On Sunday morning, during the atmospheric river event in Northern California, scientists from the Center for Western Weather and Water Extremes (CW3E) at the Scripps Institute of Oceanography at UC San Diego and their partners at Yuba Water Agency launched weather balloons to gather data on the AR and its impacts on reservoirs.
Atmospheric River events in Water Year 2021
(Editor’s Note: The Center for Western Weather and Water Extremes, or CW3E, at Scripps Institution of Oceanography, released its report October 11 on atmospheric rivers during Water Year 2021.
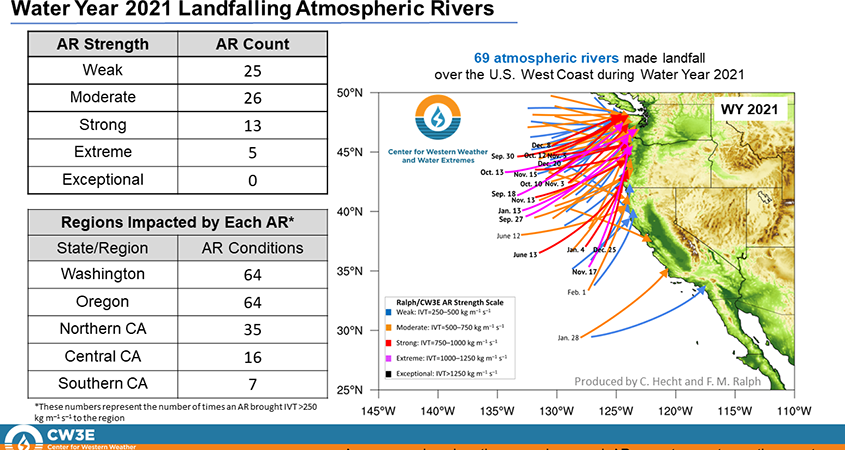
Distribution of Landfalling Atmospheric Rivers over the U.S. West Coast During Water Year 2021: End of Water Year Summary. Graphic: Center for Western Weather and Water Extremes
The San Diego County Water Authority partnered with the Scripps Institution of Oceanography, Center for Western Weather and Water Extremes, at UC San Diego in 2020 to better predict atmospheric rivers and improve water management before, during, and after those seasonal storms. The Center and its partners share best practices in forecast-informed reservoir operations, increased research around atmospheric rivers and droughts, and develop strategies for mitigating flood risk and increasing water supply reliability.)



