Attracting Pollinators to Your Garden
Flowering plants rely on insects, birds, and other creators for pollination. In turn, plants attracting pollinators feed and house beneficial insects like bees and butterflies, and nectar-loving birds like hummingbirds.
Some bugs eat too much, destroying their plant hosts and spreading disease. Other beneficial insects fight off the destructive species, eating them or disrupting their reproductive process. Birds, bats, and lizards help too, consuming pests both large and small.
Nature provides checks and balances in a garden. You can attract insects and creatures which will help maintain the health of a garden without pesticides.
Choosing a wide diversity of plants in your landscape can help attract helpful insects and predators on a regular basis. They improve the resilience of the garden and reduce the need to use chemicals for pest control.
To attract more garden helpers, create habitat for them. Consider adding a nesting box for bees. Leave a small rock pile for lizards to inhabit. Put a large tree branch in the garden and let it decompose naturally.
Planting a Butterfly Garden
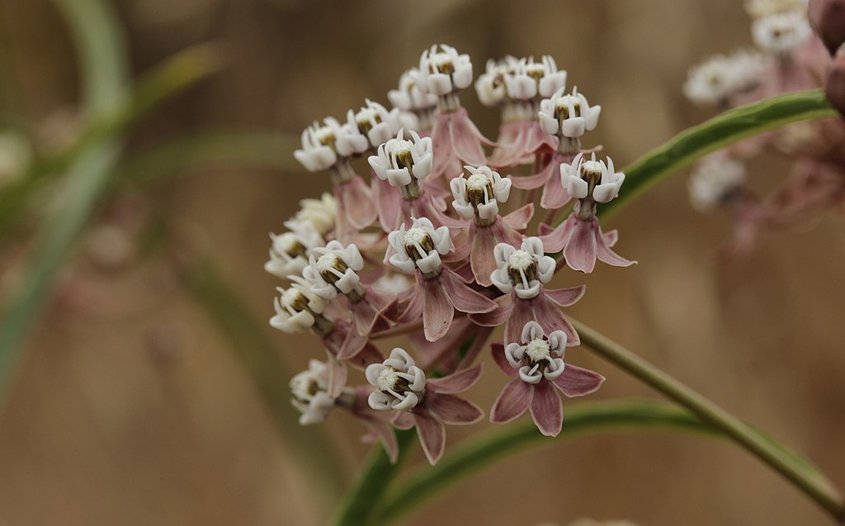

Planting Narrowleaf Milkweed prohibits habitat and for the endangered Monarch butterfly. Photo: Wikimedia
Numerous plants attract pollinators and support the life cycle of butterflies, including the threatened monarch butterfly. Plant several in the garden to help the larvae and caterpillars as well as the full-grown, nectar-seeking adults. Some good choices:
- Narrow Leaf Milkweed (Asclepias fascicularis)
- Island Alum Root (Heuchera maxima)
- San Miguel Island Buckwheat (Eriogonum grande var. rubescens)
- Cedros Island Verbena (Verbena lilacina)
- Island Bush Snapdragon (Gambelia speciosa)
What’s The Buzz?
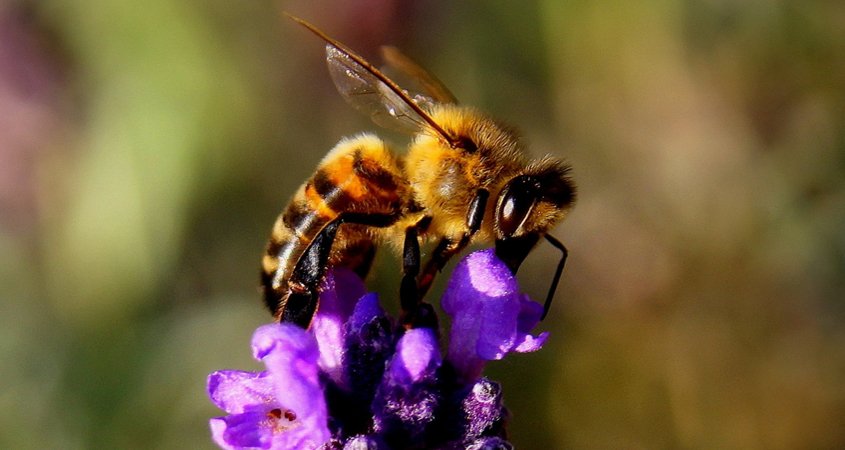

Leave open soil around plants for ground-nesting bees and insects. Photo: Pixabay/Creative Commons
Not all ground needs to be covered in mulch. Try designating a five to ten square foot patch of open soil around plants for ground-nesting bees and insects, especially if your garden contains San Diego native plants. Succulents don’t like mulch right up against their stems, for example. Create a landscape where plants and pollinators work together
This article is part of a year-long series inspired by the 71-page Sustainable Landscapes Program guidebook available at SustainableLandscapesSD.org. The Water Authority and its partners also offer other great resources for landscaping upgrades, including free WaterSmart classes at WaterSmartSD.org.