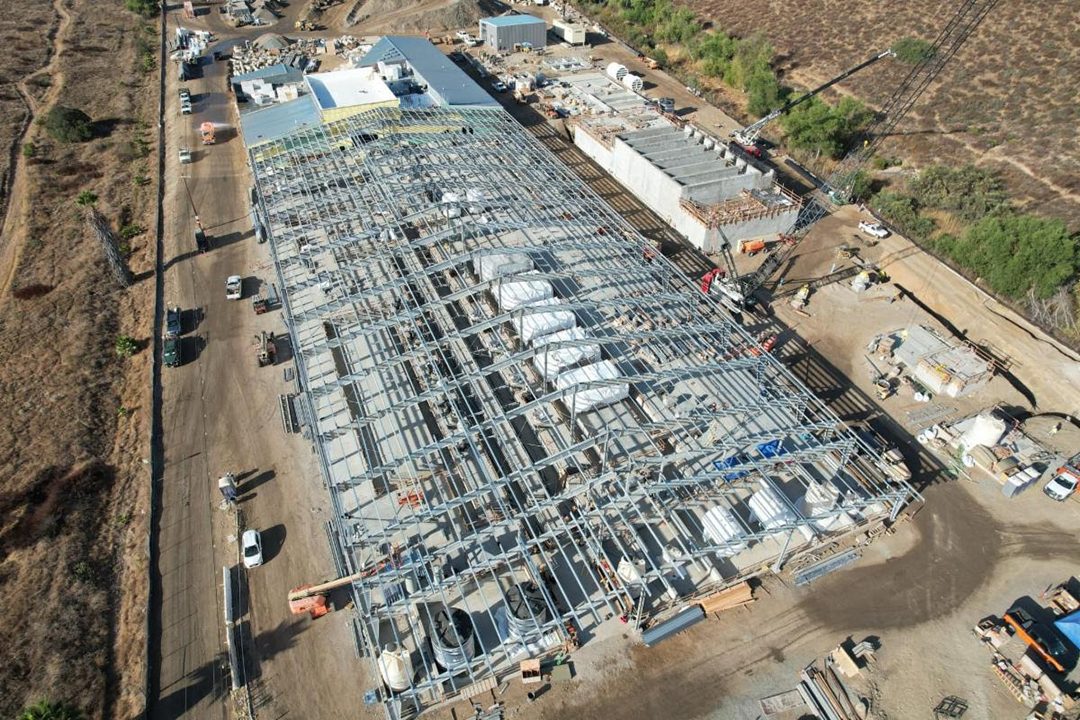

Raising the roof at the main treatment facility. Photo: East County Advanced Water Purification Program
Construction on the 23,000-square-foot Visitor’s Center will be complete at the end of 2025. It will house administrative offices, the operation control center, a testing laboratory, and a community room. Steel beam installation, including 66 columns and 100 beams, will use 350,000 pounds of U.S. steel. The roof has also been installed.
There are four water purification steps, including membrane filtration, reverse osmosis, advanced oxidation using ultraviolet light, and free chlorine disinfection. The advanced water purification facility will treat up to 11.5 million gallons daily for 50,000 households.
Water from this project will be provided to customers in Padre Dam Municipal Water District, Helix Water District, and Lakeside Water District service areas, and the northern portion of the Otay Water District.
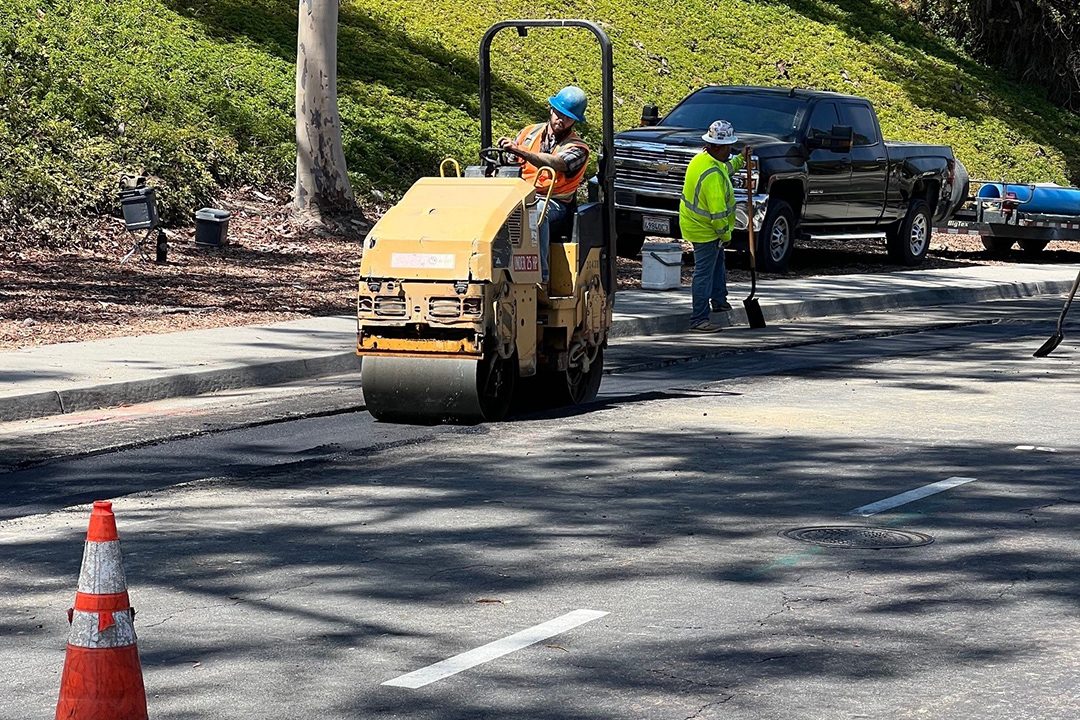
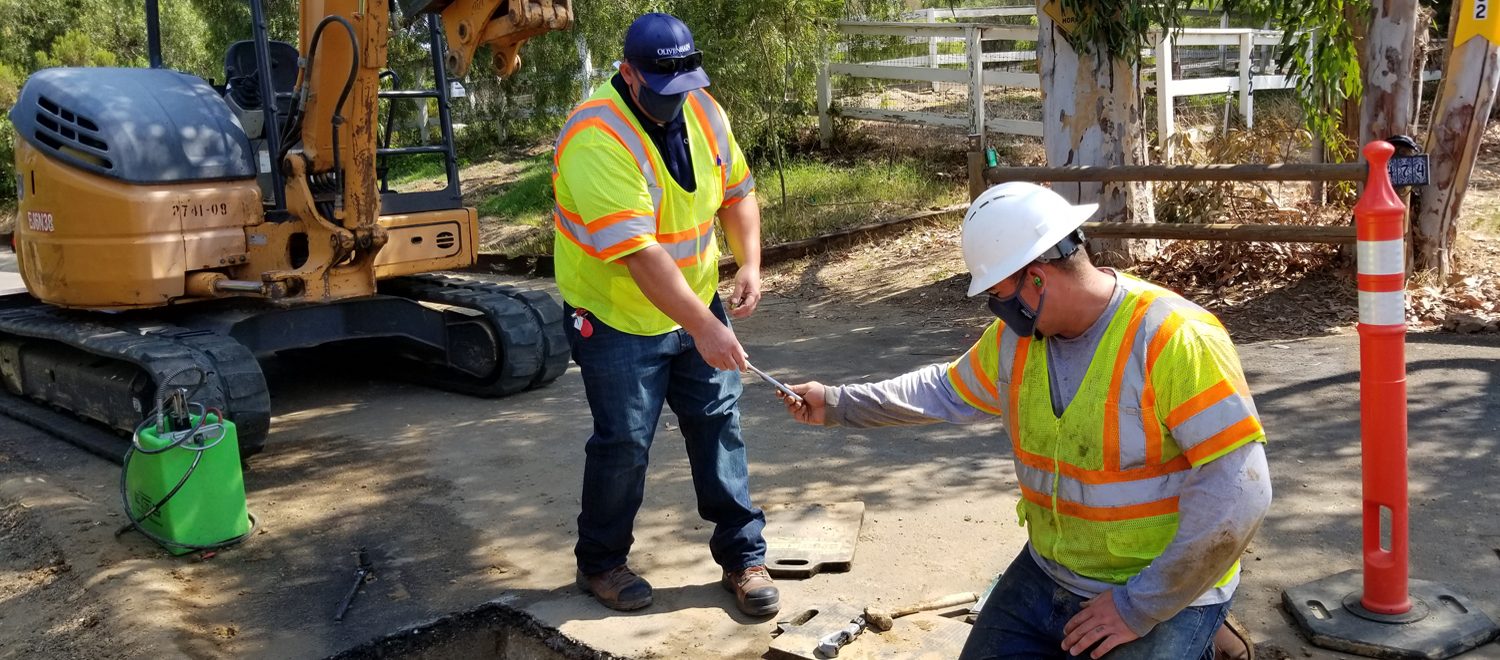
Overnight Construction Underway Into November
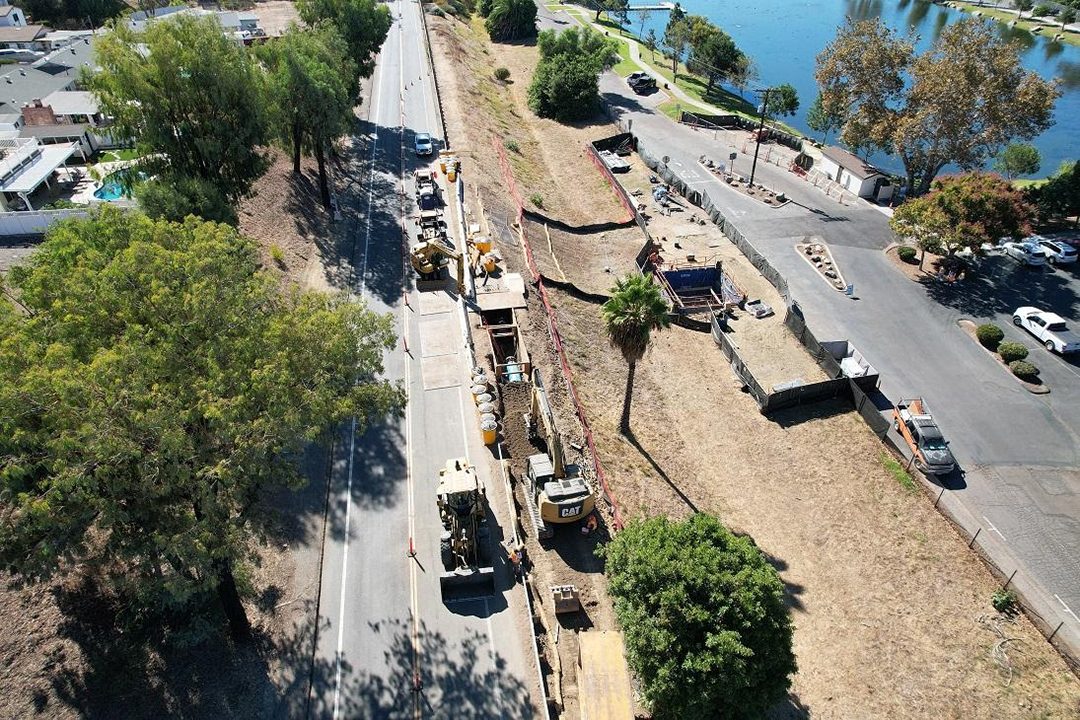

Work is underway on Fanita Drive in Santee. Photo: East County Advanced Water Purification Program
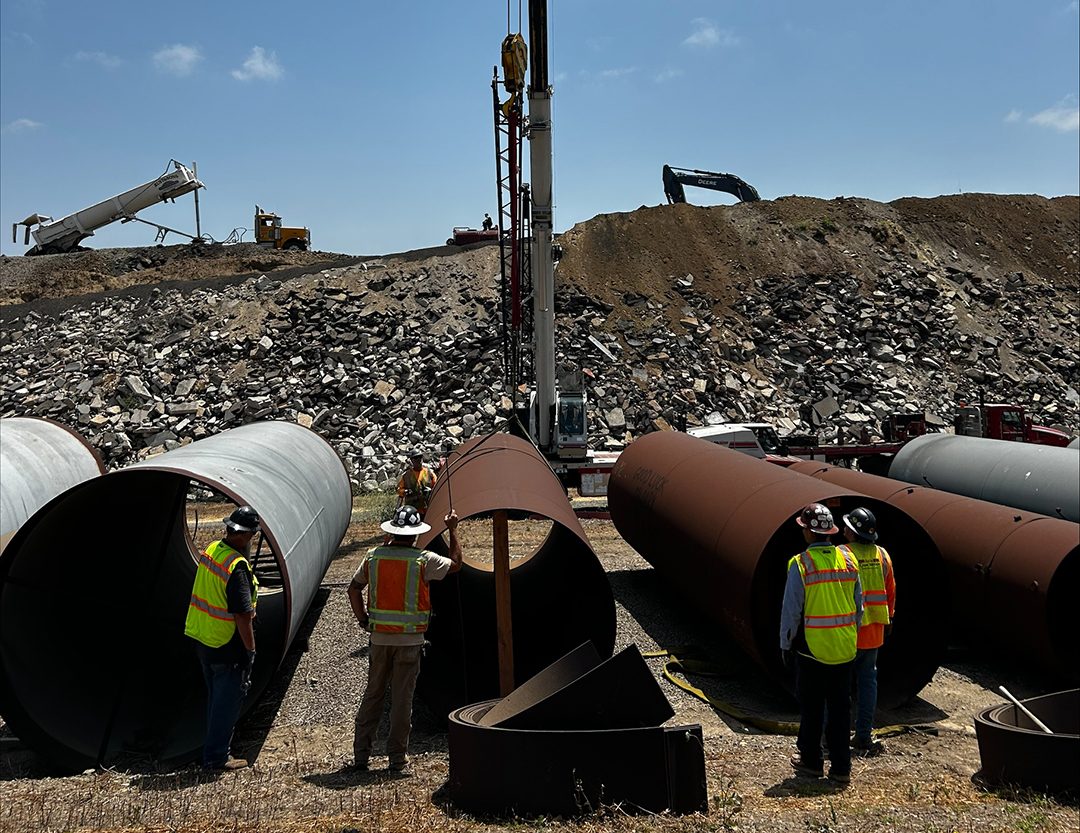
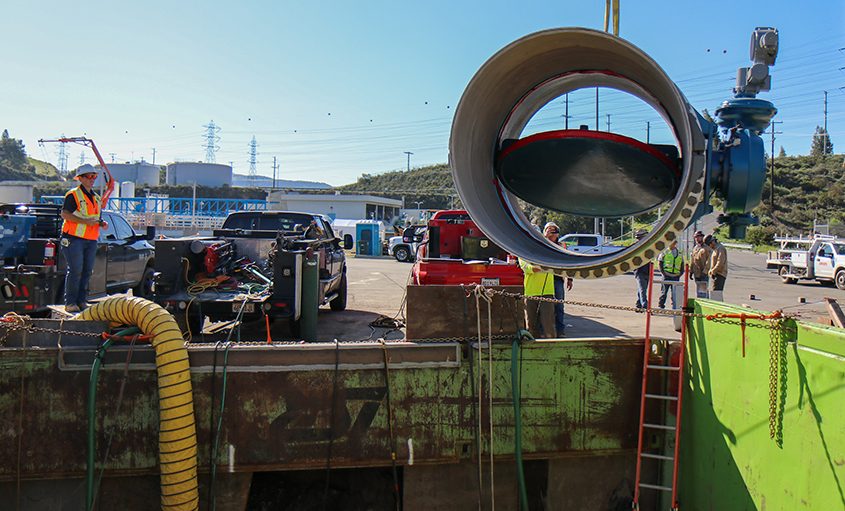
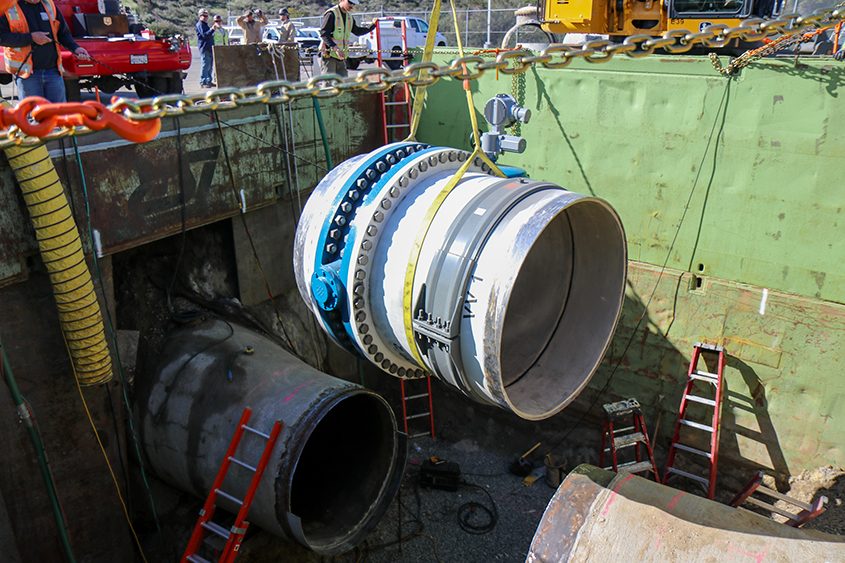
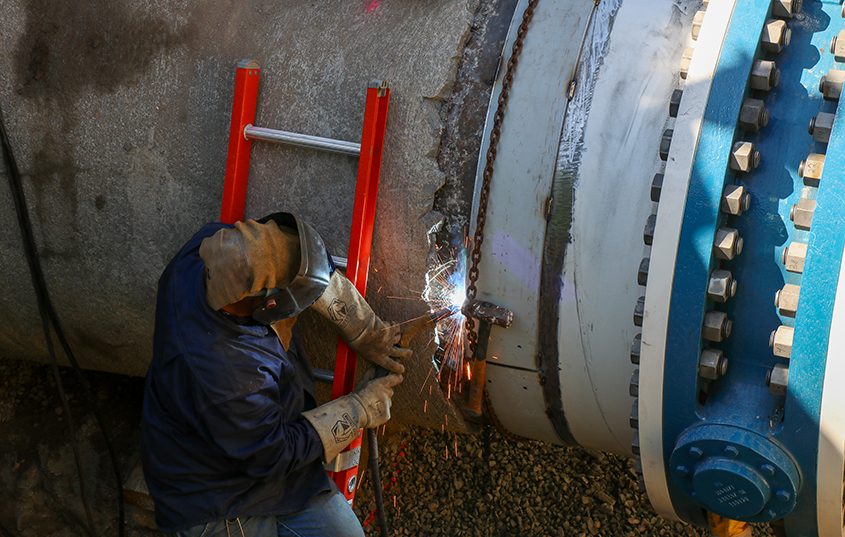
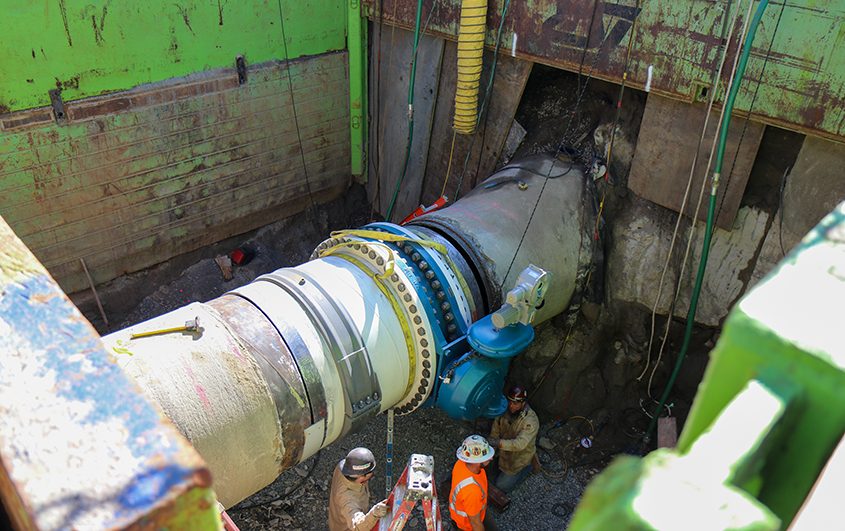
More than 70% of the purified water and wastewater pipelines are installed throughout Santee and Lakeside. In addition, an 18-inch diameter wastewater pipeline was pulled under the San Diego River and a nearby golf course. At 3,500 feet long, it is one of the longest horizontal directional drill operations ever in San Diego County.
Overnight work began in late October near and at the intersection of Mast Boulevard and Cuyamaca Street in Santee. Work hours are from 9 p.m. to 6 a.m. Monday through Friday. This night work will allow crews to install a purified water pipeline when the roads are less busy, minimizing impacts to the public.
For residents who live in the immediate area, information was mailed to affected households describing the work and providing contact information. Construction in this area is expected to last through the second week of November.
Interactive Map Helps Residents Stay Updated On Progress
With construction in multiple locations throughout East County, the Program’s interactive map continues to be a valuable tool for residents and businesses to track where work is happening. The map is updated regularly and accessible 24/7 through the EastCountyAWP.com website. Information is also available via social media at @eastcountyawp on Instagram and Facebook.